Introduction: What Are Vector Databases and Why AI Needs Them
In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence (AI), vector databases play an increasingly vital role. These specialized database systems are designed to efficiently store and process high-dimensional data points called vectors. They form the backbone of many modern AI applications, particularly in the realm of AI-powered product consulting.
Vector databases differ fundamentally from traditional relational databases through their ability to represent complex data structures—such as text, images, or audio files—in the form of numerical vectors. These vector representations enable AI systems to quickly and precisely calculate similarities between data points, which is crucial for numerous applications. Think of them not merely as storage engines, but as the long-term memory of a digital salesperson who remembers every product detail and customer preference.
The significance of vector databases for AI applications can be pinpointed across several dimensions:
- Efficiency: They enable lightning-fast similarity searches across massive datasets
- Scalability: Vector databases handle growing data volumes without performance degradation
- Flexibility: They support various types of unstructured data including text, images, and audio
- Precision: Vector-based search often delivers more accurate results than traditional text searches
- Semantic Understanding: Unlike keyword matching, they grasp the meaning behind queries
In the context of product consulting, vector databases play a key role in personalizing recommendations. They enable AI systems to identify products from a vast catalog that best match a customer's preferences and needs. This leads to significant improvements in customer experience and e-commerce platform efficiency. But more importantly, they power the transition from passive product recommendations to active, consultative selling where the AI engages customers in meaningful dialogue.
Vector Database Fundamentals: Definition and How They Work
Understanding Vectors and Embeddings
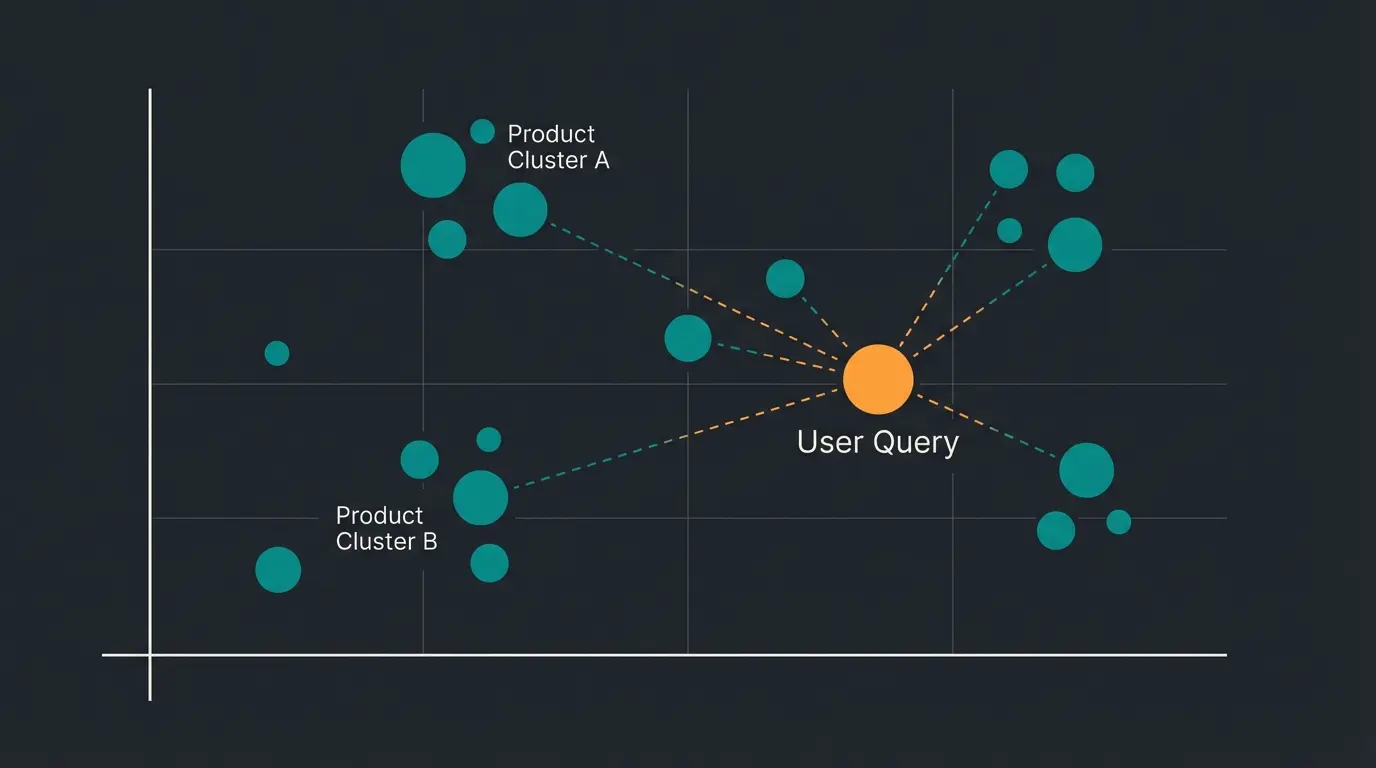
Vector databases are specialized database systems designed to store and process high-dimensional vectors. A vector is a mathematical representation of data as a series of numbers. These vectors can represent various types of information, from texts and images to complex object properties.
