Introduction: AI Is Only as Smart as Its Teachers
The fundamental truth of artificial intelligence is deceptively simple: your AI system can only be as intelligent as the data it learns from. This principle, often summarized as "garbage in, garbage out," becomes critically important when we move beyond simple recognition tasks into the realm of expert consultation and advisory systems.
Labelbox has established itself as a leading AI data labeling platform, setting the standard for high-quality data preparation in the machine learning space by 2024. The platform enables companies and developers to precisely label, manage, and optimize training data for AI models. At its core lies efficient team collaboration during data preparation, as described in the fundamentals of AI training.
However, internal labeling brings significant challenges. High personnel costs, long processing times, and the necessity for quality controls can limit the scalability and efficiency of AI projects. Most companies focus on quantity over quality, and standard chatbots fail because they are trained on generic data rather than expert consultation logic. This is where Qualimero steps in as an alternative: with our "done-for-you" approach, we handle the entire labeling process for you—quickly, scalably, and with the highest quality.
What Is AI Data Annotation? The Foundation Explained
AI data annotation is the process of labeling data so that machine learning models can understand and learn from it. Think of it as creating a comprehensive teaching curriculum for an AI student. Just as a child learns to recognize objects through repeated exposure and explanation, AI models require clearly labeled examples to develop their understanding.
The "teacher-student" analogy helps illustrate this concept, but there's a critical distinction that most industry discussions overlook. There's a fundamental difference between teaching AI to identify something ("This is a shoe") versus teaching AI to understand a need ("This shoe fits your running style and arch support requirements"). This distinction separates basic recognition from true consultative intelligence.
The Landscape of Data Labeling Types
Understanding the various types of data labeling is essential for selecting the right approach for your AI project. The landscape ranges from simple visual recognition to complex conversational understanding.
Computer Vision Annotation
Computer vision annotation focuses on visual data processing. This includes bounding boxes around objects in images, semantic segmentation that labels every pixel, and polygon annotations for irregular shapes. Applications span autonomous driving, medical imaging, and quality control in manufacturing. Tools like Labelbox excel in this domain, providing robust interfaces for image and video annotation.
Simple Natural Language Processing
Basic NLP annotation typically involves sentiment analysis—categorizing text as positive, negative, or neutral. Named entity recognition identifies people, places, and organizations within text. While valuable for basic text classification, this level of annotation falls short for complex advisory scenarios.
Deep Dive: Conversational and Logic Annotation
This is where the landscape changes dramatically for consultative AI systems. Conversational and logic annotation goes far beyond simple sentiment classification to capture the nuanced requirements of advisory interactions.
Intent Labeling identifies what a user truly wants to accomplish. When a customer says "It's cold," a basic annotation marks this as a weather fact. A consultative annotation recognizes this as an implicit need for warm clothing recommendations.
Product Attribute Extraction captures specific requirements mentioned throughout a conversation—budget constraints, style preferences, technical specifications, and compatibility requirements.
Consultation Flow Annotation evaluates whether the AI asked the right follow-up questions. Did it gather sufficient information before making recommendations? Did it clarify ambiguous requirements? This level of annotation requires domain experts who understand what constitutes good advice.
