Digital transformation continuously presents German companies, from mid-sized businesses to large corporations, with new challenges. In this dynamic environment, automation in customer dialogue and underlying business processes is no longer an optional extra but a critical success factor. Companies are searching for ways to become more efficient, reduce costs, and simultaneously improve customer experience. However, when it comes to automating more complex processes, simple solutions quickly reach their limits. The market offers a wealth of technologies that are often difficult to differentiate: from simple chatbots to intelligent dialogue systems to highly developed AI systems that act autonomously.
This technological development is not just an end in itself but reflects the growing demands of the business world. Initially, the focus was on increasing efficiency in repetitive tasks – simple chatbots were deployed here to answer standard questions. With rising customer expectations for personalized, high-quality dialogues, AI-powered chatbots became relevant, understanding natural language better. Today, however, the trend goes further: companies strive for comprehensive automation of complex processes and proactive action, not just to provide service but to actively solve problems and increase revenue. This explains the rise of so-called AI employees or AI agents.
Here's the crucial insight that most competitors miss: customer service is evolving from a cost center to a revenue generator. While traditional support focuses on deflecting tickets and reducing workload, the real opportunity lies in consultation – helping customers make purchase decisions. An AI employee doesn't just send return labels; it asks about your skin type to recommend the perfect face cream. This shift from support to advisory represents the blue ocean opportunity for forward-thinking companies.
This article aims to bring clarity to the terminology. It defines the three central categories – simple chatbots, AI chatbots, and AI employees – analyzes their functionalities, strengths, and weaknesses, and provides a detailed comparison. This understanding is essential for companies to make strategically sound decisions about deploying the right automation technology, thereby sustainably increasing efficiency, customer satisfaction, and ultimately business success.
What Are Chatbots and How Do They Work?
A chatbot is essentially a computer program designed to simulate human conversation. The term combines 'chat' (conversation) and 'bot' (short for robot). These text- or voice-based dialogue systems conduct automated conversations with users to provide information, answer questions, or handle simple tasks.
Their fundamental relevance for companies, especially in mid-sized businesses and corporations, often lies in serving as the first point of contact for customers. They can relieve customer service by answering frequently asked questions (FAQs) around the clock, for example about opening hours, product information, or delivery conditions. This 24/7 availability without human intervention is a significant advantage.
At their core, simpler variants are distinguished into two main types:
- Rule-based / Script-based Chatbots: These are the simplest form of chatbots. They function according to a fixed set of predefined rules, often following 'if-then logic.' The conversation follows a rigid dialogue tree or script established in advance. Users frequently interact by selecting from predetermined response options or buttons. A typical example would be a bot that can only answer questions about opening hours and must fail at any other inquiry. They are designed to follow a specific sequence that can range from simple to complex but is always predefined.
- Keyword-based Chatbots: This type is a slight advancement. It analyzes user input for certain predefined keywords. When the bot recognizes a keyword it knows, it triggers a likewise predefined response or action. For example, if a user asks: 'Where can I find the shipping costs?' the bot recognizes the keyword 'shipping costs' and outputs the stored standard information. Although somewhat more flexible than purely rule-based systems, their ability to understand context or nuances of a question remains severely limited.
Strengths of Simple Chatbots: The main advantage lies in their simplicity. They are comparatively easy to implement and maintain. Their responses are predictable and consistent, which is quite desirable in some use cases. For clearly defined, simple tasks, they are often the most cost-effective solution in terms of development and ongoing operation.
Weaknesses of Simple Chatbots: Simplicity is simultaneously their greatest weakness. Their flexibility is severely limited; they can only respond to exactly the scenarios or keywords for which they were programmed. They have no real language understanding and can neither grasp conversation context nor learn from interactions. If a user asks an unexpected question or phrases it differently than intended, the bot quickly reaches its limits, cannot respond, and possibly causes customer frustration. Additionally, all rules and responses must be manually created and updated when needed, which can be time-consuming with changing information.
These characteristics position simple chatbots primarily as tactical tools. They are useful for efficiently handling specific, repetitive tasks, thereby relieving customer service. They solve a narrowly defined problem. However, they lack the necessary intelligence and flexibility for profound optimization of business processes or significant improvement of customer experience with more complex concerns. They are thus more of a supplement than a strategic solution for comprehensive challenges in customer communication or process automation.