The magic happens through embeddings—the process of converting complex information into these numerical vectors. Imagine plotting a "Running Shoe" on a graph with axes representing "Comfort" and "Speed." A marathon racing flat would sit high on speed but lower on comfort, while a daily trainer occupies a different position. This spatial representation allows AI to understand relationships between products that pure text matching could never capture.
The operation of vector databases is based on the principle of similarity search. Instead of finding exact matches as traditional databases do, vector databases search for the most similar data points based on proximity in multidimensional space. This is typically achieved through algorithms like Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) that efficiently determine the closest neighbors.
Key Differences from Traditional Relational Databases
Vector databases differ from traditional relational databases in several essential ways:
| Aspect | Relational Databases | Vector Databases |
|---|---|---|
| Data Structure | Structured tables with rows and columns | Multidimensional vectors (embeddings) |
| Query Methods | SQL queries for exact matches | Similarity searches using distance metrics |
| Best For | Structured, transactional data | Unstructured data, AI/ML applications |
| Search Type | Exact keyword matching | Semantic similarity matching |
| Scalability | Vertical scaling challenges | Horizontal scaling for large datasets |
These fundamental differences make vector databases particularly well-suited for AI and machine learning applications, especially recommendation systems and advanced search functionality where understanding context matters more than matching exact terms.
How Vector Representation Transforms Your Data
Vector representation of data is a central concept in vector databases. Complex information is converted into numerical vectors through embedding models. For example, a text document can be represented as a vector where each dimension represents the frequency or importance of certain words or concepts. Similarly, images can be represented by vectors encoding visual features like colors, shapes, or textures. Vector embeddings are numerical representations of data objects organized in high dimensionality, playing a crucial function in semantic search as well as machine learning and AI applications.
These vector representations enable efficient similarity calculations between data points. Common methods for calculating similarity include cosine distance or Euclidean distance between vectors. This capability for precise similarity calculation makes vector databases particularly valuable for AI applications like personalized product recommendations or semantic search. When a customer asks for "a summer shoe for the office," the query vector lands in the space between "Sandals" and "Formal Shoes," and the database identifies the closest hybrid option—perhaps a stylish loafer that bridges both worlds.
Why Keyword Search Falls Short for Product Consulting
Traditional keyword search has served e-commerce well for decades, but it fundamentally misunderstands how customers actually shop. When someone types "winter jacket not too heavy" into a search bar, keyword matching looks for the exact word "heavy" and may paradoxically show heavy jackets. Vector search, by contrast, understands the concept of "lightweight insulation" and surfaces high-tech down jackets that match the user's true intent.
This limitation becomes critical in product consulting scenarios. Standard search bars and FAQ bots fail in modern e-commerce for predictable reasons: zero results for typos, no understanding of intent, and complete inability to handle nuanced requests. The problem intensifies when customers don't know the technical vocabulary for what they want. A customer seeking "something comfortable for long walks" shouldn't need to know the terms "arch support," "EVA midsole," or "breathable mesh upper" to find the right shoe.
Of e-commerce searches that return zero results lead to site abandonment
Higher conversion rates with semantic search vs. keyword matching
Of product searches fail due to vocabulary mismatch between user and catalog
Vector databases introduce AI "intuition" into this equation. By representing both products and queries as vectors in the same semantic space, the system bridges the vocabulary gap automatically. The customer's everyday language maps to the product's technical specifications without either party needing to adapt. This isn't just better search—it's the foundation for intelligent product consultation that moves beyond simple text retrieval.
Vector Databases and AI: A Perfect Symbiosis
The close connection between vector databases and artificial intelligence opens entirely new possibilities across various application areas. This symbiosis enables efficient processing of complex data structures and extraction of valuable insights.