| Annotation Approach | Standard Labeling | Consultative Labeling |
|---|---|---|
| User says: 'It's cold' | Weather/Fact statement | Need: Warm Jacket/Winter Gear |
| User mentions budget | Price category tag | Constraint: Budget < €100 with flexibility analysis |
| User expresses preference | Simple preference flag | Preference: Eco-friendly with priority weighting |
| Conversation evaluation | Sentiment only | Full advisory quality assessment |
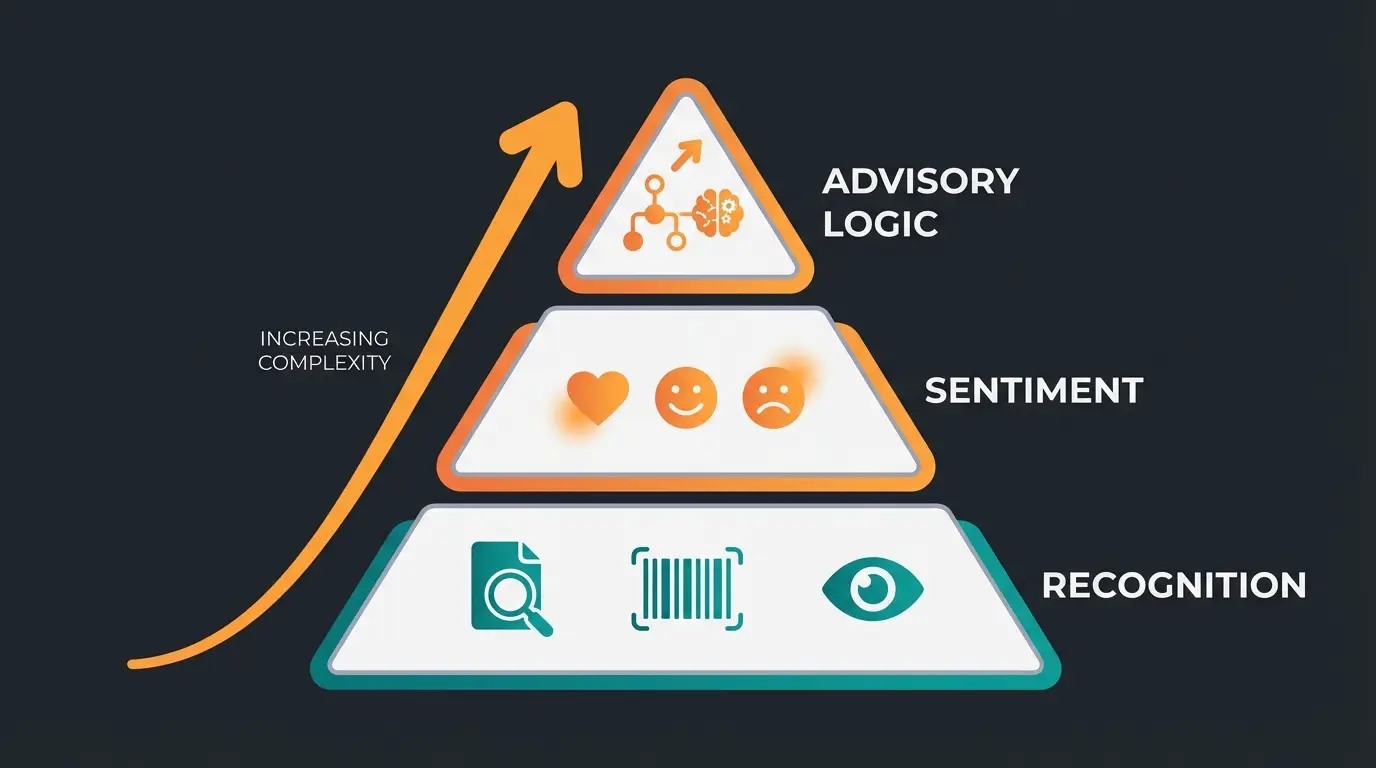
The Hierarchy of AI Understanding
Understanding how AI comprehension builds in layers helps explain why standard annotation tools struggle with consultative applications. Each layer builds upon the previous, requiring increasingly sophisticated annotation approaches.
Basic identification—'This is a car.' Standard tools handle this well with bounding boxes and classification labels.
Emotional context—'This is a nice car.' Requires understanding of subjective language and user attitudes.
Consultative reasoning—'This car fits your family needs because of X, Y, Z.' Requires domain expertise and understanding of user context, constraints, and optimal recommendations.
Most annotation tools and guides focus exclusively on the first two layers. The advisory logic layer—where true consultative AI operates—requires a fundamentally different approach to data labeling that prioritizes expert knowledge over crowd-sourced volume.
