The EU AI Act: New Rules for AI in Customer Dialog
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly transforming the business world, particularly in customer-facing areas such as sales, product consultation, and in the automation of business processes. Companies in the mid-market and enterprise segments are increasingly relying on AI-powered systems to boost efficiency, scale operations, and create personalized customer experiences. From intelligent chatbots that answer customer inquiries around the clock, to AI analytics for optimizing sales strategies, to automating repetitive support tasks—the potential is immense.
However, with growing capabilities come new regulatory requirements. The EU AI Act (Artificial Intelligence Act) represents a comprehensive legal framework governing the use of AI systems within the European Union. This legislation aims to promote innovation while simultaneously protecting fundamental rights, safety, and ethical principles. For companies using or planning to use AI, this means a new level of responsibility. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in significant consequences, including substantial fines, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Especially for mid-sized companies and corporations using AI in critical business areas such as sales, product consultation, or process automation, a deep understanding of the AI Act is essential. These applications often interact directly with customers or make decisions that can have significant impacts. Therefore, they frequently fall under the stricter categories of the legislation. The challenge lies in understanding the complex requirements and implementing them in practice without losing innovation capacity and agility.
This article serves as a guide for decision-makers in mid-market companies and corporations. It illuminates the core requirements of the EU AI Act that are specifically relevant to AI systems in sales, support, and process automation. It provides a practical compliance checklist that companies can use to evaluate the conformity of their AI solutions. Furthermore, the article analyzes leading providers of AI solutions in this segment regarding their performance capabilities, cost structure, and particularly their suitability in the context of the AI Act. A special focus is placed on the solution from Qualimero, explaining why this provider represents a particularly advantageous option for companies seeking a legally compliant, efficient, and future-proof AI implementation.
Core Requirements of the EU AI Act for Sales & Support
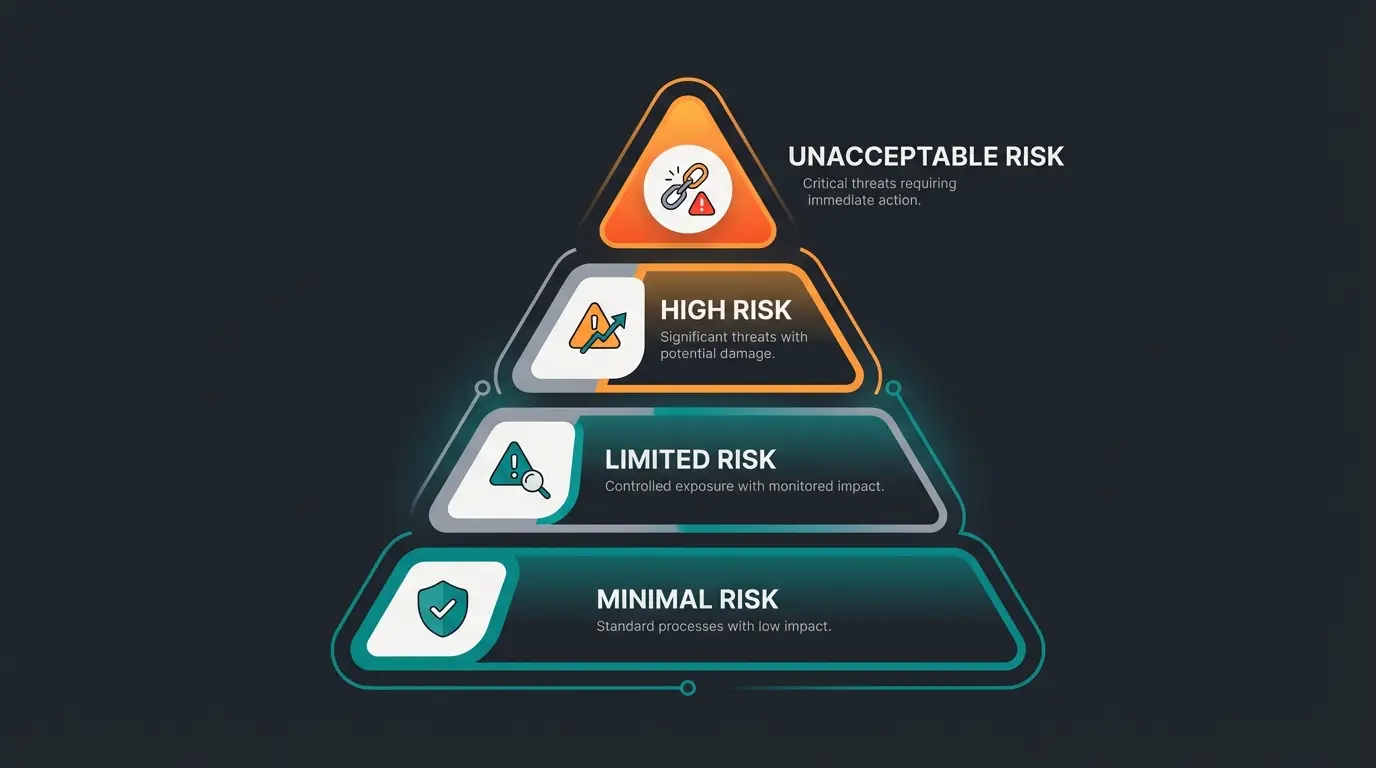
The EU AI Act follows a risk-based approach. This means that the regulatory requirements for an AI system depend on the potential risk arising from its application. According to the European Parliament's overview of the EU AI Act, the Act distinguishes four risk classes:
- Unacceptable Risk: AI systems that pose a clear threat to fundamental rights (e.g., social scoring by governments) are prohibited.
