The Next Level of Automation: From Chatbots to AI Workers
Digital transformation continues to challenge German companies, from mid-sized businesses (Mittelstand) to large corporations. While simple automation solutions are widespread, they often reach their limits when it comes to managing complex business processes and generating substantial added value. Pure efficiency gains through automating repetitive tasks are no longer sufficient to compete globally. There is a growing need for more intelligent solutions that don't just react, but act proactively, learn, and integrate seamlessly into core processes.
At the same time, the flood of new terms surrounding Artificial Intelligence (AI) leads to confusion, particularly when distinguishing between familiar technologies like chatbots and newer concepts. Everyone has a chatbot these days, but nobody actually likes talking to them. This is where the paradigm shift begins.
Current data on AI adoption rates in German companies shows that 20% of German companies now use AI (up from 12% in 2022). Large enterprises lead adoption at nearly 50%, with main applications being written language analysis and speech recognition. However, significant barriers persist: knowledge gaps (71%), legal concerns (58%), and data privacy (53%). These figures illustrate the challenges and opportunities German businesses face in the context of automation.
German companies now using AI (up from 12% in 2022)
Leading the way in AI implementation
Lack of AI expertise remains the top obstacle
Regulatory uncertainty slowing adoption
Understanding the Concepts: Chatbots and AI Workers
Chatbots have become established tools in digital communication. Many companies use them to answer customer inquiries or automate simple interactions. They simulate human conversations and provide a first point of contact for users. But here's the critical question: What happens when a customer needs more than just an answer to 'What are your opening hours?'
Parallel to this, a new, more advanced category of intelligent automation is emerging: the AI Worker. Also known by terms such as AI Agent, digital employee, or virtual agent, these are AI systems that go far beyond pure conversation. They are designed to execute specific tasks and take over entire business processes.
These concepts are anchored in the context of Germany's national AI strategy, which provides for investments of 5 billion euros by 2025 and pursues strategic goals such as competitiveness, responsible development, and ethical integration of AI. The strategy includes initiatives for research, education, and regulatory frameworks that form the foundation for deploying AI Workers.
AI Workers: The New Digital Team Members That Take Action
Definition: More Than Just Software – A Digital Employee
An AI Worker is a highly developed, AI-powered software entity. Unlike simple automation tools or chatbots, AI Workers are designed to perform specific tasks and even entire business processes autonomously or semi-autonomously.