Core Features of Labelbox Platform
Data Management System
The central data management system of Labelbox provides a structured environment for organizing and storing training data. Practical AI implementation is supported through intuitive data management tools. Teams can work on projects in parallel while the integrated versioning system documents all changes traceably.
AI-Powered Annotation Tools
AI-assisted annotation tools accelerate the labeling process through automatic suggestions and batch processing. Developers can create custom labels and establish annotation guidelines. The platform supports various annotation types including bounding boxes, segmentation, and classification.
Quality Control Mechanisms
A comprehensive quality assurance system continuously monitors the accuracy of data labeling. Automated verification processes identify inconsistencies and enable quick corrections. Performance metrics provide insight into the annotation team's efficiency and the quality of generated training data.
Tools Compared: Labelbox vs. Specialized Solutions
Labelbox represents the gold standard for general-purpose annotation, particularly excelling in computer vision applications. The platform offers enterprise-grade security, scalable team management, and robust API integration. For autonomous driving, medical imaging, and similar perception-based AI applications, it remains an excellent choice.
However, for consultative AI systems, general tools like Labelbox face inherent limitations. Product advisory scenarios require tools that can visualize dialogue trees, map product databases, and evaluate the quality of recommendation logic—not just highlight text spans.
| Feature | General Tools (Labelbox) | Specialized Consultation Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Image annotation | Excellent—industry leading | Adequate but not primary focus |
| Simple text classification | Strong capabilities | Adequate |
| Multi-turn dialogue annotation | Limited support | Purpose-built functionality |
| Product knowledge integration | Requires custom development | Native integration |
| Advisory logic evaluation | Not supported | Core feature |
| Domain expert workflows | Generic labeler focus | Expert-centric design |
The Pivot Point for Consultative AI
When your AI needs to advise rather than simply recognize, the annotation requirements shift fundamentally. You need tools that understand conversation context across multiple turns, can integrate product knowledge bases, and can evaluate whether recommendations actually serve user needs.
Let our experts handle your AI data annotation while you focus on building your product consultation system.
Get Expert AnnotationTechnical Integration Requirements
Technical integration of annotation platforms requires a structured approach. The platform offers various possibilities for embedding into existing systems and workflows.
System Requirements
Labelbox runs as a cloud-based solution requiring minimal local resources. A modern web browser and stable internet connection form the foundation. For larger datasets, a bandwidth of at least 50 Mbit/s is recommended. The platform supports all common operating systems including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Hardware: Standard cloud servers or on-premise systems with at least 16GB RAM
- Browser: Current versions of Chrome, Firefox, or Safari
- Storage: Minimum 500GB for datasets and annotations
- Network: Stable internet connection with at least 50 Mbit/s
API Integration
The REST API enables seamless integration into existing ML pipelines. The API supports both JSON and GraphQL for flexible queries. Both synchronous and asynchronous calls are available with comprehensive developer documentation. The ability for automated data processing proves particularly valuable, as demonstrated in AI-powered lead generation.
Supported Data Formats
Annotation platforms process a wide range of file formats. For image data, JPG, PNG, and TIFF are supported. Text data can be imported as TXT, CSV, or JSON. Video formats like MP4 and MOV are also compatible. The platform automatically converts data into the optimal format for processing.
- Images: JPG, PNG, TIFF, BMP
- Video: MP4, AVI, MOV
- Text: TXT, CSV, JSON, XML
- Audio: MP3, WAV, FLAC
Security Considerations
Multi-layered security measures protect sensitive data throughout the annotation process. SSL encryption protects all data transfers. Role-based access controls enable granular management of user permissions. Regular security audits and SOC 2 Type II certification guarantee the highest security standards.
- Encryption: AES-256 for data at rest
- Authentication: Two-factor authentication
- Access Control: Role-based permissions
- Compliance: GDPR, HIPAA, SOC2
Scaling Capabilities
Cloud-native architecture allows flexible scaling according to your project requirements. The elastic infrastructure automatically adapts to increasing data volumes. Performance monitoring tools help with optimization. Additional resources can be provisioned quickly when needed. The platform can grow seamlessly from small teams to large enterprise implementations, as shown in practical AI implementations.