- High Risk: AI systems used in critical areas with potentially significant impacts on safety or fundamental rights (e.g., critical infrastructure, medical devices, but also certain applications in HR or credit scoring) are subject to strict requirements.
- Limited Risk: AI systems with specific transparency obligations. Users must be informed when they are interacting with an AI (e.g., chatbots).
- Minimal Risk: AI systems with little or no risk (e.g., spam filters, AI in video games). Here, only minimal or no additional obligations apply beyond existing laws.
Or 7% of global annual turnover for prohibited AI practices
Or 3% of turnover for non-compliance with high-risk requirements
When the majority of AI Act provisions become fully applicable
Risk Classification for AI Sales Support & Automation
The crucial question for companies is: Which risk category do the deployed or planned AI systems for sales, product consultation, and process automation fall into? A blanket answer is difficult, as classification strongly depends on the specific use case and context.
Potential High-Risk Systems: Certain AI applications in these areas could be classified as high-risk. This is particularly the case when the AI system has significant influence on decisions affecting access to essential services, financial opportunities, or fundamental rights. Examples from other areas include AI for credit scoring or applicant selection. In the sales context, this could become relevant if an AI significantly decides on granting discounts, personalized pricing, or access to certain products, especially if this could have discriminatory effects. AI systems that become integral parts of safety-critical processes (e.g., in heavily regulated industries) could also fall under this category.
Limited Risk as Minimum Standard: Many common AI applications in customer dialogue, such as chatbots or virtual assistants for product consultation, fall at least under the limited risk category. The central transparency obligation applies here: users must be able to clearly recognize that they are interacting with an AI system. This ensures that people are not unknowingly influenced or deceived by a machine. Detailed information on classification and specific requirements for AI chatbots can be found in our article on EU AI Act impacts on AI chatbots.
The Gray Zone of Process Automation: AI systems primarily used for internal process automation (e.g., automatic data extraction from emails, intelligent routing of support tickets) could potentially be classified as minimal risk, as long as they have no direct, significant impacts on external individuals or critical decisions. However, the distinction is not always trivial. As soon as an automated process decision (e.g., prioritization of support requests) has noticeable consequences for the customer, a higher risk classification becomes more likely.
This differentiated consideration reveals a central challenge: Correct risk classification requires careful analysis of the specific deployment scenario. Companies often need external expertise or a provider who supports them in this assessment to correctly identify and implement the corresponding compliance requirements.