The analogy to 'employee' or 'worker' is central here: AI Workers are conceived as digital team members that integrate into existing workflows and teams to take over tasks that were traditionally performed by humans. They are not just tools, but acting entities within the organization. This classification as digital team members also implies a different approach to their implementation and management, which can include aspects such as onboarding, training, and performance management.
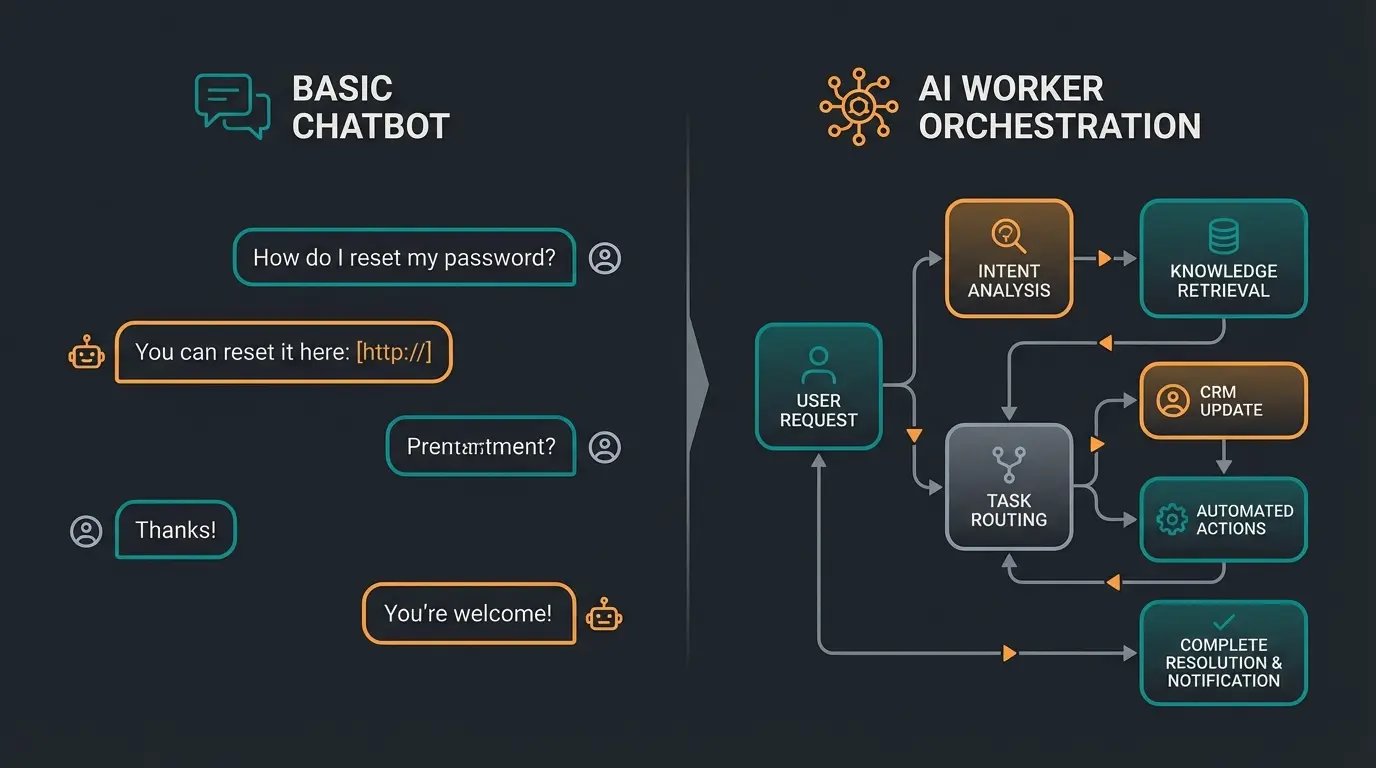
The Crucial Difference: Proactive Action and Task Execution
The fundamental difference from chatbots lies in the ability for proactive action and task execution. While chatbots primarily respond to requests and provide information, AI Workers are designed to perform actions, control systems, and complete workflows.
A key characteristic is their ability for 'reasoning' (drawing conclusions). They don't just follow rigid scripts but can analyze situations, interpret data, make decisions (within defined boundaries), and determine the optimal path to achieving goals. They can understand complex instructions, break them down into sub-steps, and execute them independently.
Core Capabilities Overview: The Powerhouse for Your Business
- Task Execution & Process Automation: They can automate complex, multi-step tasks and entire end-to-end business processes that go far beyond simple interactions. This includes orchestrating steps across different systems.
- System Integration: Deep integration with central enterprise systems (such as ERP, CRM, SCM, HRIS) via Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) is crucial. This enables AI Workers to access necessary data and execute actions directly in these systems.
- Learning & Adaptability: Through the use of Machine Learning (ML), AI Workers continuously improve. They learn from processed data, conducted interactions, and received feedback to increase their performance and adapt to changing business requirements or new tasks.
- Autonomy & Reasoning: After initial instruction or goal setting, AI Workers can operate largely independently. They evaluate goals, break down tasks, develop their own workflows, and make decisions for problem-solving.
These capabilities enable AI Workers to manage not just individual tasks, but complex, dynamic processes while demonstrating high autonomy – a core difference from reactive systems like chatbots.
Technology Stack: What Powers AI Workers
AI Workers are not a single technology, but rather the result of intelligent orchestration of various advanced technologies to fulfill specific business functions. These typically include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): As the basis for learning capability, pattern recognition, and decision-making.