Intelligence in Dialogue: AI Chatbots Understand and Learn
The next evolutionary stage consists of AI-powered chatbots. These use Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies to not only recognize human language but also understand it and respond in a way that more closely resembles human-like conversation. The decisive difference from simple, rule-based systems lies in their ability to process natural language and learn from interactions. They are no longer rigidly bound to predefined scripts.
Key Technologies Explained
Natural Language Processing (NLP): This is a field of AI that enables machines to understand and interpret human language – both written and spoken. NLP analyzes the structure, grammar, and meaning of sentences. It identifies keywords, recognizes user intent, and considers conversation context. NLP comprises two essential sub-areas:
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Focuses on understanding the meaning and intent behind user input. NLU transforms unstructured human language into structured data that a machine can process. It's about understanding what the user really means, not just what they say.
- Natural Language Generation (NLG): Handles generating human-like language as a response. Based on processed information, NLG formulates an appropriate and natural-sounding answer.
Machine Learning (ML): This technology gives AI chatbots their learning capability. Instead of being explicitly programmed for every possible question, ML models learn from large amounts of interaction data. They recognize patterns, understand relationships, and can independently improve their performance and response accuracy over time. There are various learning approaches: In Supervised Learning, the model is trained with examples where the correct answer is known. Unsupervised Learning helps find patterns in unstructured data. Reinforcement Learning enables learning through feedback on generated responses.
Advanced Capabilities of AI Chatbots
Through the use of NLP and ML, AI chatbots possess capabilities far beyond simple bots:
- Context Understanding: They can maintain the thread of a conversation across multiple interactions and use information from earlier statements to give more relevant answers.
- Intent Recognition: They are better at recognizing the actual intent behind a user query, even when formulated vaguely or colloquially.
- Personalization: They can personalize responses and recommendations based on user profiles, past behavior, or current conversation context.
- More Flexible Dialogue Management: They can respond to unexpected questions or more complex inquiries that didn't occur exactly in the training dataset. They can often engage in small talk or react to slight deviations from the core topic.
- Continuous Improvement: Through ML, they learn from every interaction and become increasingly better at understanding and answering user queries over time.
Advantages Over Simple Chatbots: These capabilities lead to clear advantages: AI chatbots offer significantly higher flexibility and adaptability to different conversation situations. This results in more natural dialogues and potentially higher customer satisfaction, as users feel better understood. They can also scale better for complex conversations than rule-based systems. Additionally, collected interaction data can provide valuable insights into customer needs and problems.
Limitations of AI Chatbots: Despite their intelligence, AI chatbots also have limits. Their main focus remains on conversation, understanding inquiries, and providing information or simple actions in dialogue. They are typically not designed to autonomously execute complex, cross-system business processes. Their implementation often requires extensive, high-quality training data, and training and maintenance can be more complex and costly than with simple bots. With very multifaceted problems requiring deep integration into backend systems and independent decisions, they too reach their limits.
AI chatbots thus mark an important transition. They move away from pure efficiency through automation toward improved, more intelligent interaction. They address customers' heightened expectations for personalized and context-sensitive communication. This represents a step toward more strategic use of automation by optimizing the customer interface. However, their core competency remains dialogue, not autonomous action or profound process automation, as offered by the next level – AI employees.
AI Employees: Autonomous Agents for Complex Tasks
The evolution of automation technology leads us to the next level: AI employees. These systems, also known as AI agents, AI workers, digital workers, or intelligent agents, represent a significant leap compared to traditional chatbots, even AI-powered ones. They are not primarily designed as dialogue systems but as advanced AI software that can act autonomously to achieve defined business goals.
The Decisive Difference: Action Instead of Just Talk
Here lies the core distinction: While chatbots (rule-based or AI-based) mainly aim to deliver information, answer questions, and conduct dialogues, AI employees are designed to perform actions. They make independent decisions and can not only support but actively control and automate complex, often cross-system business processes. They are aptly described as action-activated AI-powered assistants whose focus lies on goal-oriented task processing and problem-solving. They act more like 'digital employees.'
Core Characteristics and Capabilities
- Autonomy: They can operate largely independently of direct human control to pursue their goals. They make decisions and execute actions independently.