Detailed Requirements for High-Risk AI Systems
If an AI system is classified as high-risk, comprehensive obligations apply throughout the entire lifecycle of the system. But systems with limited risk must also meet certain requirements. The most important points for AI in sales, support, and process automation are:
Data Quality and Governance
High-risk AI systems must be developed and operated with high-quality training, validation, and test datasets. This data must be relevant, representative, error-free, and complete to minimize risks and discriminatory outcomes. In practice, this means:
- Bias Testing: Active search for and mitigation of biases in the data that could lead to unfair or discriminatory results (e.g., disadvantaging certain customer groups).
- Data Validation: Ensuring the correctness and suitability of data for the intended purpose.
- Governance Processes: Establishing clear processes for data collection, processing, and management.
This requirement is fundamental, as data quality significantly determines the performance and fairness of AI.
Technical Documentation
Providers and operators of high-risk AI systems must create and maintain comprehensive technical documentation. This must contain detailed information about the system, including:
- General description, intended purpose, and capabilities
- Algorithms and logic used
- Information about the data used (origin, preparation, quality criteria)
- Testing procedures and results for validating accuracy, robustness, and cybersecurity
- Risk management and quality management systems
This documentation is crucial for traceability, conformity assessment by authorities, and for internal audits.
Transparency and Information Requirements
- For Users (Limited Risk): As mentioned, users must be informed when interacting with an AI (e.g., chatbot labeling).
- For Operators (High Risk): Operators of high-risk systems must receive detailed information about the system's functionality, capabilities, performance limits, and intended purpose to use it safely and correctly. This includes instructions for interpreting system outputs and handling potential risks.
Human Oversight Requirements
High-risk AI systems must be designed so that they can be effectively supervised by humans. This includes:
- Intervention Capability: Humans must be able to understand the AI's decisions, question them, and if necessary, correct them or override the system.
- Clear Responsibilities: Definition of who is responsible for oversight and how it should be conducted.
Implementing effective human oversight in dynamic sales or support processes without compromising efficiency represents a considerable practical challenge. It requires not only technical interfaces but also well-trained employees and adapted workflows.