- Generative AI (GenAI) and Large Language Models (LLMs): For highly developed language processing, understanding complex instructions, generating content (e.g., emails, reports) as part of tasks, and enabling natural interactions.
- Natural Language Processing/Understanding (NLP/NLU): For understanding unstructured data (text, speech) and user intentions.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Often integrated to automate structured, rule-based sub-steps within a larger, AI-controlled process.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): As essential interfaces for integration and communication with other enterprise systems.
This combination enables AI Workers to unite both cognitive capabilities (understanding, learning, deciding) and executive capabilities (interacting with systems, automating steps).
Chatbot vs. AI Worker: The Direct Comparison
To facilitate the strategic decision for the appropriate automation technology, a direct comparison between chatbots and AI Workers is essential. The differences lie not only in functionality but fundamentally in the potential business value and implementation requirements.
| Feature | Traditional Chatbot (Old) | AI Worker (New) |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Answer questions (Reaction) | Solve problems (Action) |
| Knowledge | Pre-programmed scripts | Dynamic product knowledge |
| Complexity | "What are your opening hours?" | "Which part fits my machine?" |
| Context | Forgets everything immediately | Remembers preferences & history |
| Integration | Often isolated | Deeply integrated (CRM, ERP, PIM) |
| Core Function | Respond, conduct conversation | Act, execute tasks, orchestrate processes |
| Autonomy | Low (reactive, script-based) | High (proactive, goal-oriented) |
| Reasoning | Low (information retrieval) | High (inference, problem-solving) |
| Business Value | Efficiency (communication) | Core process optimization, strategic advantage |
Detailed Explanation of the Differences
Functionality & Action: The core difference of 'Answering vs. Acting' manifests in all other areas. Chatbots are communication interfaces, AI Workers are execution units. A chatbot might tell a customer their order status by querying a database. An AI Worker, however, can manage the entire ordering process – from checking availability, updating inventory in the ERP, informing logistics, updating customer status in the CRM, to proactively notifying the customer about shipping.
Complexity & Autonomy: AI Workers are designed to handle complex, multi-step processes that require human judgment or coordination across multiple systems. Their higher autonomy allows them to act independently after an initial goal specification, recognize problems, and find solution paths. Chatbots remain mostly reactive and limited to their predefined paths or the immediate user request.
Integration: The ability of AI Workers to act is largely based on their deep integration into the company's IT landscape. Via APIs, they access data from various sources (ERP, CRM, databases) and trigger actions in these systems. Chatbots are often only loosely connected or focused on specific communication channels. This deep integration is a prerequisite for the action-oriented nature of AI Workers.
Learning & Reasoning: While AI chatbots learn to better understand language, AI Workers learn to optimize processes, handle exceptions, and execute their tasks more effectively. Their reasoning capability allows them to draw conclusions and solve problems, rather than just retrieving stored information.
Implications for Mid-Sized Companies and Corporations
The choice between a chatbot and an AI Worker is a strategic decision. For companies that primarily want to make their customer communication more efficient for simple inquiries, an AI chatbot can be a sensible solution.
However, if the goal is to fundamentally automate complex core processes, significantly increase efficiency in areas such as sales, order processing, or HR management, and enhance the scalability of the business model, then AI Workers offer far greater potential. Especially for mid-sized companies and corporations, which often face grown system landscapes and complex processes, AI Workers can represent a lever for digital transformation and increasing competitiveness.
Discover how an AI Worker can revolutionize your product consultation – providing personalized recommendations 24/7 while your team focuses on high-value relationships.
Start Your Free TrialUse Case 1: Revolution in Sales and Product Consultation
Traditional Chatbot Use in Sales
Chatbots are frequently used in sales for clearly defined, rather simple tasks:
- Answering standard questions: They provide answers to frequently asked questions about products, prices, or delivery times.
- Simple lead qualification: They collect basic contact information from website visitors or ask simple questions to determine interest.
- Appointment scheduling: They can book simple demo appointments or callbacks based on predefined availability.