- Proactivity: Unlike purely reactive systems, AI employees can take initiative to achieve goals or anticipate and solve problems, for example in proactive customer service.
- Planning & Reasoning: They understand complex goals, can derive action plans from them, and draw logical conclusions to determine the best approach. Modern AI employees often use the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) for improved planning and reasoning processes.
- Decision-Making: Based on goals, collected data, their perception of the environment, and learned patterns, they make independent decisions, even in complex and dynamic situations.
- Learning Ability & Adaptation: They continuously learn from their experiences, feedback, and new data. This improves their performance and allows them to adapt to changing conditions or new tasks.
- Perception: They can perceive and process relevant information from their digital environment (e.g., system data, sensor data, user inputs) to make informed decisions.
- Memory/Context: They store relevant information about past interactions and process steps to ensure continuity and act context-appropriately.
- Integration: A key component is their ability for deep integration into existing IT landscapes. Through APIs (interfaces), they can access data from CRM, ERP, logistics, or other systems and trigger actions in these systems.
- Task Complexity: They are capable of handling complex, multi-step tasks that often require human judgment, planning, and coordination of various steps.
'I need a gift for my wife' - vague request received via chat or WhatsApp
AI analyzes past purchases, browsing history, and available budget signals
'What are her interests? Any preferred price range? Is there a special occasion?'
Real-time search through entire product catalog based on gathered preferences
'Based on her love for gardening, I recommend this premium tool set with personalized engraving'
AI processes order, schedules delivery, and sends confirmation - all autonomously
Technology Stack
AI employees are based on a combination of various advanced technologies, including Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) for understanding and planning, NLP for language processing, Machine Learning for learning and adaptation, often supplemented by Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for automating rule-based subtasks and APIs for system integration.
Application Examples Beyond Chat
- Process Automation: Complete handling of business processes such as invoice processing from matching to payment, automated claims processing in insurance, order processing and returns management in e-commerce.
- Sales & Marketing: Intelligent lead qualification through analysis of user needs and direct appointment booking, personalized product recommendations based on real-time data analysis, control of automated marketing campaigns.
- Customer Service: Proactive problem-solving (e.g., informing about delivery delays before customer inquiry), handling complex complaints and refunds, intelligent ticket routing.
- Supply Chain & Logistics: Optimization of supply chains through analysis of inventory and demand forecasts, intelligent route planning.
- Finance & Accounting: Automated bookings and reconciliations, support for financial reports and audits through continuous data monitoring.
- IT Support: Automated error diagnosis, password resets, device provisioning.
- Human Resources (HR): Automated analysis of applications (screening), support for onboarding new employees.
- Cybersecurity: Real-time threat detection and automatic initiation of countermeasures.
The capabilities of AI employees, especially their autonomy, decision-making, and deep integration ability, make them strategic tools. Unlike chatbots, which primarily optimize the communication interface, AI employees target the transformation and automation of core processes. They enable not only efficiency gains but potentially entirely new ways of working and can have a direct impact on revenue and costs. This fundamental shift from optimizing interactions to optimizing processes and outcomes makes AI employees a key element of the next wave of enterprise automation.
