Why Traditional IT Support No Longer Meets Modern Demands
Imagine your laptop suddenly crashes. You open a support ticket. Hours later, you receive a standard response or a link to an FAQ page that doesn't address your specific problem. This is the reality in many organizations: the IT helpdesk is often viewed as a pure cost center whose primary goal is to close tickets as quickly as possible ("deflection") rather than genuinely helping users.
But requirements are changing dramatically. We're at a turning point. According to recent studies from NTT DATA, 99% of companies plan to continue investing in Generative AI (GenAI) to boost their performance. However, simply introducing technology isn't enough. Alarming figures show that up to 95% of AI pilot projects fail to deliver measurable business value, often because they occur in isolation from actual workflows, as reported by IT-Sicherheit Online.
The solution doesn't lie in faster processing of incident reports, but in a paradigm shift: From the reactive IT helpdesk to the proactive Product Consultant. This transformation represents one of the most significant opportunities in AI Customer Service today.
In this article, you'll learn how to transform your IT support, why the difference between "helpdesk" and "service desk" is crucial for your strategy, and how to use AI not just to solve problems but to provide genuine consultation—all while remaining compliant with data protection laws and employee participation rights.
What Is an IT Helpdesk? Fundamentals and Structure
To understand the evolution, we must first define the basics. The term IT helpdesk is often used synonymously with IT support but specifically refers to the tactical level of problem resolution.
Definition and Core Functions
An IT helpdesk is the central point of contact (Single Point of Contact - SPOC) for end users to report incidents or submit service requests. The focus traditionally lies on the "break/fix" approach: Something is broken, and the helpdesk ensures it works again.