Accuracy, Robustness, and Cybersecurity
High-risk AI systems must demonstrate an appropriate level of accuracy, technical robustness, and cybersecurity:
- Accuracy: The system must consistently deliver the defined performance throughout its entire lifecycle.
- Robustness: It must be resilient against errors, disruptions, and inconsistent inputs.
- Cybersecurity: It must be protected against unauthorized access, manipulation, or theft of data and algorithms.
These requirements make clear that EU AI Act compliance is far more than a purely technical matter. It requires profound organizational adjustments, the establishment of new processes (e.g., for data governance, documentation maintenance, risk management), and often a shift in corporate culture. Particularly for mid-sized companies that may not have dedicated compliance departments or extensive IT resources, this represents a significant challenge. The burden of compliance implementation can therefore heavily depend on choosing the right AI provider—a partner who not only delivers technology but also actively supports establishing the necessary processes.
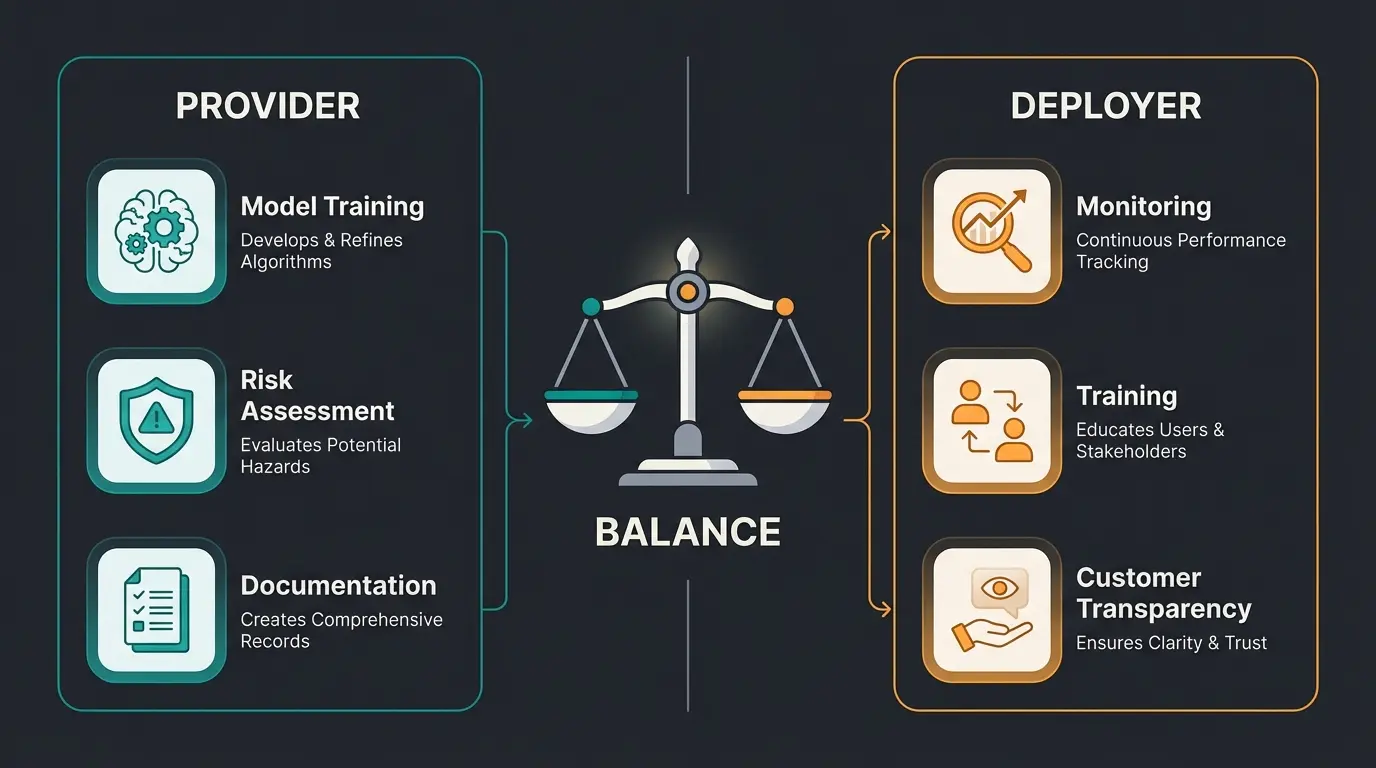
Model training, risk assessment, technical documentation, quality management systems, CE marking (if high-risk)
Output monitoring, employee training, informing end-customers about AI interaction, maintaining logs
Incident reporting, ongoing compliance monitoring, adaptation to regulatory updates
Furthermore, there is a close interaction between the core quality of AI and compliance. An AI solution that is inherently inaccurate, error-prone, or not robust will inevitably cause more problems. This leads to an increased need for human oversight and intervention, diminishing efficiency gains. Errors and unexpected behavior also require greater effort in troubleshooting and documentation to trace causes. Often, the causes lie in poor data quality or undetected bias. Conversely, a high-quality, reliable, and well-validated AI significantly simplifies fulfilling many other compliance requirements. Focusing solely on the feature set of an AI solution without evaluating its fundamental quality and reliability in the context of the AI Act therefore carries significant risks.
Your Practical EU AI Act Compliance Checklist
To provide companies with practical assistance in evaluating and ensuring the conformity of their AI systems in sales, product consultation, and process automation, the following checklist serves as a guide. It is based on the previously discussed core requirements of the EU AI Act and concretizes them for relevant use cases. This checklist can be used as a tool for self-assessment of existing systems or as a requirements catalog when selecting new AI solutions.