However, the limits are quickly reached. Chatbots typically cannot provide in-depth, individually tailored consultation based on the customer's specific context. They struggle with configuring complex products or services, cannot create dynamic, individual offers, and their ability to meaningfully and contextually update the CRM system is often limited. They are unable to conduct complex sales conversations or map the often non-linear paths of a customer journey.
The Product Consultation Revolution: Your Unique Differentiator
Here's where AI Workers transform the game. The problem with traditional approaches: Standard search bars and filters are frustrating for complex products. Customers searching for 'Laptop 16GB RAM' don't find what they need when they actually want 'a laptop for video editing.'
The solution is an AI Worker that leads a consultation interview – a true needs analysis (Bedarfsanalyse). Instead of searching for technical specs, the customer describes their problem: 'I need a laptop for video editing,' and the AI Worker recommends 3 specific models with detailed reasoning based on your product catalog.
AI Worker as Intelligent Sales Assistant
AI Workers go far beyond the capabilities of chatbots and can act as proactive, intelligent assistants for the sales team:
- Personalized Consultation & Recommendations: By integrating with CRM and other data sources, an AI Worker analyzes customer history, previous behavior, and specific needs. Based on this, it can provide highly personalized product recommendations, suggest individual solutions, and offer deeper, context-related consultation. It can guide customers through complex product selection processes.
- Complex Product Configuration: AI Workers can interactively guide customers through the configuration of sophisticated products or services, checking dependencies, suggesting options, and ensuring compatibility – tasks that often require deep product knowledge.
- Automated Quote Generation (Configure, Price, Quote - CPQ): One of the strongest capabilities is automated creation of precise and individualized quotes. The AI Worker accesses product catalogs, price lists, and discount rules, considers customer-specific conditions from the CRM, and generates error-free quotes in the shortest time. This process, which manually often takes hours, is reduced to minutes.
- Seamless CRM Integration: AI Workers act directly in the CRM system. They automatically log interactions, update lead status, create new contacts, save generated quotes, and thus ensure an always up-to-date database without sales staff having to make manual data entries.
- Initiating Follow-up Processes: Based on the interaction or reaching certain milestones, the AI Worker can proactively initiate the next steps in the sales funnel: routing qualified leads to the right sales rep, creating follow-up tasks, scheduling appointments for human colleagues, or even initiating the downstream ordering process.
These capabilities demonstrate a paradigm shift: from reactive answering of questions to proactive, data-driven management and execution of sales tasks.
A practical example of AI Workers in action can be seen in AI-powered product consultation, showing how companies can significantly increase revenue through personalized recommendations and automated consultation. Additionally, AI Workers not only support consultation but also optimize AI-powered lead generation through personalized interactions and seamless CRM integration, leading to higher efficiency and better closing rates.
Impact Assessment for Mid-Sized Companies and Corporations
The deployment of AI Workers in sales offers significant advantages for companies of all sizes:
- Accelerated Sales Cycle: By automating tasks like quote creation, lead nurturing, and appointment scheduling, the time to close is shortened. Improved lead qualification and prioritization ensure sales staff focus on the most promising opportunities.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Customers receive faster, more precise, and highly personalized responses and quotes. 24/7 availability even for complex inquiries increases satisfaction and promotes customer loyalty.
- Increased Efficiency & Scalability: Sales teams are relieved of administrative and repetitive tasks and can focus on strategic sales conversations and relationship building. Companies can handle a higher volume of inquiries and leads without linearly scaling their sales force. AI Workers act as multipliers for the human team.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Continuous analysis of interactions and CRM data by the AI Worker provides valuable insights for optimizing sales strategies and product offerings.
Use Case 2: Process Automation at a New Level
While chatbots primarily operate at the communication interface, AI Workers unfold their full potential in automating complex, internal business processes that often span multiple departments and IT systems.