Core functions include:
- Ticketing: Recording and tracking requests
- Incident Management: Restoring normal service operations
- Asset Management: Managing hardware and software licenses
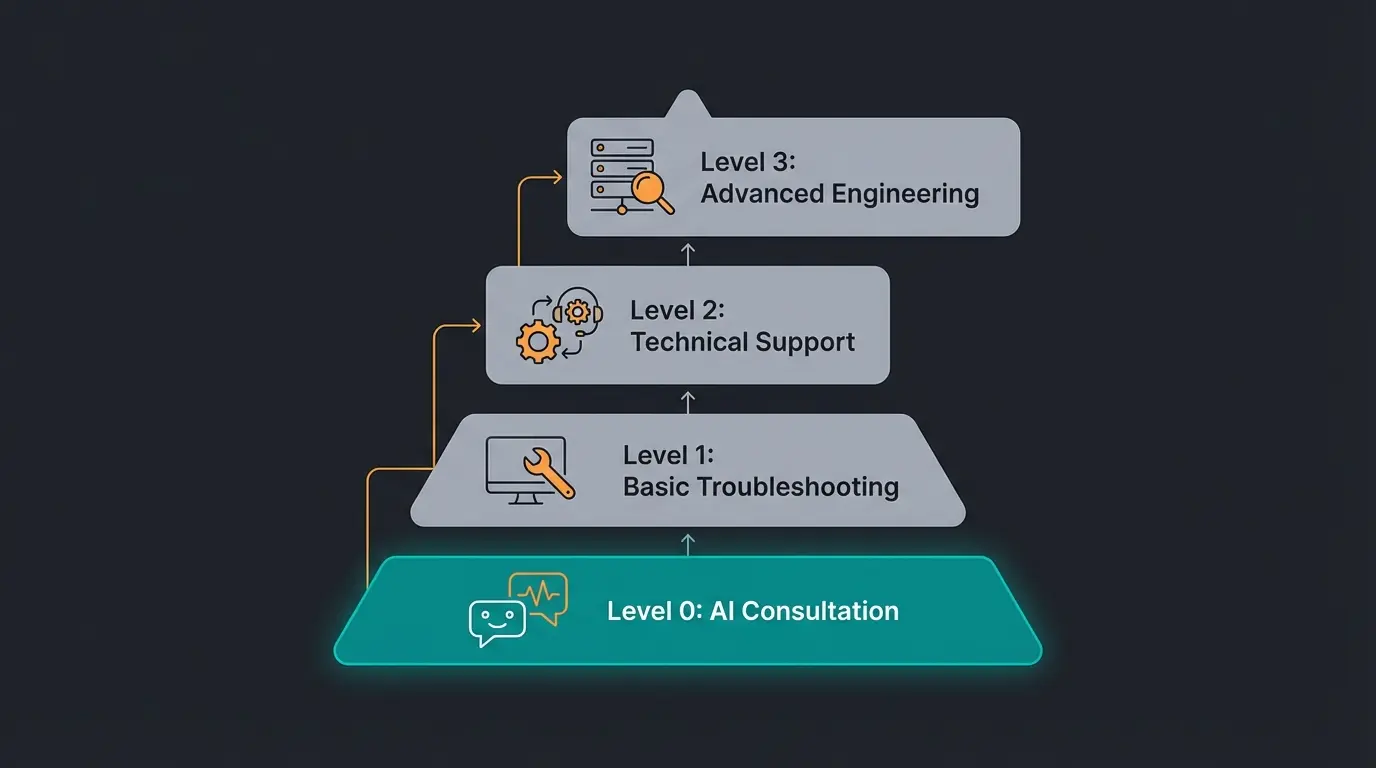
The Support Level Structure
An efficient IT helpdesk is hierarchically organized to optimally utilize resources. However, the greatest revolution is currently happening at "Level 0," as documented by Desk365 and Plain-IT.
| Level | Designation | Description | Typical Tasks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 0 | Self-Service & Automation | Users help themselves through AI or portals. This is where the potential for the 'Product Consultant' lies. | Password reset, software download, AI-assisted consultation |
| Level 1 | First Line Support | First human point of contact. Filters and resolves simple problems. | Ticket categorization, known issue resolution (SOPs) |
| Level 2 | Technical Support | Experienced technicians for more complex problems. | Software configuration, hardware diagnosis, on-site support |
| Level 3 | Expert Support | Specialists, developers, or external vendors. | Code bugfixes, network architecture, server failures |
Internal Helpdesk vs. IT Service Desk: Clarification
Many organizations use the terms IT helpdesk and IT service desk interchangeably, but strategically there are significant differences that are important for your planning.
The IT Helpdesk: The 'Firefighter'
The helpdesk is tactically oriented. It's a subset of the service desk and focuses on immediate problem resolution.
- Focus: Incident Management (disruption resolution)
- Goal: Quick restoration of work capability
- Users: Often internal (employees) or external (customers with product issues)
The IT Service Desk: The Strategist
The IT service desk is more broadly positioned and usually aligns with the ITIL framework (IT Infrastructure Library). It views IT as a "service" for the organization, as explained by Pure Consultant and OTRS.