From Raw Data to Model Optimization: The Process
The journey from raw conversation data to a well-optimized consultation AI follows a structured process that differs significantly from standard computer vision annotation workflows.
Gather real customer conversations, support interactions, and consultation sessions. Quality over quantity—100 expert consultations beat 10,000 generic chats.
Define what constitutes 'good advice' for your domain. Establish clear criteria for successful recommendations and proper follow-up questions.
Domain specialists—not generic crowd workers—label conversations for intent, constraints, preferences, and advisory quality.
Implement active learning cycles where model predictions are reviewed and corrected, continuously improving annotation quality.
Step 1: Strategic Data Collection
The annotation process begins with collecting real customer conversations. Unlike image datasets where volume often matters most, consultative AI benefits more from carefully selected, representative dialogues that showcase the full range of consultation scenarios.
Step 2: Defining Excellence in Advice
Before any labeling begins, you must establish clear guidelines defining what constitutes excellent consultation. What questions should the AI ask? How should it handle ambiguous requirements? When should it recommend alternatives? These guidelines become the annotation framework.
Step 3: Subject Matter Expert Involvement
This step is where most standard approaches fail. Generic crowd workers can identify a stop sign or classify sentiment, but they cannot evaluate whether a product recommendation truly serves a customer's needs. Domain experts—people who understand your products, your customers, and what constitutes good advice—must be central to the annotation process.
Step 4: Active Learning Integration
The annotation process should not be linear. As your model begins making predictions, those predictions need expert review. Correct predictions reinforce learning; incorrect predictions become new training examples. This feedback loop continuously improves both model performance and annotation quality.
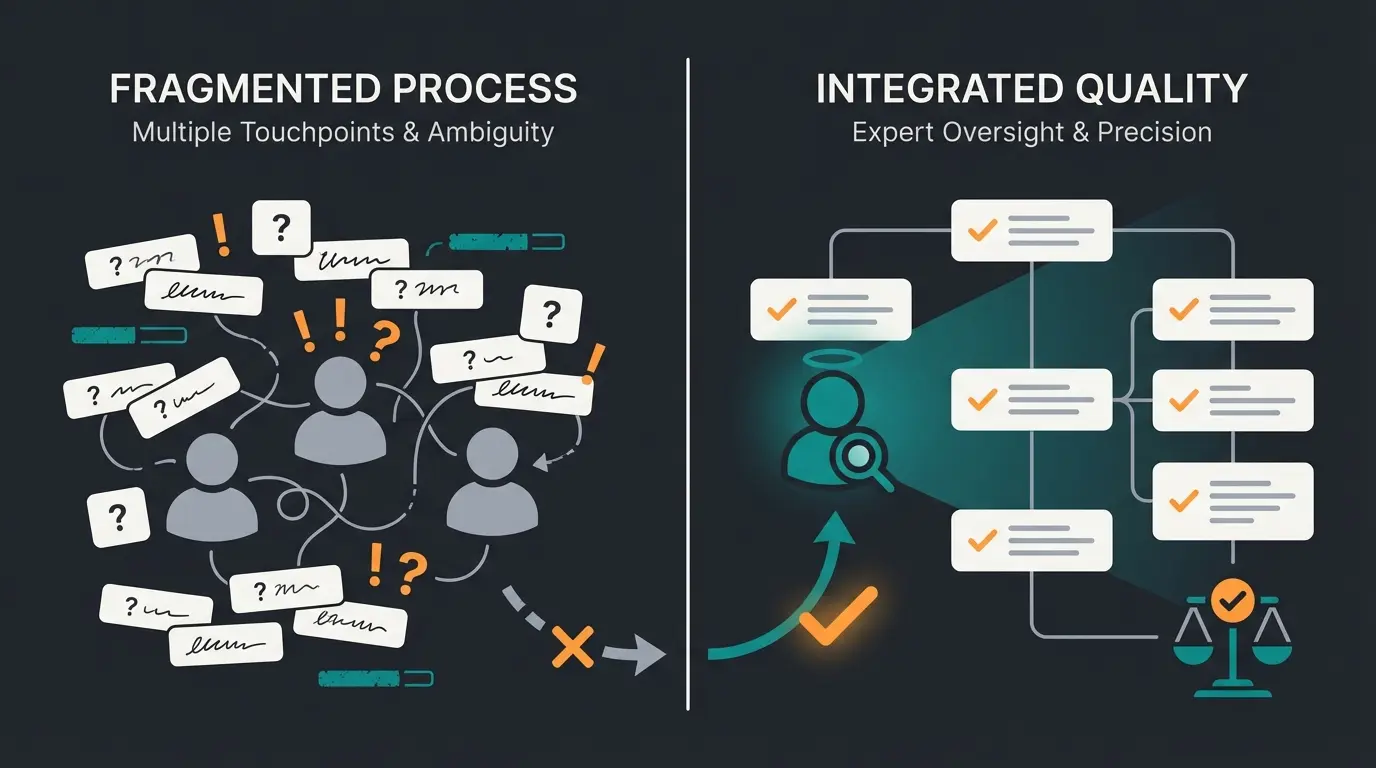
Quality Over Quantity: Why Crowd Labeling Fails
The dominant narrative in AI data annotation emphasizes scale—more data, more labels, more workers. This approach works well for perception tasks but fails catastrophically for consultative AI applications.
Carefully labeled by domain specialists who understand product nuances and customer needs
Generic annotations from workers without domain expertise or consultation experience
Expert-annotated models show significantly higher consultation accuracy and customer satisfaction