Machine Learning Integration and Training Efficiency
In the field of machine learning, vector databases play a central role. They enable efficient storage and rapid access to high-dimensional data essential for training models. Through the use of vector databases, advanced AI models like GPT-5 can significantly increase their performance and handle more complex tasks. Additionally, various tools allow the creation of powerful vector search engines that continuously learn from user interactions.
The feedback loop between vector databases and machine learning creates compounding improvements. Each customer interaction generates new data that refines the embedding models, which in turn improves the quality of future similarity searches. This virtuous cycle means your product consulting AI gets smarter with every conversation.
Natural Language Processing Applications
In the field of Natural Language Processing, vector databases revolutionize how we handle language. They enable precise capture and analysis of semantic relationships between words and sentences. This leads to improved translation systems, intelligent chatbots, and advanced text analysis tools. The combination of NLP and vector databases opens new possibilities in AI-powered product consulting, enabling customer inquiries to be more accurately understood and answered.
When a customer asks "I need something for hiking but my knees hurt," the NLP layer converts this into a query vector that captures both the activity (hiking) and the constraint (joint support). The vector database then finds products that sit near "hiking boots" in the activity dimension but also near "cushioning" and "support" in the comfort dimension. No keyword system could make these multi-dimensional connections.
Image Processing and Computer Vision
In image processing and computer vision, vector databases offer decisive advantages. They enable efficient storage and comparison of image properties in vector form. This leads to faster and more accurate image recognition systems used in various areas such as autonomous driving, medical image analysis, and facial recognition. The use of vector databases in these applications improves not only speed but also the precision of results—crucial for visual product search where customers can upload photos to find similar items.
See how vector-powered AI can turn browsers into buyers with personalized, conversational product recommendations.
Request Your DemoFrom Search to Consultation: How Vector Databases Power AI
Most articles about vector databases discuss "Recommender Systems" in generic terms—"Customers who bought X also bought Y." But there's a crucial distinction that separates passive recommendations from active product consultation, and understanding this difference is key to leveraging vector databases effectively.
Recommender Systems vs. Interactive Consultation
A recommender system is inherently static and backward-looking. It analyzes past purchase data and browsing behavior to suggest products based on historical patterns. While useful, it cannot adapt to a customer's current, evolving needs expressed in real-time conversation.
An AI product consultant, powered by vector databases, operates differently. It's dynamic and conversation-based, actively asking clarifying questions to narrow down the vector search space in real-time. When a customer says "I want something for hiking," the consultant doesn't immediately dump a list of hiking products. Instead, it asks: "What terrain will you be covering? How many hours will you be walking? Do you have any foot conditions I should consider?" Each answer adjusts the query vector, progressively zeroing in on the perfect match.
| Feature | FAQ Bot | AI Product Consultant (Vector-Powered) |
|---|---|---|
| Handling Unknowns | Says "I don't understand" | Asks clarifying questions to adjust vector search |
| Data Source | Static text snippets | Dynamic product attributes and embeddings |
| Response Type | Retrieves pre-written answers | Assembles persuasive, personalized arguments |
| Learning | No adaptation | Continuously improves from interactions |
| Product Knowledge | Limited to FAQ content | Full catalog with semantic understanding |
The Consultation Workflow Explained
Understanding the technical workflow reveals why vector databases are essential for true product consultation:
Customer shares a vague or specific requirement in natural language
AI converts the query into a high-dimensional vector capturing semantic meaning
Database finds semantically nearest products using ANN algorithms
Hybrid search applies hard filters (size, price, availability)
Language model explains WHY the product fits, creating consultative dialogue
The crucial step that most implementations miss is the final one: explaining why this product fits the customer's expressed needs. This is the consultation layer—the "Business Logic" that maps vague user intent to specific technical product attributes without hallucinations. The vector database provides the candidates; the LLM provides the persuasive explanation.