- Focus: The entire lifecycle of IT services (including Change Management, Problem Management)
- Goal: Improving IT service quality and alignment with business objectives
- Strategy: Proactive action rather than just reacting
The Internal Helpdesk
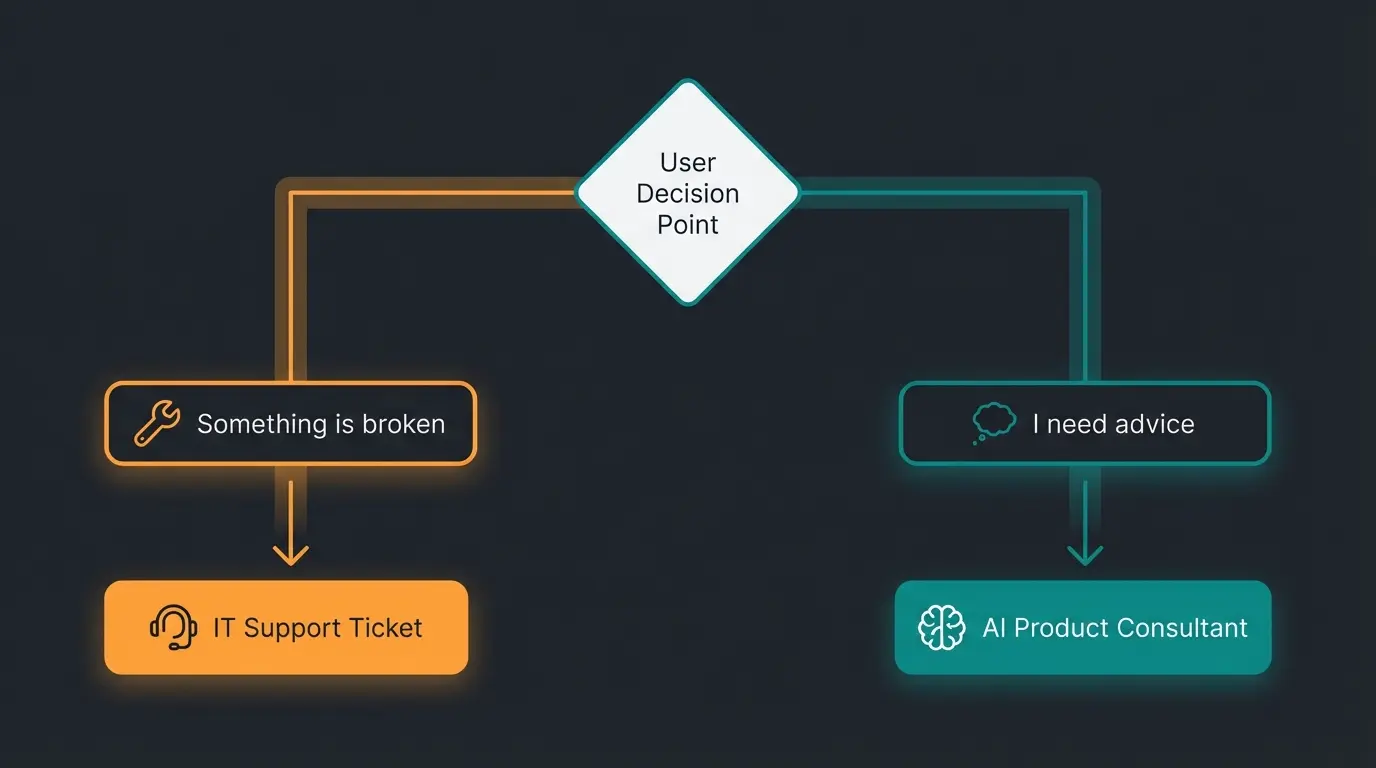
An internal helpdesk exclusively serves the organization's own workforce. This involves onboarding new employees, provisioning laptops, and managing access permissions. This is exactly where a significant gap often exists:
Employees often don't know what they need. They ask: "My laptop is slow" (Incident), but actually need consultation: "Which device do I need for my new video editing tasks?" (Consultation). Understanding the basics of Artificial Intelligence helps organizations identify where AI can bridge this gap.
The Limitations of Classic Helpdesk Software
Why do so many organizations fail to achieve high user satisfaction despite expensive software suites like Jira, ServiceNow, or Zendesk?
1. The 'Ticket Ping-Pong'
Classic systems are based on forms. Users select a category (often incorrectly), write text, and wait. The agent asks for details, the user responds. This asynchronous process costs time and nerves.
2. Static Knowledge Bases
"Have you already checked the FAQ?" is the phrase users hate most. Static articles quickly become outdated and cannot establish context. An article about "setting up a printer" doesn't help when users want to know which printer they're allowed to order for printing A3 construction plans.
3. Basic Chatbots (The First Generation)
The first wave of chatbots was based on rigid decision trees (If X, then Y). They fail at any nuance. Understanding the history of chatbots reveals why these early systems couldn't handle complex queries.
- User: "I need access to Project Alpha."
- Bot: "I didn't understand 'Project.' Did you mean 'Projector'?"