Consider the challenge: a random clickworker can identify a stop sign with near-perfect accuracy. But can they evaluate whether a jacket recommendation is appropriate for a customer who mentioned they're planning a hiking trip in spring? Can they assess whether the AI asked the right follow-up questions about terrain, expected weather, and layering preferences?
Domain Expertise Cannot Be Crowdsourced
Effective consultation requires understanding product nuances, customer psychology, and the subtle art of matching needs with solutions. A fashion expert understands why certain fabric combinations work for specific occasions. A technical specialist knows which product specifications matter for different use cases. This expertise cannot be replaced by annotation volume.
Practical Applications Across Industries
Image Processing Applications
In the field of AI-powered product consultation, companies use annotation platforms for precise labeling of product images. The automatic recognition of product features significantly improves consultation quality. Examples include:
- Quality Control: Automatic detection of product defects
- Product Categorization: AI-assisted sorting of article images
- Feature Extraction: Automatic capture of product properties
With Labelbox: Companies can use Labelbox to label product images internally. This requires trained employees and manual quality assurance.
With Qualimero: We handle the complete labeling process, so companies can focus on analyzing and using the data.
Text Analysis Applications
Automated lead generation benefits from precisely labeled text data. Platforms support processing of various text formats and enable efficient analysis of customer feedback, support inquiries, and product descriptions. AI models learn to recognize customer intentions and sentiments from labeled data.
- Sentiment Analysis: Emotion detection in customer feedback
- Classification: Document categorization
- Extraction: Recognition of relevant information
Industry-Specific Solutions
Various industries deploy annotation platforms for specialized applications. In retail, platforms improve product recognition and inventory management. In healthcare, they support analysis of medical images. Manufacturing uses annotation for quality control in production.
- Automotive: Autonomous driving and driver assistance systems
- E-Commerce: Product cataloging and image recognition
- Finance: Document processing and compliance
- Healthcare: Medical image analysis and diagnostic support
Whether e-commerce, healthcare, or industry—high-quality training data is crucial for AI model success across all domains. While Labelbox offers the ability to perform annotations internally, Qualimero provides a turnkey solution that handles the entire process for you.