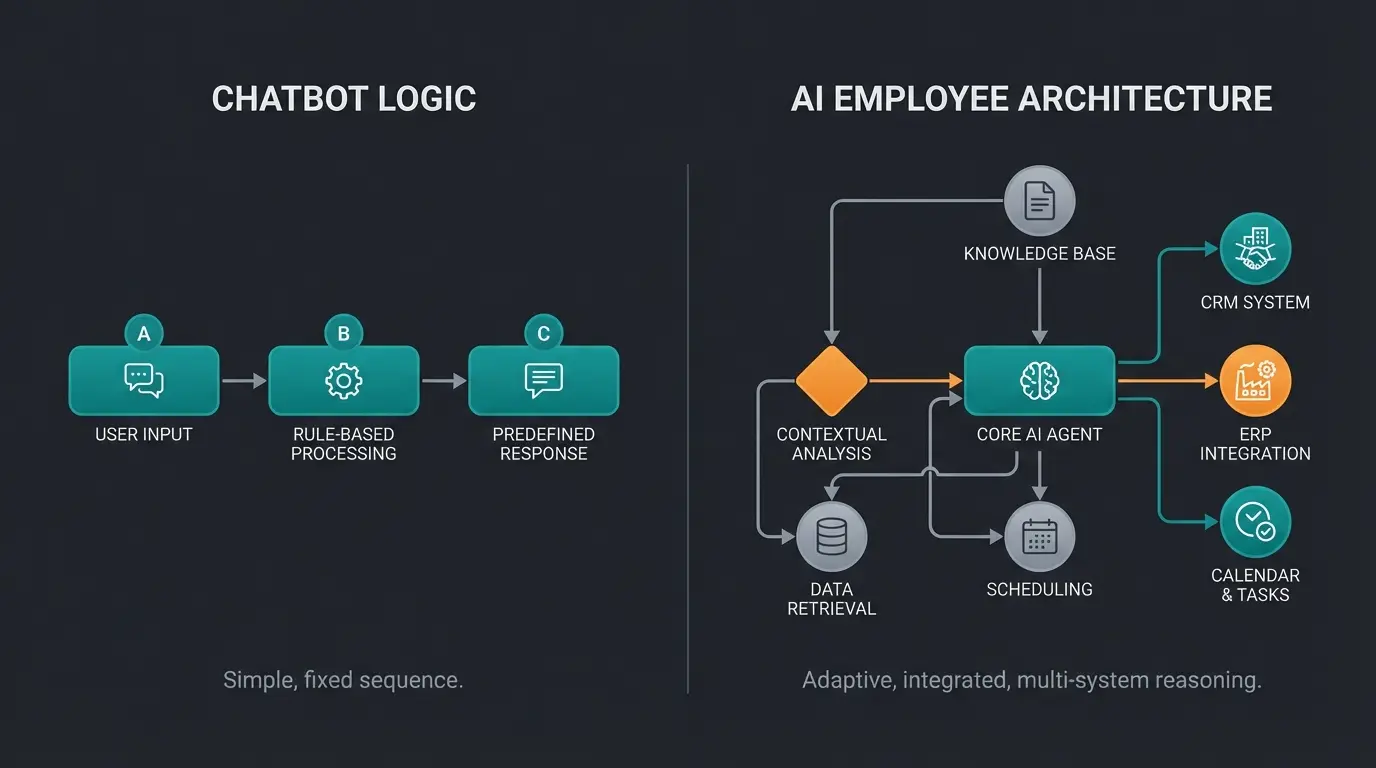
Chatbots vs. AI Chatbots vs. AI Employees: Comparison
To develop the right automation strategy for your own company – whether mid-sized business or corporation – a clear distinction between the various technologies is essential. The choice between a simple chatbot, an AI chatbot, and an AI employee depends significantly on specific goals, processes to be automated, and desired capabilities. The following table and subsequent analysis illuminate the decisive differences.
Comparison Table: Rule-based Chatbot vs. AI Chatbot vs. AI Employee
| Criterion | Rule-based Chatbot | AI Chatbot | AI Employee / AI Agent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software that responds according to fixed rules/scripts | AI-powered software for natural language dialogues | Autonomously acting AI software for goal achievement & process execution |
| Core Technology | Predefined rules, decision trees, keywords | AI, NLP (NLU, NLG), Machine Learning (ML) | AI, NLP, ML, often combined with RPA, APIs, decision logic, Generative AI (LLMs) |
| Intelligence/Learning | No learning capability | Learns from interactions (ML), improves dialogue ability | Actively learns from experience, feedback & data; adapts behavior & strategies |
| Context Understanding | Minimal to non-existent; limited to current rule | Can understand dialogue context across multiple turns | Comprehensive context understanding (dialogue, process, system data, environment) |
| Autonomy | Very low; only reacts to matching inputs | Limited; focus on dialogue management, can trigger simple actions in dialogue | High; makes independent decisions and executes actions to achieve goals |
| Task Complexity | Very simple, repetitive (e.g., FAQs) | Simple to moderately complex dialogues, information retrieval | Complex, multi-step, dynamic tasks & processes; problem-solving |
| Flexibility | Rigid, inflexible; only predefined paths | More flexible in dialogue management; can react to variations | Very flexible; dynamically adapts to new situations & goals |
| Scalability | Scales for simple queries; limited with complexity | Scales well for dialogue volume; limited with process complexity | Highly scalable for complex tasks and processes across systems |
| Integration Capability | Usually simple website/app embedding | Can connect to data sources via APIs | Deep integration into core systems (CRM, ERP etc.) for data use & action execution |
| Typical Use Cases | Answering FAQs, simple forms | Customer service dialogues, product information, lead generation (dialogue) | Process automation (Sales, Support, HR, Finance), proactive service, lead qualification (with action) |
| Implementation Effort/Cost | Low | Medium to High (training, data) | High (integration, training, possibly customization), but potentially high ROI |
| Main Advantage | Simple, cost-effective for simple tasks | More natural conversation, better user experience | Autonomous problem-solving & process automation, strategic value |
| Main Disadvantage | Inflexible, no learning ability, breaks on deviation | Focus on dialogue, limited action capability, training effort | Higher complexity & costs, requires clear goals & good integration |
Detailed Analysis of Differences
The table illustrates the gradual development and significant leaps between categories:
Intelligence & Learning: The most striking difference lies in intelligence. Rule-based bots are static. AI chatbots use ML to learn from dialogue data and improve their conversation skills. AI employees go further: they actively learn from their actions, feedback, and environment to adapt and optimize their strategies for goal achievement.