This frustration leads users to bypass official IT support ("shadow IT") or bother colleagues, reducing productivity across the entire organization. Modern AI Chatbots offer fundamentally different capabilities.
Due to poor workflow integration
When works councils are involved too late
Enterprises investing in generative AI
The New Era: AI as Product Consultant (Your USP)
Here lies your opportunity for differentiation. Instead of using AI only to deflect tickets, deploy Generative AI (GenAI) to provide consultation services. This transforms the IT helpdesk from a cost center to a value driver.
What Makes an 'AI Product Consultant' Different?
An AI Consultant (based on LLMs like GPT-4 or specialized models) understands context, company policies, and technical specifications simultaneously. It acts like an experienced pre-sales consultant or a senior IT architect. This is where AI Product Consultation truly shines.
Comparison: Classic Bot vs. AI Consultant
| Feature | Classic Chatbot | AI Product Consultant |
|---|---|---|
| Understanding | Only recognizes keywords ("printer," "password") | Understands intent and context ("I need a device for graphic design") |
| Goal | Avoid tickets (deflection) | Solve the right problem (consultation) |
| Data Basis | Static FAQ texts | Dynamic knowledge from inventory, policies & technical datasheets |
| Interaction | Rigid, script-based | Natural dialogue, asks clarifying questions |
| Result | Link to an article | Concrete recommendation or triggered ordering process |
Use Case: Hardware Procurement (Provisioning)
Consider this scenario: A marketing employee needs a new laptop.
Classic Approach: They open a ticket "New laptop." IT asks back: "Windows or Mac? Standard or Performance?" The employee guesses. Often the wrong device is ordered (too expensive or too weak).
AI Consultant Approach:
- Employee: "I need a new computer for video editing and 3D rendering."
- AI: "For these tasks, I recommend our 'Performance Class.' According to our policies, you can choose between the MacBook Pro M3 or the Dell Precision Workstation. Since you work in marketing and your team primarily uses Apple, the MacBook would be the more compatible choice. Should I request approval from your supervisor (Mr. Miller)?"
This level of intelligent assistance is what separates modern AI employees from basic automation tools.
Why This Prevents AI Project Failures
Studies show that 95% of AI projects fail because they throw generic tools at specific workflows without adapting processes, as noted by The AI People. An "AI Product Consultant," however, is deeply integrated into the process chain (Inventory -> Needs Analysis -> Approval -> Order). It solves a real business problem (wrong orders, waiting time) rather than just generating text.
See how AI-powered product consultation can reduce wrong orders, eliminate ticket ping-pong, and boost employee satisfaction across your organization.
Start Your Free TrialData Protection & Compliance in Germany
Using AI in an internal helpdesk in Germany isn't just a technology topic—it's a highly sensitive legal and cultural matter. Those who don't do their homework here risk fines and project stoppages.
GDPR and AI Chatbots
AI systems process personal data (employee IDs, chat content). According to HÄRTING Rechtsanwälte and Lime Technologies, key requirements include:
- Transparency: Users must know they're speaking with an AI (labeling requirement)
- Purpose Limitation: Data from support chats may not be secretly used for performance monitoring
- Data Processing Agreement (DPA): If you use external LLMs (like OpenAI via Azure), a robust DPA must exist ensuring no data is used to train public models
Understanding how AI in customer service handles data privacy is essential for compliant implementations.
The EU AI Act (AI Regulation)
In effect since August 2024 and becoming fully operational in 2025, the AI Act introduces critical requirements as outlined by IHK and IT-Service Network:
- AI Competency (AI Literacy): Article 4 requires companies to ensure that employees using AI (including in support) have sufficient competency. Your helpdesk must not only use AI but also train employees in using it.
- Transparency Requirements: Chatbots in customer service or internal support are usually considered limited-risk systems but are subject to strict information obligations.
The Works Council: Friend or Foe?