EU AI Act Compliance Checklist for Sales & Support AI
| Requirement | Specification for Sales/Support/Automation | Key Questions for Companies |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Classification | Evaluation of specific AI use (e.g., chatbot, lead scoring, process automation) according to AI Act criteria (High/Limited/Minimal) | Has a documented risk assessment been conducted for each specific AI application? Is the result justifiably documented? |
| Data Quality & Governance | Ensuring training, validation, and input data (e.g., customer data, product data, process data) is relevant, representative, error-free, and free from discriminatory bias | Are there defined processes for testing and ensuring data quality? Is data regularly checked for bias? Is data governance documented? |
| Technical Documentation | Availability of comprehensive, current, and understandable documentation (especially for high-risk) | Is there technical documentation describing architecture, algorithms, data, performance limits, tests, and risk management? |
| User Transparency | Clear information to users (customers, employees) when interacting with an AI system | Are users clearly informed (e.g., in chat window, application interface) that they are communicating with an AI? |
| System Transparency | Availability of information about AI system capabilities, limitations, and purpose for operators | Are capabilities and performance limits clearly defined and communicated? Do responsible employees understand how the system works? |
| Human Oversight | Implementation of effective mechanisms for human monitoring, control, and intervention (especially for high-risk) | Are there defined processes and technical capabilities for human review and correction of AI decisions/actions? |
| Accuracy & Robustness | Ensuring appropriate performance and resilience under real operating conditions | Has accuracy been validated for the specific use case? Are there measures ensuring robustness against errors? |
| Cybersecurity | Protection of the AI system and processed data against unauthorized access and manipulation | Are appropriate technical and organizational measures implemented (e.g., access controls, encryption)? |
| Logging | Recording AI system operations to ensure traceability (especially for high-risk) | Are relevant actions and decisions logged to enable investigation of errors or incidents? |
| Conformity Assessment | Conducting and documenting required conformity assessment procedures | Has the required conformity assessment been conducted? Is an EU conformity declaration available (if required)? |
This checklist makes clear that ensuring EU AI Act compliance is not a one-time project. Rather, it is a continuous process requiring regular reviews and adjustments. Data must be continuously monitored, technical documentation must be updated with system changes, and the effectiveness of human oversight processes must be regularly evaluated. This underscores the importance of selecting an AI provider who not only provides a technological solution but also acts as a long-term partner supporting compliance maintenance and possessing the necessary expertise to respond to future regulatory or technological developments. An approach where technology is implemented and then left to itself is hardly sustainable under the AI Act and carries significant risks.
Get started with a compliance-native AI solution that handles the heavy lifting. Our experts will guide you through risk assessment, documentation, and implementation.
Start Your Free TrialMarket Overview: AI Solution Providers Under Compliance Focus
The market for AI solutions in sales, product consultation, and process automation is dynamic and diverse. Numerous providers advertise intelligent features for efficiency improvement and enhanced customer experience. However, not all solutions are equally prepared for the specific challenges of the EU AI Act or optimally meet the needs of mid-market companies and corporations.
The following analysis examines typical provider categories and illuminates potential strengths and weaknesses based on pricing, AI quality, support, go-live speed, and ROI criteria—each critically examined in light of EU AI Act compliance requirements. It's important to emphasize that this analysis is based on general market observations and commonly cited challenges, representing illustrative examples of potential weaknesses to consider when selecting providers.
Competitor Analysis: Large US Technology Platforms
Pricing: Often characterized by complex, multi-tier licensing models. AI features are frequently paid add-ons. Additionally, there are often considerable costs for integration into existing processes, individual customizations, and training.
Disadvantage: The non-transparent cost structure makes reliable ROI calculation and budget planning difficult, especially for mid-sized companies. Total cost of ownership (TCO) can significantly exceed initial license costs.
AI Quality: The underlying AI models are often generic in nature, designed for a broad mass of customers. Deep customization to specific company contexts (unique products, niche markets, specific customer language, internal processes) requires considerable effort and specialized internal know-how.
Disadvantage: Without intensive customization and training with high-quality, company-specific data, there is a risk of lower accuracy and effectiveness. Additionally, generic models may contain undetected bias, making it difficult to meet the AI Act's data quality and non-discrimination requirements. Responsibility for data quality often lies entirely with the customer.
Support & Compliance Challenge: Support is often standardized and focused on the core platform. Specialized support for AI modules, particularly deep know-how regarding the specific requirements of the EU AI Act, is often lacking or only available through expensive premium support contracts. Companies may receive insufficient support implementing AI Act-compliant processes, such as creating necessary technical documentation or designing effective human oversight mechanisms. The compliance risk largely remains with the user company.
Competitor Analysis: Specialized Chatbot Providers
Pricing: Entry can be attractively priced, often based on the number of interactions or users. However, costs can quickly increase with growing volume or when extended features and integrations are needed.
Disadvantage: Scalability can become expensive. The feature set may be limited to dialogue management and insufficient for complex end-to-end process automation or deep, data-driven product consultation.