The Limits of Chatbots in End-to-End Automation
Chatbots can serve as a frontend for certain processes, for example to receive an incident report or start a simple request. However, they are typically unable to orchestrate and autonomously execute the entire underlying, often complex workflow. They lack deep system integration and the ability to perform actions across different applications and make decisions based on process context.
AI Worker as Driver of Complex, Cross-System Automation
AI Workers are predestined for taking over such end-to-end processes:
Order Processing: An AI Worker can manage the entire lifecycle of an order. This starts with receiving (e.g., from a webshop or via email), includes automatic verification of order data against inventory and customer data in CRM/ERP, triggers picking and shipping in the corresponding systems, generates the invoice in the accounting system, updates order status in the CRM, and proactively informs the customer about progress. A case study of a German manufacturing company showed that 96% of order updates could be automated by an AI Agent, reducing manual processing time by 89%. This goes far beyond simple status queries by a chatbot.
Order updates automated by AI Agent
Manual processing time eliminated
Processing orders around the clock
Consistent rule application eliminates human error
Employee Onboarding: The process of hiring new employees typically involves HR, IT, the department, and sometimes the legal department. An AI Worker can orchestrate this complex, cross-departmental workflow: It automatically collects necessary documents from the new employee, creates user accounts in Active Directory (AD) and other systems, requests and provisions required hardware and software based on the role (possibly with AI-supported suggestions), assigns initial training, sends welcome information, and updates employee status in the HR system. It can even serve as the first point of contact for new employee FAQs.
IT Support Management: While chatbots often only handle first-level support for simple requests, AI Workers can intervene more deeply in incident and problem management. They can analyze complex error messages, diagnose issues, perform automated resolution attempts across different systems (e.g., restarting services, patch installation), intelligently categorize and prioritize tickets in the ITSM system (like ServiceNow), escalate to the right specialist when needed, and document the entire process.
Additional Examples: The range extends from automated invoice processing (data capture, verification, posting) to supply chain optimization through demand analysis and route planning to predictive maintenance of machines through sensor data analysis and complex financial analyses.

Benefit Analysis for Mid-Sized Companies and Corporations
Automating complex core processes through AI Workers leads to tangible benefits:
- Significant Efficiency Gains: Reducing manual interventions and accelerating throughput times in complex workflows leads to substantial productivity increases.
- Sustainable Cost Savings: Automating labor-intensive processes directly reduces operational costs. Resources are freed up for more value-adding activities.
- Improved Scalability: Companies can handle increasing transaction or process volumes without proportionally increasing their workforce. AI Workers can be flexibly scaled.
- Error Reduction: Eliminating manual data entry and consistently applying process rules minimizes error sources and improves data quality and process accuracy. This is particularly important in processes like order processing or financial accounting.
- Increased Compliance and Standardization: AI Workers ensure that processes consistently run according to predefined rules and guidelines, facilitating compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Agility and Resilience: Automated processes can be adapted more quickly to changing market conditions or internal requirements, increasing organizational agility.
A crucial aspect is the ability of AI Workers to handle variability and exceptions – situations that often cause traditional, rigid automation to fail. Through learning and adaptation, they can automate processes that were previously considered too complex or dynamic.
Under the Hood: How AI Workers Learn, Integrate, and Act
Autonomous Task Execution: Concrete Examples
The 'action capability' of AI Workers manifests in concrete, sequential actions within a business process. Let's look more closely at the examples already mentioned in terms of the steps performed:
Automated Order Update Process:
- Receive & Identify: The AI Worker recognizes an incoming document (e.g., email with attachment) as an order update.
- Extract: It reads the document and extracts relevant data points (product codes, quantities, delivery address, etc.) using NLP and possibly image recognition.
- Update: It logs into the ERP system via an API and updates the corresponding order with the extracted data.
- Notify: It automatically informs relevant stakeholders (e.g., sales, logistics) about the completed update.
Automated Quote Creation Process:
- Analyze: The AI Worker analyzes a customer inquiry (e.g., from an email or web form) and the associated customer data in the CRM.
- Configure & Price: It accesses product catalogs and pricing engines, configures the desired product/service, and determines the correct price taking into account discount rules and customer conditions.