In Germany, the works council has a mandatory co-determination right when introducing AI systems (§ 87 BetrVG), especially when the software could theoretically be used for behavior or performance monitoring, as documented by Haufe, AUB, and Dr. Datenschutz.
- The Risk: According to PlotDesk, 60% of AI projects encounter resistance when the works council is involved too late.
- The Solution: Position the AI Consultant as an assistance system that relieves employees, not replaces them. Conclude a works agreement that explicitly excludes using data for performance evaluation. Studies from the Weizenbaum Institute show that AI acceptance increases when works councils actively participate in the implementation process.
Involve works council from project inception, not after decisions are made
Establish clear data usage policies excluding performance monitoring
Draft comprehensive works agreement covering AI system usage
Ensure AI literacy training for all employees as required by EU AI Act
Continuously review compliance and adjust based on feedback
Checklist: What Defines a Modern IT Helpdesk
Want to future-proof your IT support? Evaluate your current setup against these points:
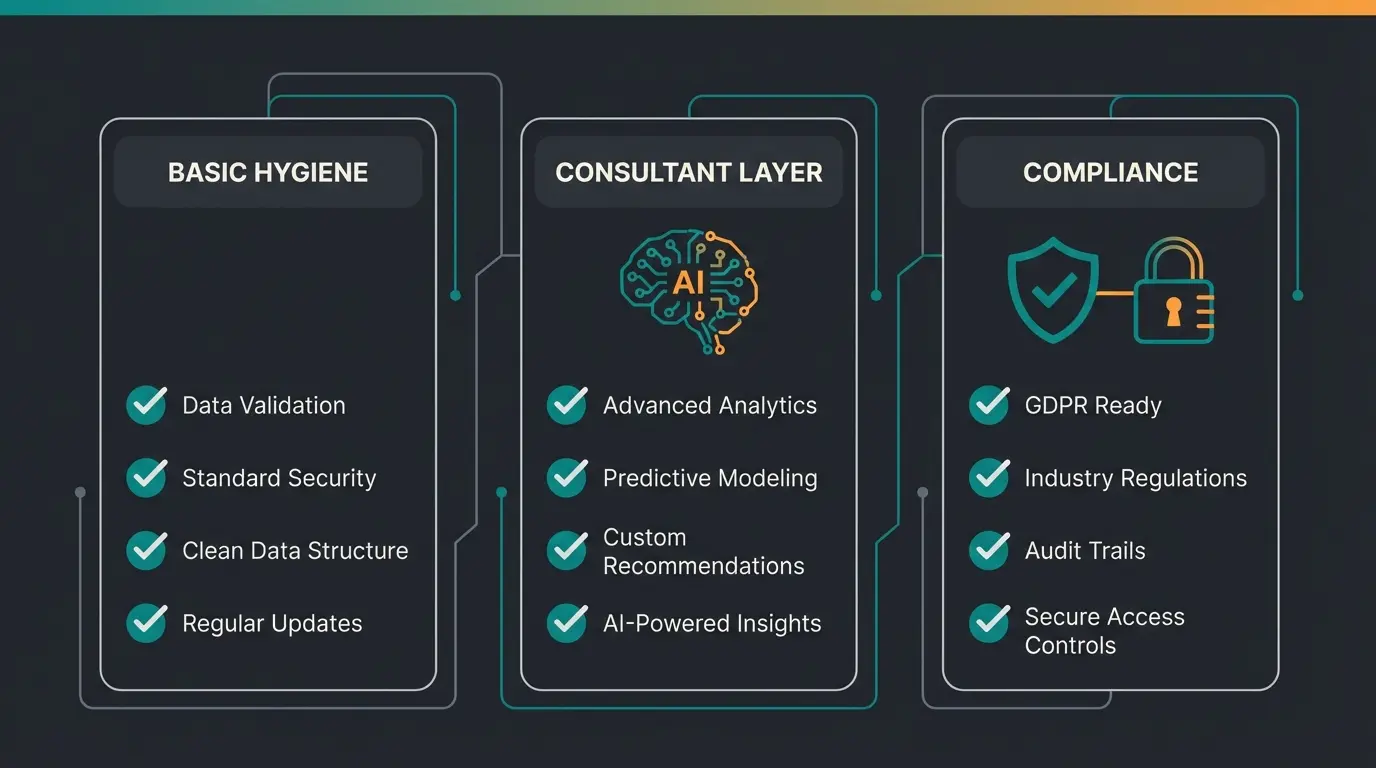
Basic Hygiene (Must-Haves)
- Central Ticketing: No more email chaos. Every request has an ID.