AI Quality: Strength typically lies in natural language processing (NLP) and dialogue control. However, weaknesses may appear in deeper process understanding, integration with backend systems (e.g., CRM, ERP, knowledge bases), or processing complex, multi-step inquiries.
Disadvantage: Robustness with unexpected or very specific inquiries may be limited. Meeting the AI Act's accuracy requirements in demanding sales or support scenarios that go beyond simple FAQs can be questionable.
Compliance Challenge: The transparency obligation (labeling as AI) is usually met. However, challenges may exist with detailed technical documentation and proving the quality and bias-freedom of specific training data, especially when the provider offers little insight into their models. Human oversight mechanisms are often only rudimentarily implemented (e.g., handoff to a human agent) and don't cover all potential risks.
Competitor Analysis: Open-Source / DIY Solutions
Pricing: At first glance, license costs are eliminated. However, this is offset by high and often difficult-to-calculate internal costs for development, customization, integration, maintenance, hosting, and especially for required highly qualified personnel.
Disadvantage: Total cost of ownership (TCO) is frequently massively underestimated. This option binds significant internal resources and is unrealistic for most mid-sized companies without their own large AI development department.
AI Quality: Solution quality depends entirely on internal know-how and available resources. There is risk of isolated solutions, lack of scalability, and difficulties with maintenance and further development.
Compliance Challenge: The entire compliance burden lies with the developing company. This includes risk assessment, creating complete technical documentation, implementing and operating human oversight, ensuring all technical requirements, and guaranteeing data quality and governance. This requires massive, specialized internal know-how and considerable personnel resources that are not available in most companies. The risk of inadvertently or knowingly violating regulations is particularly high with this approach.
| Criterion | Large Platform | Chatbot Specialist | DIY / Open Source | Compliance-Native Provider |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price Complexity | High | Medium (scaling) | High (TCO) | Transparent |
| AI Customization Effort | High | Medium | Very High | Managed |
| AI Act Support | Low / Standard | Limited | Non-existent | Comprehensive |
| Go-Live Speed | Slow | Medium / Slow | Very Slow | Fast |
| ROI Horizon | Medium / Long | Medium | Long / Uncertain | Short / Medium |
| Compliance Risk | Significant (customer burden) | Medium (gaps) | Very High | Minimized |
This analysis of different provider categories shows a recurring pattern: Many standard solutions or do-it-yourself approaches deliver technology but largely transfer the complexity and risk of AI Act compliance to the user company. The specific, procedural, and documentary requirements of the law are often insufficiently addressed or require considerable additional effort on the customer side. This creates significant hidden costs and operational risks, especially for mid-sized companies without large compliance or IT departments. This is precisely where providers position themselves who offer not just technology but a comprehensive solution including compliance support.
Qualimero: Native AI for Seamless Compliance and Superior ROI
After examining the challenges with common provider categories, Qualimero comes into focus—a provider specializing in addressing the specific needs of mid-market and enterprise companies when introducing AI in sales, support, and process automation, with explicit consideration of EU AI Act requirements. The analysis of Qualimero follows the same criteria but focuses on the company's communicated advantages and their relevance for successful and compliant AI implementation.
Simple Integration & Fast Go-Live
A core promise of Qualimero is the "Done-for-you" service. This approach means that Qualimero not only provides the software but takes over essential parts of implementation, configuration, and integration into the customer's existing system landscape (e.g., CRM, ERP, knowledge bases). This significantly reduces the need for internal IT resources and specialized know-how on the customer side.
The consequence of this approach is a significantly shortened implementation time ("Faster Go-Live") compared to complex platform integrations or in-house developments. Companies can use the AI solution productively faster and benefit from advantages sooner.
Connection to Compliance: Crucially, this service according to the provider also includes support in setting up AI Act-compliant processes. This can include help creating relevant parts of technical documentation or conceptualizing and technically implementing human oversight mechanisms. The advantage for the customer company lies in significantly reducing internal effort and complexity in achieving and maintaining compliance.
Higher ROI Through Quality and Speed
Return on Investment (ROI) is positively influenced by several factors. Faster go-live means value creation through AI begins earlier. The high effectiveness of a well-integrated and customized solution maximizes achievable results (e.g., higher conversion rates in sales, faster processing times in support, stronger automation levels).