- Generate: It creates the quote document in a predefined format.
- Update & Send: It saves the quote in the CRM, updates the opportunity status, and sends the quote to the customer.
- Schedule: It automatically schedules a follow-up task for the responsible sales representative in the CRM.
In more complex scenarios, multi-agent systems may also be used, where different, specialized AI Workers collaborate. One agent might be responsible for data acquisition, a second for validation, and a third for report generation or execution. Such systems require a sophisticated orchestration platform to coordinate the collaboration of the agents.
The Key Role of APIs for Seamless Integration
The ability of AI Workers to execute tasks like those described above depends crucially on their integration into the existing IT landscape. Here, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) play the central role.
APIs function as standardized communication bridges between different software applications. They enable the AI Worker to securely and controllably:
- Retrieve Data (Read): Access information from CRM systems (customer data, history), ERP systems (inventory, production data), databases, cloud services, or external sources.
- Execute Actions (Write): Update data in systems (e.g., change CRM status), trigger processes (e.g., invoice creation in accounting system), send notifications, or call other software functions.
Without robust, well-documented, and secure APIs, AI Workers could not interact with core systems and thus could not automate real business processes. The quality and availability of APIs in enterprise IT is therefore a critical success factor for implementing AI Workers. Integration often requires technical expertise and careful planning to ensure data synchronization and process consistency.
Machine Learning: The Engine for Continuous Improvement
The intelligence and adaptability of AI Workers is largely based on Machine Learning (ML). ML enables systems to learn from experiences and improve their performance over time, rather than remaining static.
This learning process often works through a feedback loop:
- Action: The AI Worker executes a task or process step (e.g., classifies a customer inquiry, creates a quote).
- Result & Measurement: The result of this action is evaluated – either explicitly through human feedback (e.g., correction of an incorrect classification) or implicitly through subsequent process data (e.g., was the quote accepted? Was the inquiry successfully resolved?).
- Model Adjustment: Based on feedback or results, the underlying AI models are adjusted and updated.
- Improved Performance: The next time the task is executed, the AI Worker can draw on what it has learned and perform a more precise, efficient, or appropriate action.
This continuous learning cycle enables AI Workers to become increasingly better at recognizing patterns, making predictions, optimizing decisions, and adapting to new data or changed business requirements. However, it also means that AI Workers are not 'set-and-forget' solutions. They require continuous monitoring, management, and potentially targeted retraining to ensure they learn correctly and their performance aligns with business goals. The quality of training data is of crucial importance for the system's performance and fairness.
Implementation Guide: 3 Steps to Your First AI Colleague
Evaluate your existing data landscape. Do you have clean, structured product data? Assess your PDFs, databases, and knowledge bases. Identify gaps and data quality issues that need addressing before AI training.
Teach the AI your company's 'Tone of Voice,' product expertise, and business rules. Configure integrations with your CRM, ERP, and other systems. Define decision boundaries and escalation paths.
Deploy your AI Worker with human oversight. Monitor performance metrics, gather feedback, and continuously optimize. Establish KPIs for success measurement and regular review cycles.
The implementation of an AI Worker is more comprehensive than deploying a simple chatbot. It requires a clear strategy, stakeholder alignment, and careful consideration of your existing technology landscape. However, companies that invest in this preparation typically see faster time-to-value and more sustainable results.
Addressing Trust and Accuracy: The German Market Context
For German SMEs (Mittelstand) and enterprises, specific considerations around trust and compliance are paramount:
Skilled Labor Shortage (Fachkräftemangel): AI Workers help fill the gap of missing qualified sales and support staff, enabling companies to maintain service quality despite recruitment challenges.
24/7 Consultation: Selling complex B2B products on Sunday evenings becomes possible, capturing opportunities that would otherwise be lost to competitors.
Data Privacy (DSGVO/GDPR): Modern AI Workers can be hosted securely in Europe, with data residency options that satisfy the stringent requirements of German data protection law. This is a key trust factor for German businesses and their customers.