Autonomy & Action Capability: This is the critical differentiating factor. Simple chatbots and most AI chatbots are primarily reactive – they respond to user inputs. AI employees, however, possess a high degree of autonomy. They can make independent decisions and act proactively to complete tasks and pursue goals without waiting for a specific human command.
Task Complexity: Rule-based bots are only suitable for very simple, clearly defined tasks like answering FAQs. AI chatbots can conduct more complex dialogues and consolidate information from various sources. AI employees are designed to handle complex, multi-step processes that often require interaction with multiple systems and dynamic adjustments.
Integration Depth: While simple bots are often only embedded on a website, AI chatbots can already access external data via APIs. AI employees need and enable deep integration into a company's core systems (such as CRM, ERP, logistics software) to comprehensively use data and control processes across systems.
Flexibility & Adaptability: The rigidity of rule-based systems contrasts with the dialogical flexibility of AI chatbots. AI employees offer the highest flexibility as they can dynamically adapt not only to conversation flows but also to changing process requirements and environmental conditions.
Implementation Effort & Costs: Costs and effort tend to increase with the complexity and capabilities of systems. While simple chatbots can be set up quickly and cheaply, AI chatbots require investments in training and data. AI employees represent the highest investment but promise the potentially highest Return on Investment (ROI) through automation of complex core processes.
Implications for Companies
The choice of technology is thus a strategic decision about the desired degree of automation and the type of problems to be solved:
- Simple Chatbot: Sufficient when primarily addressing very frequent, standardized questions (e.g., opening hours, simple product info) around the clock and relieving the service team from these repetitive inquiries.
- AI Chatbot: The right choice when the goal is improving customer experience through more natural, personalized, and context-related dialogues. Suitable for more complex information provision, consultation in dialogue, or smarter lead generation where conversation is the focus.
- AI Employee: Companies should consider this when strategic goals like automating end-to-end business processes, solving complex customer problems through actions, proactive service, or scaling demanding tasks are the focus. They are relevant when it's not just about communication but about measurable results through autonomous action – whether revenue increase, cost reduction, or significant efficiency gains in core areas.
Discover how AI employees can handle complex consultations, qualify leads, and automate processes while your team focuses on high-value activities.
Start Your AI JourneyIntelligent Automation in Practice: How Qualimero Deploys AI Employees
After illuminating the differences between the various stages of chat automation, the question arises: what does the most advanced stage – AI employees – look like in practice? The Düsseldorf-based company Qualimero has specialized in exactly this area and offers solutions that go beyond pure dialogue management and are described as 'AI employees' or 'digital employees.'
Qualimero's Approach
Qualimero clearly positions its technology in the segment of acting AI systems. The focus lies on achieving measurable business results such as revenue increase and cost reduction by having AI employees actively take over tasks and optimize processes. The company emphasizes 'Human results' – the AI should act with human-like intelligence, whether in customer consultation, support, or even recruiting.