Simple integration and the done-for-you approach also reduce initial project costs and binding of internal resources, relieving the denominator side of the ROI calculation.
Connection to Compliance: An often-overlooked aspect of ROI is risk minimization. Proactive support in complying with the EU AI Act helps avoid potential fines, litigation costs, and reputational damage that could significantly diminish ROI. Compliance is thus not just a duty but also a factor in securing economic success.
True Native AI Solution with High Quality
Qualimero positions its solution as a "true native AI solution." This implies that AI functionality was not retrofitted to existing software but that the solution was developed from the ground up with AI at its core. Such architectures are often better optimized, more flexible, and more powerful.
This is intended to lead to higher accuracy, better adaptability to specific customer needs, and greater robustness in operation. A native AI can often be trained more efficiently with company-specific data and delivers more precise results in defined use cases.
Connection to Compliance: An AI conceived and well-trained from the ground up has the potential to inherently minimize bias and errors. This facilitates meeting the AI Act's strict data quality requirements. Higher accuracy and robustness also reduce the need for constant human intervention and correction, increasing efficiency. Furthermore, native AI systems can often provide better transparency and traceability than complex "black box" models, simplifying documentation obligations and explainability to users and authorities.
Expert Team with Deep AI and Regulatory Knowledge
Another highlighted advantage is the deep expertise of the Qualimero team. This encompasses not only AI technology itself but also an understanding of specific application domains (sales, customer support, process automation) and relevant regulatory requirements, particularly the EU AI Act.
Connection to Compliance: This combined expertise flows into both product development and the consulting process and support. Customers benefit from competent advice and support with the complex task of AI Act compliance—from initial risk assessment through implementation of technical and organizational measures to ongoing monitoring. This represents significant risk minimization for the customer company, which can rely on a partner who understands the regulatory landscape.
How Qualimero Fulfills the Compliance Checklist
Systematically considered, Qualimero's approach addresses the points of the previously introduced compliance checklist as follows:
- Risk Classification: The experienced team supports customers in correctly categorizing their specific use case according to AI Act criteria.
- Data Quality: Through the use of high-quality, native models and support in preparing and using customer-specific data, there is a focus on high data quality and bias minimization.
- Technical Documentation: As a provider of a specific solution, Qualimero can provide comprehensive and standardized documentation about its own technology that customers can use for their compliance evidence.
- Transparency: The solution presumably offers configurable mechanisms to meet transparency obligations to users. For operators, clear presentation of system capabilities and limitations is targeted.
- Human Oversight: The approach likely includes integrated tools and support in defining processes to enable effective and efficient human oversight tailored to the specific use case.
- Accuracy & Robustness: The focus on native AI architecture aims at high performance, reliability, and resilience in productive use.
- Cybersecurity: As a professional provider, Qualimero must implement established cybersecurity standards to protect the solution and processed data.
- Logging & Conformity Assessment: The solution should provide necessary logging functions. Qualimero also supports customers with information and expertise in conducting necessary conformity assessment procedures.
Qualimero's value proposition thus lies not solely in the technological performance of the AI but significantly in the complete package of technology, implementation service ("Done-for-you"), and deep expertise (AI and compliance). This approach aims to significantly reduce implementation and compliance burden for the customer. This represents a decisive strategic advantage over providers who primarily deliver technology components and largely leave responsibility for integration and compliance to the customer.
Strategic Decision: Future-Proof AI for Your Business
The analysis of EU AI Act requirements, potential pitfalls with various provider categories, and specific advantages of compliance-native solutions leads to a clear strategic conclusion. Choosing the right AI partner is not just a technological but above all a strategic decision with significant impacts on costs, risks, and long-term success of AI deployment.