- Structured Levels: Clear separation between L1 (basic) and L2/L3 (experts).
- Integrations: The helpdesk is where users are (Microsoft Teams, Slack), not just in an external web portal.
The 'Consultant' Layer (Competitive Advantage)
- Level 0 as Advisor: Do you offer more than a search bar? Is there a dialogue-capable assistant?
- Context Awareness: Does the system know the user's role, department, and hardware before they ask?
- Automated Approval: Can the AI independently validate and approve standard requests (e.g., software under €50)?
Organizations implementing digital sales assistants internally are seeing significant improvements in employee satisfaction and procurement accuracy.
Compliance & Culture (The German Way)
- Works Council Buy-In: Is there a works agreement for AI deployment?
- GDPR Compliance: Are server locations and data flows clarified?
- AI Literacy: Are support staff and end users trained in using AI (prompting, AI limitations)?
The Future Belongs to Consultative Support
The classic IT helpdesk has served its time. In a world where technology becomes increasingly complex and individualized, it's no longer enough to just repair broken things. Employees and customers expect guidance and consultation when selecting and using their tools.
The integration of Generative AI as a "Product Consultant" is the key to meeting this expectation without costs exploding. It bridges the gap between the rigid internal helpdesk and the strategic IT service desk. Companies already leveraging AI Chatbots for this purpose are seeing dramatic improvements in both efficiency and satisfaction.
However, technology alone isn't a silver bullet. Success in Germany significantly depends on how well you integrate human and legal factors: data protection, co-determination, and employee enablement. Those who master this create support that's no longer perceived as a tiresome obligation but as a genuine partner.
Real-world implementations like the AI Employee case study and the AI employee for product consultation demonstrate what's possible when organizations embrace this transformation.
Ready for transformation? Start by analyzing your most frequent "consultation tickets" and examine where an AI Consultant can deliver the greatest value. The AI Chatbot for E-Commerce approach can be adapted for internal helpdesk use cases with remarkable results.
Frequently Asked Questions About IT Helpdesks
An IT helpdesk focuses on tactical, immediate problem resolution (break/fix incidents), while an IT service desk takes a broader strategic approach aligned with ITIL frameworks. The service desk manages the entire IT service lifecycle including change management and problem management, focusing on proactive improvement rather than just reactive fixes.
AI transforms helpdesks by moving beyond simple ticket deflection to providing contextual consultation. Instead of just routing "I need a laptop" tickets, AI consultants understand user needs, company policies, and available options to recommend the right solution. This includes analyzing requirements, suggesting appropriate hardware/software, and even initiating approval workflows.
German organizations must address GDPR requirements (transparency, purpose limitation, data processing agreements), the EU AI Act (AI literacy training, transparency obligations), and works council co-determination rights (§ 87 BetrVG). Early works council involvement and clear data usage agreements are essential for successful implementation.
Level 0 represents self-service and automation capabilities where users can resolve issues or get assistance without human intervention. Modern Level 0 goes beyond static FAQs to include AI-powered consultation that understands context and provides personalized recommendations. This is where the biggest transformation opportunity exists.
Most AI projects fail because they deploy generic tools without adapting underlying workflows and processes. Successful AI implementation requires deep integration into the process chain (inventory, needs analysis, approval, ordering) rather than simply adding a chatbot layer on top of existing systems.
Join leading organizations that have evolved from break/fix support to AI-powered product consultation. Start delivering real value to your employees and customers today.
Get Started Free