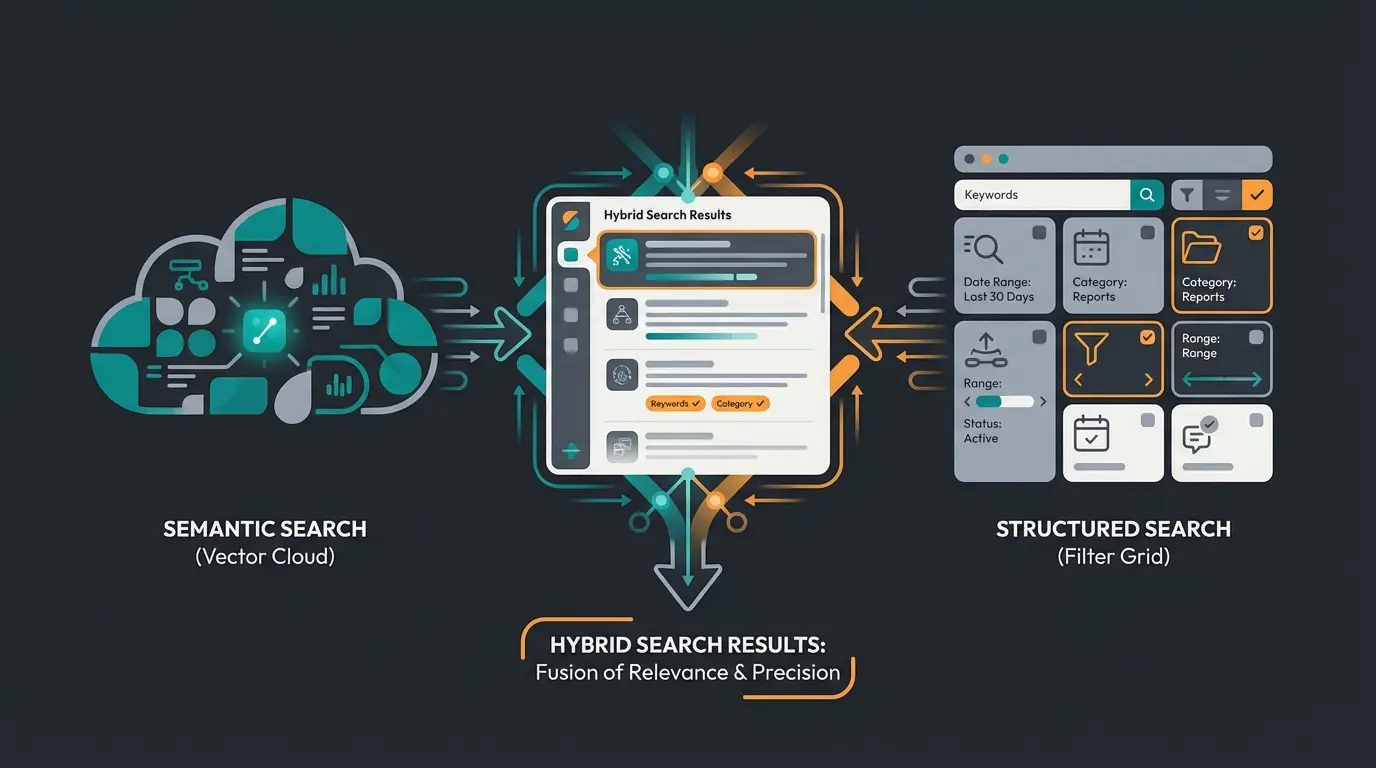
Hybrid Search: The Secret Weapon for Precise Recommendations
Here's a truth that generic vector database articles consistently miss: vector search alone isn't enough for products. When a customer searches for a "stylish hiking shoe," vector similarity handles the "vibe"—the semantic concept of stylish outdoor footwear. But when that customer wears size 42 and has a €150 budget, you need hard filters that vectors can't provide.
This is where Hybrid Search becomes essential. It combines the semantic understanding of vector search with the precision of traditional metadata filtering. The vector component finds products that match the customer's intent and preferences, while the filter component ensures only available products in the right size, color, and price range make it through.
Consider this practical example:
- Customer query: "Lightweight summer dress for a beach wedding, under €200"
- Vector search finds: Dresses semantically close to "lightweight," "summer," "beach," and "wedding appropriate"
- Metadata filters apply: Price ≤ €200, Category = Dresses, Season = Summer, In Stock = True
- Final results: A curated selection of semantically relevant AND practically suitable options
Without hybrid search, you either get semantically relevant products that are out of stock, wrong size, or over budget (pure vector), or you get keyword-matched products that miss the customer's actual style intent (pure keyword). The combination delivers precision that neither approach achieves alone—and this hybrid capability is what separates amateur implementations from production-ready product consulting systems.