A key characteristic of this approach is the focus on customized solutions instead of standard products. Qualimero develops AI applications that seamlessly integrate into the specific workflows and goals of the customer company. This is supported by a 'Done-for-You' service approach intended to minimize implementation effort for the customer – a difference from platforms where customers must largely handle implementation themselves.
Concrete Use Cases and Solutions
- [AI Product Consultant in E-Commerce](https://www.qualimero.com/blog/ki-conversational-commerce-ecommerce-suche): This digital employee interacts with customers on the website or via messaging services like WhatsApp. It analyzes customer needs and preferences in real-time, answers detailed product questions, recommends suitable items, and can even check order status or initiate returns. The goal is to increase conversion rate and average order value while relieving the support team. One customer reports that inquiries to the sales team could be reduced by up to 95% through the AI product consultant.
- [Lead Qualification in Sales](https://www.qualimero.com/leadgenerierung-per-ki): The AI employee conducts qualifying conversations with potential customers via chat or WhatsApp. It inquires about needs, collects relevant information, and can directly book an appointment in the sales representative's calendar upon appropriate qualification. This is intended to maximize sales team efficiency by allowing them to focus on already pre-qualified and scheduled leads, reducing Cost per Lead (CPL). Qualimero states this achieves up to 10x higher conversion rates compared to conventional forms. One user highlights that AI employees handle routine questions and qualify leads so personnel can focus on closing deals.
- Automated Customer Support: The digital employees answer customer inquiries around the clock through various channels (webchat, WhatsApp, email, even phone is mentioned). They can resolve standard cases immediately and independently, routing only complex or escalation-requiring cases to human agents. One customer reports that 97% of inquiries are immediately answered by AI, leading to a significant increase in customer satisfaction.
- Process Automation: More generally, it is mentioned that Qualimero's AI employees automate routine activities in companies to increase efficiency. This can relate to various internal or external processes.
Improvement in customer service operations
Through process optimization
Improvement in CSAT scores
Support inquiries answered immediately by AI
Compared to traditional lead forms
Connection to AI Employee Concepts
The described Qualimero solutions reflect the core characteristics of AI employees:
- Autonomy & Action: The systems don't just answer questions but actively execute actions like giving product recommendations, booking appointments, or initiating returns.
- Integration: Seamless integration into existing tools and processes (calendar, e-commerce platforms, possibly CRM) is a central promise.
- Learning: It is emphasized that digital employees learn with every interaction and continuously improve their consultation and communication.
- Context & Personalization: Customized solutions and the ability to analyze individual customer needs and respond to them are core components of the offering.
Unique Selling Points
- Reliability with Complex Knowledge: The technology is designed to give correct and well-founded answers even on complex topics without 'hallucinating' (i.e., inventing false information).
- Fast Implementation: A 'Go Live in days, not months' is promised, emphasizing quick value for companies.
- Partnership Approach: Even after implementation, Qualimero offers continuous support, monitoring, and adaptation.
- Security and Compliance: As a product developed in Germany, adherence to high security standards (GDPR, EU AI Act) is emphasized.
The Future Belongs to Acting AI Systems
The development from simple, rule-based chatbots to intelligent, learning dialogue systems and finally to autonomously acting AI employees shows a clear trend: the future of automation lies in systems that not only communicate but actively act and independently handle complex tasks. This shift from mere conversation partners to proactive problem-solvers and process managers has profound strategic significance for companies.
AI employees are more than just the next step in the automation chain. They have the potential to fundamentally change established ways of working and enable new business models. By taking over complex tasks previously reserved for human experts – from intelligent process control through data-driven decision-making to proactive customer service – they become strategic partners in digital transformation.
For companies, especially German mid-sized businesses and corporations, this means an opportunity for significant competitive advantages. Those who deploy this technology early and strategically can benefit from higher efficiency, improved scalability for demanding tasks, and superior customer experience. The ability to reliably automate complex processes around the clock frees up resources and allows human employees to focus on higher-value, creative, and strategic activities.
Success Factors for AI Employee Implementation
However, successful introduction of AI employees requires more than just selecting the right technology. It is an organizational transformation project that needs a holistic strategy:
- Clear Goal Setting & Process Analysis: Companies must precisely define which goals are to be achieved with the AI employee and which processes are suitable for such deep automation. A thorough analysis of existing processes is essential.