Implementation Guide: Getting Started Right
Successful introduction of annotation platforms requires a structured approach. A thorough setup process forms the foundation for efficient AI data labeling. Integration into existing machine learning workflows enables seamless collaboration between teams and systems.
Setup and Project Structure
The first step involves technical platform configuration. The data infrastructure is configured and adapted to specific project requirements. Basic configuration includes connecting data stores, defining annotation guidelines, and establishing quality control mechanisms.
Optimal Team Structure
A clear role distribution within the team is crucial for project success. Core roles include project managers, annotation experts, and quality reviewers. Each team member requires specific access rights and responsibilities within the platform.
- Project Manager: Coordination and monitoring of labeling processes
- Annotation Experts: Execution of data labeling with domain knowledge
- Quality Reviewers: Ensuring data quality through systematic checks
- AI Developers: Integration of labeled data into ML models
Process Optimization Strategies
Continuous improvement of workflows stands at the center of process optimization. Through regular analysis of annotation quality and throughput times, bottlenecks can be identified and eliminated. Integration of automated verification processes helps maintain consistently high labeling quality.
Annotated Dialogue: What Expert Labeling Looks Like
Visualizing Consultative Annotation
To understand the difference between standard and consultative annotation, consider how a single customer message might be labeled for advisory AI:
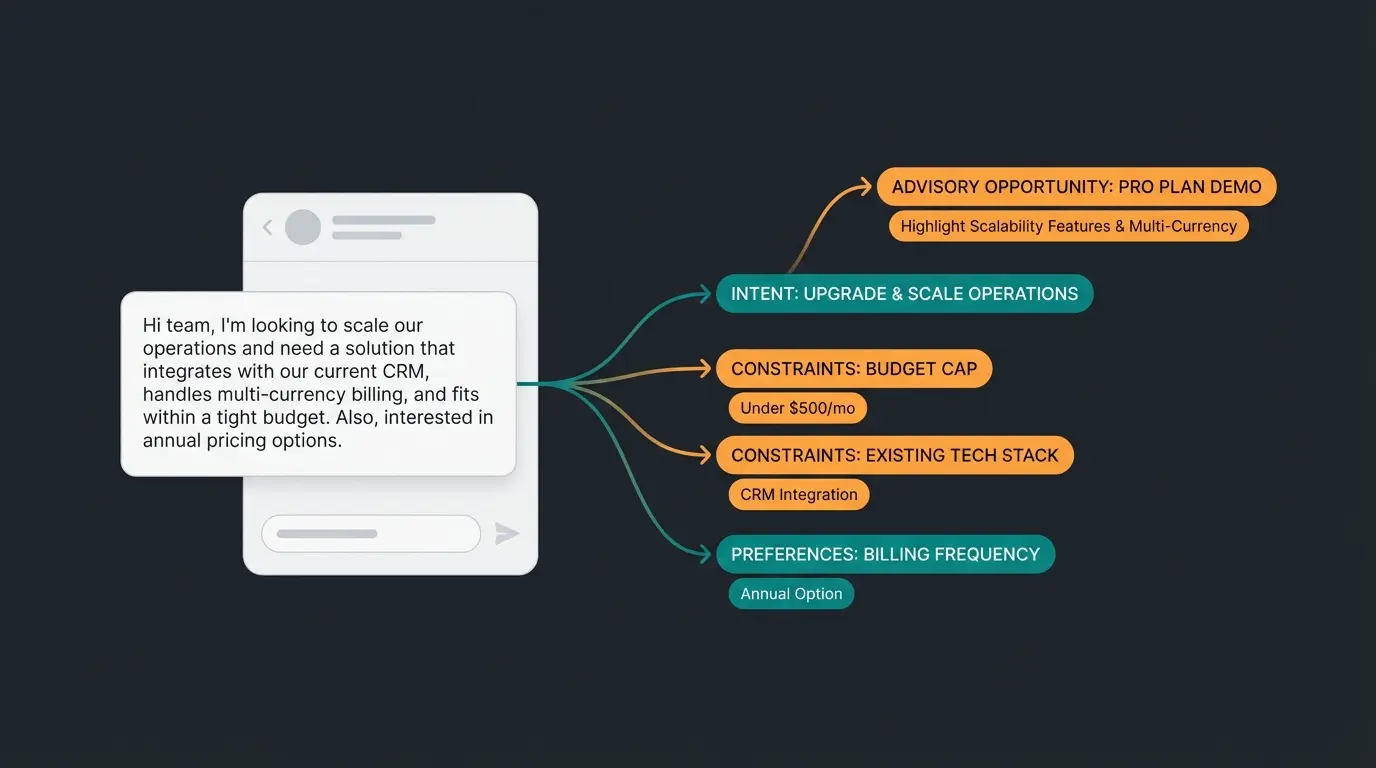
Customer message: "I need something for my daughter's first hiking trip, probably around €80, and she cares a lot about the environment."