Benefits of Vector Databases for AI Applications
The integration of vector databases into AI applications brings numerous advantages that significantly enhance the performance and efficiency of these systems. In the context of product consulting, these benefits become particularly evident.
Improved Search Speed and Accuracy
Vector databases enable lightning-fast search queries in high-dimensional data spaces. This is especially important for AI applications that need to access large amounts of data in real-time. In product consulting, this means customers can receive matching recommendations within fractions of a second, based on complex similarity calculations between product properties and customer preferences. The speed difference is dramatic—what might take minutes with traditional database queries happens in milliseconds with optimized vector indexes.
Scalability and Flexibility
Another decisive advantage of vector databases is their excellent scalability. They can handle growing data volumes without problems while maintaining performance. This is especially important for AI systems that must continuously process and learn from new data. In product consulting, this scalability enables constant expansion of the product catalog and integration of new customer data without impacting system performance. Whether you have 10,000 products or 10 million, the query time remains consistent.
Efficient Processing of Large Data Volumes
Vector databases are optimized to process enormous data volumes efficiently. This is crucial for AI applications that rely on big data analytics. In product consulting, this enables the analysis of millions of customer profiles and product data to generate highly precise and personalized recommendations. The vectorization of data thus forms the foundation for advanced generative AI systems that can handle the complexity of modern e-commerce catalogs.
Support for Real-Time Applications
The ability of vector databases to process real-time queries is a decisive advantage for modern AI applications. This enables interactive and dynamic user experiences that are essential in today's fast-paced digital world. In product consulting, this means customers can receive immediate answers to their inquiries, leading to significantly improved customer satisfaction. An example of this is the AI employee Flora, who advises customers in real-time while accessing an extensive knowledge base. Additionally, security plays a crucial role in ensuring secure data management and storage throughout the consultation process.
Vector Databases to Improve Product Consulting
Revolutionizing E-Commerce with Vector-Powered Consulting
In the modern e-commerce landscape, vector databases play a decisive role in improving product consulting. Through their ability to efficiently process complex data structures, they enable a new dimension of personalized customer interaction that goes far beyond traditional recommendation engines.
Personalized Recommendations Through Similarity-Based Search
Vector databases revolutionize how AI-powered product consulting functions. They enable similarity-based search that goes far beyond traditional filter methods. By representing products and customer preferences as multidimensional vectors, similarities can be precisely calculated and tailored recommendations generated. The system doesn't just match keywords—it understands that a customer who liked Product A will likely appreciate Product B because they occupy similar positions in the semantic space, even if they share no common keywords.
Processing Customer Feedback and Preferences
Vector databases excel at processing unstructured data like customer reviews and preferences. They can convert natural language into meaningful vectors, capturing subtle nuances in customer feedback and using them for future recommendations. This leads to a deeper understanding of customer needs and enables continuous improvement of consulting quality. A review mentioning "great for my morning jog" adds semantic context that influences future recommendations for similar customers—even without explicit feature tagging.
Dynamic Adjustment of Product Recommendations
A key advantage of vector databases is their ability to adjust product recommendations in real-time. Through efficient processing of large data volumes, they can react instantly to changes in customer behavior or new product information. This ensures recommendations remain current and relevant, leading to higher customer satisfaction and conversion rates. When new inventory arrives or customer preferences shift mid-conversation, the AI consultant adapts immediately.
Case Study: Successful Implementation in E-Commerce
An outstanding example of successful vector database deployment in product consulting is provided by the AI employee Flora. As a virtual assistant for garden and plant care products, Flora uses vector databases to precisely answer complex customer queries and provide personalized product recommendations. The results are impressive:
- Precision: 97% accuracy in product recommendations
- Speed: Average response time under 5 seconds
- Efficiency: Cost savings of 99.2% per chat interaction
- Availability: 24/7 customer service in multiple languages
This case study underscores the enormous potential of vector databases in AI-powered product consulting and demonstrates how they can lead to significant customer service improvements while simultaneously achieving cost savings. Flora doesn't just retrieve FAQ answers—she dynamically assembles product attributes into persuasive recommendations tailored to each customer's specific situation.
Data Quality: The Foundation of Effective Vector Search
Data quality is a decisive factor for the success of AI applications, especially in the context of vector databases. High-quality data forms the foundation for precise and reliable AI models used in product consulting.
Why High-Quality Data Matters for AI Models
In the AI-powered sales revolution, high-quality data plays a key role. It enables AI models to make accurate predictions and provide relevant recommendations. When working with vector databases, data quality is particularly critical because any inaccuracy or distortion in input data leads to faulty vector representations and thus misleading results. Garbage in, garbage out applies doubly to embedding-based systems.