- Integration & Data: Seamless integration into existing IT infrastructure (CRM, ERP, etc.) and access to relevant, high-quality data are critical to success.
- Security & Compliance: Handling potentially sensitive data requires the highest security standards and strict adherence to data protection regulations like GDPR. New regulations like the EU AI Act must also be considered. Providers like Qualimero emphasize this aspect as part of their offering.
- Human Oversight & Change Management: Despite their autonomy, AI employees need human monitoring and correction capability, especially in the initial phase. Equally important is the involvement and training of human employees who will work with the new digital colleagues. Acceptance and understanding are crucial for success.
- Continuous Optimization: AI employees are not a 'set-and-forget' solution. Their performance must be continuously monitored, analyzed, and optimized through adjustments or further training to ensure maximum benefit.
Technology is developing rapidly. Experts expect increasing proliferation of AI agents, more user-friendly tools for their creation (e.g., no-code platforms), deeper integration into standard business software, and intelligent combination of various specialized agents to solve even more complex tasks. The synergy with classic process automation (RPA) is also seen as a promising trend, with AI agents taking over intelligent control.
Success in implementing this future-oriented technology thus depends significantly on whether companies pursue a strategic and holistic approach that equally considers technology, processes, and people.
Conclusion: From Support Ticket to Revenue Driver
The journey of automation in customer dialogue and business processes has reached a new, transformative stage. The evolution from simple, rule-based chatbots through AI-powered dialogue systems to today's available AI employees marks a fundamental paradigm shift: from pure communication and information provision to autonomous action, intelligent decision-making, and profound process automation.
AI employees are far more than just advanced chatbots. They act as digital colleagues who proactively act, learn from experiences, seamlessly integrate into existing system landscapes, and independently solve complex tasks. This potential offers companies – from agile mid-sized businesses to established corporations – the opportunity to elevate efficiency, scalability, customer experience, and ultimately business results to a new level.
The choice of the right technology is a strategic decision. Companies should carefully analyze their specific needs, process complexity, and automation goals. While simple chatbots continue to have their place for clearly defined, repetitive tasks and AI chatbots improve the quality of direct customer interaction, AI employees represent the forward-looking approach for companies striving for profound automation of core processes and seeking measurable results through intelligent, autonomous action.
The key insight remains: the future of customer service isn't about reducing costs through deflection – it's about generating revenue through consultation. AI employees that can guide customers through complex purchase decisions, recommend the perfect products, and execute the entire transaction represent not just operational efficiency but a fundamental competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Employees
A chatbot primarily focuses on conversation – answering questions and providing information through dialogue. An AI employee goes further by autonomously taking action: making decisions, executing processes, integrating with business systems (CRM, ERP), and achieving measurable business outcomes without waiting for human commands. While a chatbot might tell you about return policies, an AI employee can process the return, update inventory, and initiate the refund.
In many cases, yes. AI employees have instant access to the entire product catalog, can process customer preferences in real-time, never experience cognitive overload, and maintain consistent quality 24/7. They excel at asking the right clarifying questions and matching customer needs to products. However, they work best in combination with human experts for highly emotional or unprecedented situations.
With providers like Qualimero offering 'Done-for-You' services, implementation can happen in days rather than months. The key factors affecting timeline are the complexity of integration with existing systems, the breadth of the knowledge base to be trained, and the specific use cases being deployed. Starting with a focused use case (e.g., lead qualification) allows for faster deployment with expansion over time.
Reputable providers, especially those based in Germany and the EU, design their AI employee solutions with GDPR compliance as a core requirement. This includes transparent data processing, secure EU-based hosting, clear consent mechanisms, and compliance with the emerging EU AI Act. Always verify that your provider offers detailed documentation on data handling and security certifications.
AI employees are designed to handle routine tasks, freeing human workers to focus on higher-value activities requiring creativity, empathy, and complex judgment. Rather than replacement, successful implementations show a 'human-in-the-loop' model where AI handles volume and routine complexity while humans manage exceptions, relationship building, and strategic decisions. The result is typically more satisfied employees handling more meaningful work.
See how AI employees can automate complex processes, provide expert product consultation 24/7, and deliver measurable business results. Join leading companies already benefiting from intelligent automation.
Schedule Your Demo