Standard annotation: Intent: Purchase. Category: Outdoor gear.
Expert consultative annotation:
- [User Intent: Purchase - Gift for family member]
- [Experience Level: Beginner - first trip indicator]
- [Constraint: Budget €80 - some flexibility implied by 'around']
- [Preference: Eco-friendly - high priority indicated by 'cares a lot']
- [Context: Youth sizing needed - 'daughter']
- [Advisory Opportunity: Ask about terrain type, expected weather, and existing gear]
This level of annotation enables AI models to provide genuinely helpful consultation rather than generic product listings.
Conclusion: Turning Chatbots into Consultants
Labelbox has established itself as a central platform for AI data labeling and model optimization. The combination of powerful annotation tools, comprehensive quality control mechanisms, and flexible team collaboration makes it a valuable tool for ML projects.
The platform's potential continues to expand through ongoing developments and new features. For companies looking to professionalize their AI development, Labelbox provides the necessary infrastructure and scalability.
However, the investment in professional annotation pays off through more precise ML models and more efficient development processes only when approached correctly. With the right implementation strategy and structured approach, maximum benefit can be derived from any platform.
The key insight: Good annotation transforms a chatbot into a consultant. The difference lies not in the volume of labeled data but in the quality and depth of understanding captured in that data.
Labelbox is an excellent choice for companies that want to label their data themselves and can provide appropriate resources. But if you want to save time and costs while ensuring higher annotation quality, Qualimero represents the ideal alternative.
With our "done-for-you" approach, we handle the entire data labeling process for you, so you can focus entirely on developing your AI models. Let's take your AI projects to the next level together.
Frequently Asked Questions
AI data annotation is the process of labeling data so machine learning models can learn from it. It matters because model accuracy directly depends on data quality—following the 'garbage in, garbage out' principle. For consultation AI specifically, annotation quality determines whether your system provides generic responses or genuinely helpful advice.
Labelbox excels at general-purpose annotation, particularly computer vision tasks like autonomous driving and medical imaging. However, for consultative AI that needs to understand multi-turn dialogues, product relationships, and advisory logic, specialized tools designed for conversation annotation provide better results.
Crowd workers can accurately label simple recognition tasks, but they lack the domain expertise needed to evaluate consultation quality. A fashion expert understands why certain recommendations work; a technical specialist knows which specifications matter. This expertise cannot be replaced by annotation volume.
Major platforms support a wide range of formats: images (JPG, PNG, TIFF, BMP), video (MP4, AVI, MOV), text (TXT, CSV, JSON, XML), and audio (MP3, WAV, FLAC). Data is typically converted automatically to optimal processing formats.
Implementation timeline varies based on complexity. Basic setup can take days, while establishing comprehensive annotation guidelines, training expert annotators, and implementing feedback loops for consultative AI typically requires several weeks. The done-for-you approach eliminates this learning curve entirely.
Stop struggling with generic annotation tools. Our expert team delivers consultation-quality labeled data that turns your AI into a true advisor.
Start Your Project