Improving Data Quality Through Vector Representation
Vector databases offer innovative possibilities for improving data quality. By converting complex data structures into high-dimensional vectors, subtle relationships and patterns can be recognized that might be overlooked in traditional database systems. This richer data representation enables AI models to develop a deeper understanding of underlying information and thus make more precise analyses and predictions. Inconsistencies in product descriptions or metadata become visible when similar products end up in distant vector space locations.
Data Consistency and Integrity in Vector Databases
Vector databases offer advanced mechanisms to ensure data consistency and integrity. Through the use of specialized indexing techniques and similarity metrics, they can efficiently identify and handle anomalies and inconsistencies in data. This is especially important in dynamic environments like product consulting, where customer preferences and product information constantly change.
Maintaining high data quality standards in vector databases is a continuous process requiring regular reviews, data cleansing, and updates. By implementing robust quality assurance processes, companies can ensure their AI-powered consulting systems always operate on the basis of the best possible data, leading to more precise recommendations and higher customer satisfaction.
Implementing Vector Databases in Existing Systems
The integration of vector databases into existing IT infrastructures, particularly in the context of product consulting, presents companies with some challenges. At the same time, it offers enormous opportunities for improving AI-powered recommendation systems. To ensure successful implementation, companies must proceed carefully and consider best practices.
Integration Challenges to Anticipate
When introducing vector databases into existing systems, the following challenges can arise:
- Data Conversion: Existing data must be converted into vector representations, which requires specialized know-how and embedding model selection
- Infrastructure Scaling: The infrastructure must be adapted to handle increased data volumes and processing requirements
- Performance Optimization: Efficient algorithms for similarity searches must be implemented to fully exploit vector database advantages
- Team Training: Teams must be trained in handling the new technology to realize its full potential
- Index Management: Choosing the right indexing strategy (HNSW, IVF, etc.) significantly impacts query performance
Best Practices and Solution Approaches
To master these challenges, companies can apply the following best practices:
Start a Pilot Project: Begin with a limited use case, such as AI-powered product consulting, to gather experience and demonstrate value before enterprise-wide rollout.
Ensure Data Quality: Invest in preparing and cleansing your data before transferring it to the vector database. This is crucial for the accuracy of AI recommendations and prevents the "garbage in, garbage out" problem.
Seek Expert Support: Work with specialists who have experience implementing vector databases and AI systems. This can accelerate the process and avoid costly mistakes.
Continuous Optimization: Monitor your vector database performance and optimize it continuously. This is especially important for applications like AI-powered product consulting, where accuracy and speed are decisive for customer satisfaction.
Step-by-Step Migration Strategy
A successful migration to vector databases requires a structured approach:
1. Needs Analysis: Identify the areas where vector databases can provide the greatest added value, such as personalized product recommendations or semantic search functionality.
2. Proof of Concept: Test the vector database in a controlled environment to validate its capabilities with your specific data and use cases.
3. Parallel Operation: Initially operate the new vector database parallel to existing systems to ensure a smooth transition and enable A/B testing of results.
4. Stepwise Expansion: Gradually expand the use of the vector database to additional application areas based on insights gained from initial deployment.
5. Full Integration: Fully integrate the vector database into your IT landscape and use it as a core component for AI-powered applications like AI-powered sales support.
Through a carefully planned and phased approach, companies can fully exploit the benefits of vector databases for their AI applications, particularly in product consulting, while minimizing associated challenges.
Top Vector Databases Compared (2024/2025)
Choosing the right vector database depends on your specific requirements, technical capabilities, and scale of operations. Here's a comparison of leading options:
| Database | Best For | Key Strengths | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pinecone | Managed cloud deployments | Fully managed, easy scaling, low ops overhead | Vendor lock-in, cost at scale |
| Milvus | Self-hosted flexibility | Open source, highly customizable, strong community | Requires DevOps expertise |
| Weaviate | Hybrid search needs | Built-in hybrid search, GraphQL API, modules ecosystem | Learning curve for modules |
| Chroma | Rapid prototyping | Lightweight, Python-native, great for development | Limited production features |
| Specialized Solutions | E-commerce consultation | Pre-built logic layers, consultation workflows, integrated LLM orchestration | May require customization |
For serious e-commerce product consulting, generic vector databases often require significant additional development to handle the "Business Logic" layer—the crucial middle layer between database storage and LLM generation that maps vague user intent to specific product attributes. Specialized solutions that bundle vector search with consultation logic can dramatically reduce time-to-value.