Key Challenges with Standard Providers
- High complexity in implementation and customization (especially large platforms, DIY)
- Significant compliance gaps and transfer of risk to the customer
- Hidden costs and unclear ROI (especially large platforms, DIY)
- Slow go-live and delayed value creation
- Lack of specialized support for AI Act compliance
Advantages of Compliance-Native Solutions
- Simplicity: Reduced complexity through done-for-you service and clear focus
- Integrated Compliance: Proactive support in meeting AI Act requirements, risk minimization
- Fast Go-Live: Faster implementation and earlier value creation
- Clear ROI: More transparent cost structure, faster amortization, risk avoidance
- High AI Quality: Native AI architecture for better performance and reliability
- Expertise: Deep know-how in AI, application domains, and regulatory matters as success factor
The EU AI Act is not a one-time hurdle but establishes permanent requirements for operating AI systems. The regulatory landscape will continue to evolve. Therefore, future-proofing is a crucial criterion in provider selection. A partnership with a provider like Qualimero that understands compliance as an integral part of its solution and service and has the necessary expertise to respond to future changes minimizes long-term risks and adaptation efforts for the user company. Companies can focus on using AI for value creation instead of constantly deploying resources for compliance readjustment.
The compliance-native approach appears particularly suitable for the target group of mid-market and enterprise companies:
- Mid-Market Companies: Benefit from resource conservation through done-for-you service, fast go-live, clear ROI, and risk minimization through outsourced compliance expertise. This enables even smaller companies to access powerful and compliant AI.
- Enterprises: Appreciate the scalability of a native AI solution, high reliability and performance for business-critical applications, and professional risk management regarding the AI Act. The provider's expertise can relieve and complement internal compliance teams.
Frequently Asked Questions About EU AI Act Compliance
Most sales chatbots and product consultation AI systems fall under the 'Limited Risk' category. This requires transparency—users must be clearly informed they're interacting with an AI. However, if your AI significantly influences access to financial products, credit decisions, or essential services, it may be classified as 'High Risk' with stricter requirements.
Both share responsibility, but the burden differs significantly. The Provider (AI vendor) handles the majority of technical compliance: model training, risk assessment, technical documentation, and quality management. The Deployer (your company) is responsible for monitoring outputs, employee training, and informing customers about AI interaction. Choosing a compliance-native provider substantially reduces your compliance workload.
Penalties can be severe: up to €35 million or 7% of global annual turnover for prohibited AI practices, and up to €15 million or 3% of turnover for failing to meet high-risk system requirements. Beyond fines, companies face reputational damage and potential legal disputes. Proactive compliance is significantly more cost-effective than remediation.
The EU AI Act entered into force in 2024 with a phased implementation. Provisions on prohibited AI practices apply first, with the majority of requirements for high-risk systems becoming fully applicable in 2026. Companies should begin compliance preparations now to ensure smooth transitions.
The AI Act restricts or bans emotion recognition in workplaces, schools, and other sensitive contexts. However, sales AI that avoids invasive emotion tracking and focuses on understanding explicit customer needs and preferences remains compliant. This makes specialized product consultation AI a safe choice for compliance-conscious businesses.
Conclusion: Master Compliance and Secure Competitive Advantage
The EU AI Act marks a turning point for the use of artificial intelligence in Europe. Particularly for applications in sensitive areas such as sales, support, and process automation, clear rules now apply that are intended to ensure safety, transparency, and non-discrimination. Compliance with these rules is not optional but a necessity to avoid legal risks and maintain the trust of customers and partners.
Choosing the right technology partner is of crucial importance. As the analysis has shown, solutions available on the market differ considerably in their ability not only to equip companies with powerful AI but also to actively support them in mastering complex compliance requirements. Many providers largely leave this task to the customer, which can lead to hidden costs, delays, and significant risks.
Companies, especially in the mid-market and enterprise segments, are well advised to critically evaluate their current or planned AI implementation against the compliance checklist. When selecting a provider, criteria such as simple integration, demonstrable support for AI Act compliance, the quality and transparency of the underlying AI technology, and available expertise should play a central role.
The approach of combining a native AI solution with comprehensive "done-for-you" service and proven expertise in AI and regulatory matters appears particularly promising for mastering the challenges of the EU AI Act. By reducing implementation complexity, accelerating go-live, and proactively supporting compliance, such solutions enable companies to use AI's potential safely, efficiently, and successfully, thereby securing sustainable competitive advantages. Investing in a compliant and powerful AI solution is thus an investment in your company's future viability.
Don't let regulatory complexity slow down your AI adoption. Partner with experts who understand both cutting-edge AI and EU compliance requirements.
Schedule Your Demo