Handling Hallucinations: A major concern with AI systems is the generation of incorrect information. Leading AI Worker platforms address this through 'citation' features – the AI explains its recommendations by referencing specific sources: 'I recommend Product X because of specification Y in your product manual.' This transparency builds trust and reduces liability concerns.
Conclusion: Why AI Workers Shape the Future of Automation
Summary: The Leap from Conversation to Action
Chatbots, even in their most advanced AI-powered forms, remain primarily reactive systems that respond to requests and provide information. Their strength lies in communication efficiency. AI Workers, on the other hand, are proactive, learning systems designed to execute tasks, make decisions, and orchestrate complex, cross-system business processes. Their core competencies – autonomous task execution, deep system integration via APIs, and continuous improvement through machine learning – enable them to step in where chatbots reach their limits.
The Strategic Advantage for Companies
For German companies, from established mid-sized businesses to globally operating corporations, the strategic value of AI Workers lies in their ability to transform core business processes. They offer a way to intelligently automate not just peripheral communication tasks, but central, value-creating processes in sales, order processing, HR, IT, and beyond.
The resulting benefits – significant efficiency increases, cost reductions, improved scalability, higher accuracy, and enhanced compliance – directly contribute to the strategic goals of many companies: increasing competitiveness, accelerating digital transformation, and enhancing organizational resilience. The detailed examination of use cases in sales/product consultation and process automation has shown how AI Workers can solve concrete operational challenges and generate measurable business value. The decision for AI Workers is thus less a purely technological upgrade, but rather a strategic direction that can sustainably influence core operations and competitive positioning.
Outlook: AI Workers as Partners in Digital Transformation
AI Workers are more than just an evolution of existing automation technologies; they are pioneers for future business models and operational excellence. Their ability to learn, adapt, and autonomously handle complex tasks makes them potential digital partners in the enterprise.
However, successful implementation requires a thoughtful and responsible approach. Aspects such as ethics, avoiding bias in algorithms, data security, and data privacy must have the highest priority. Equally crucial is proactively shaping change for the workforce through transparent communication, training, and redefining roles where human strengths like strategic thinking, creativity, and empathy take center stage.
For companies in the German Mittelstand and corporations that are ready to think beyond pure efficiency gains and climb to the next level of intelligent automation, AI Workers offer enormous transformative potential. They are not only an answer to current challenges but a key to shaping a more agile, efficient, and data-driven future.
The fundamental difference lies in action versus reaction. Chatbots primarily respond to questions and provide information through conversation. AI Workers, however, are designed to execute tasks, make decisions, and orchestrate complete business processes autonomously. While a chatbot might tell you your order status, an AI Worker manages the entire order lifecycle from processing to fulfillment.
AI Workers integrate deeply through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), which serve as standardized communication bridges. This enables them to read data from and write data to systems like CRM, ERP, HRIS, and databases. The quality and availability of APIs in your IT infrastructure is a critical success factor for AI Worker implementation.
Modern AI Worker platforms can be configured to meet stringent GDPR (DSGVO) requirements. This includes European data residency options, data encryption, access controls, and audit trails. When evaluating solutions, ensure the provider offers EU-hosted options and has appropriate certifications for data protection compliance.
Implementation timelines vary based on complexity and integration requirements. A basic implementation with clean data and well-documented APIs can be achieved in 4-8 weeks. More complex deployments involving multiple systems and custom workflows may take 3-6 months. The key phases are: data audit, training/configuration, and go-live with monitoring.
Yes, this is a key differentiator from traditional automation. AI Workers use machine learning to continuously improve and can adapt to handle variability and exceptions that would cause rigid rule-based automation to fail. However, they should be configured with clear escalation paths to human experts for truly novel situations or high-stakes decisions.
Stop settling for basic chatbots. Deploy an AI Worker that truly understands your products, executes tasks autonomously, and delivers measurable ROI. Start your free pilot today.
Get Started Now