Future Perspectives: Vector Databases and AI
The rapid development of AI technologies and the growing importance of vector databases promise an exciting future for product consulting and numerous other application areas. Current trends and emerging technologies indicate that vector databases will assume an even more central role in the AI landscape.
Emerging Trends in Vector Database Development
Improved Scalability: Future vector databases will handle extremely large data volumes even more efficiently, which is decisive for processing complex product catalogs and customer profiles at enterprise scale.
Increased Precision: Advances in similarity search algorithms will further improve the accuracy of product recommendations, leading to even more personalized consulting experiences that feel genuinely helpful rather than generically automated.
Real-Time Data Integration: Vector databases will increasingly be able to integrate real-time data from various sources to deliver even more current and context-aware recommendations. Inventory changes, price updates, and trending items will reflect instantly.
Multimodal Processing: The ability to process different data types like text, images, and audio in a unified vector space will revolutionize product consulting. This enables, for example, the integration of visual product search into AI-powered WhatsApp bots for e-commerce where customers can snap a photo and find similar products instantly.
Potential New Application Areas
Augmented Reality (AR) in Product Consulting: Vector databases could form the foundation for AR applications that allow customers to virtually place and evaluate products in their environment, with recommendations adapting based on spatial context.
Predictive Maintenance: In the industrial sector, vector databases can be used to recognize patterns in sensor data and predict potential failures, leading to more efficient maintenance scheduling and reduced downtime.
Personalized Health Recommendations: In the healthcare sector, vector databases could be used to develop personalized treatment plans and prevention strategies based on genetic data and lifestyle information.
Advanced Language Models: The integration of vector databases into advanced language models like GPT-5 could lead to even more natural and context-aware interactions in product consulting, making conversations indistinguishable from human expert advice.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
Quantum Computing: The combination of quantum computing with vector databases could lead to exponential performance improvements in complex search operations, elevating real-time personalization to an entirely new level with calculations that currently take seconds happening in microseconds.
Edge Computing: Relocating vector databases to the network edge could lead to faster response times and improved data privacy in product consulting, processing queries locally without sending sensitive customer data to central servers.
Federated Learning: This technology could enable training AI models across distributed vector databases without centralizing sensitive customer data, improving privacy in product consulting while maintaining recommendation quality.
Blockchain: The integration of blockchain technology could increase transparency and traceability of product recommendations, strengthening trust in AI-powered consulting systems by providing auditable recommendation provenance.
The future of vector databases in connection with AI promises an era of ultra-personalized, context-aware, and ethical product consulting. Companies that adopt these technologies early and integrate them into their strategies will be able to offer their customers an unprecedented level of service and consulting quality.
Frequently Asked Questions About Vector Databases
Traditional relational databases store structured data in tables and use SQL queries for exact matches. Vector databases store high-dimensional numerical representations (embeddings) and use similarity algorithms to find the closest matches based on semantic meaning. This enables them to understand context and intent rather than just matching keywords.
Vector databases convert products and customer queries into the same semantic space, enabling similarity searches that understand intent. When a customer asks for 'something comfortable for long walks,' the vector database finds products semantically close to comfort and walking, even if those exact words don't appear in product descriptions. Combined with hybrid search filters, this delivers highly relevant, personalized recommendations.
Hybrid search combines vector similarity search (for semantic understanding) with traditional metadata filtering (for hard constraints like size, price, and availability). Pure vector search might find semantically perfect products that are out of stock or wrong size. Hybrid search ensures recommendations are both semantically relevant AND practically purchasable.
Implementation timelines vary based on complexity. A proof-of-concept can be ready in 2-4 weeks. Full production deployment typically takes 2-4 months, including data preparation, embedding model training, index optimization, and integration with existing systems. Working with specialized partners can significantly accelerate this timeline.
At minimum, you need product catalog data (titles, descriptions, attributes) and a way to generate embeddings. For optimal results, you should also include customer interaction data, reviews, and purchase history. The quality of your source data directly impacts recommendation accuracy—clean, consistent product information is essential.
Join leading e-commerce brands using vector-powered AI consulting to increase conversions, reduce support costs, and delight customers with personalized recommendations.
Start Your Free Consultation