Understanding the Helpdesk: More Than Just Ticket Processing
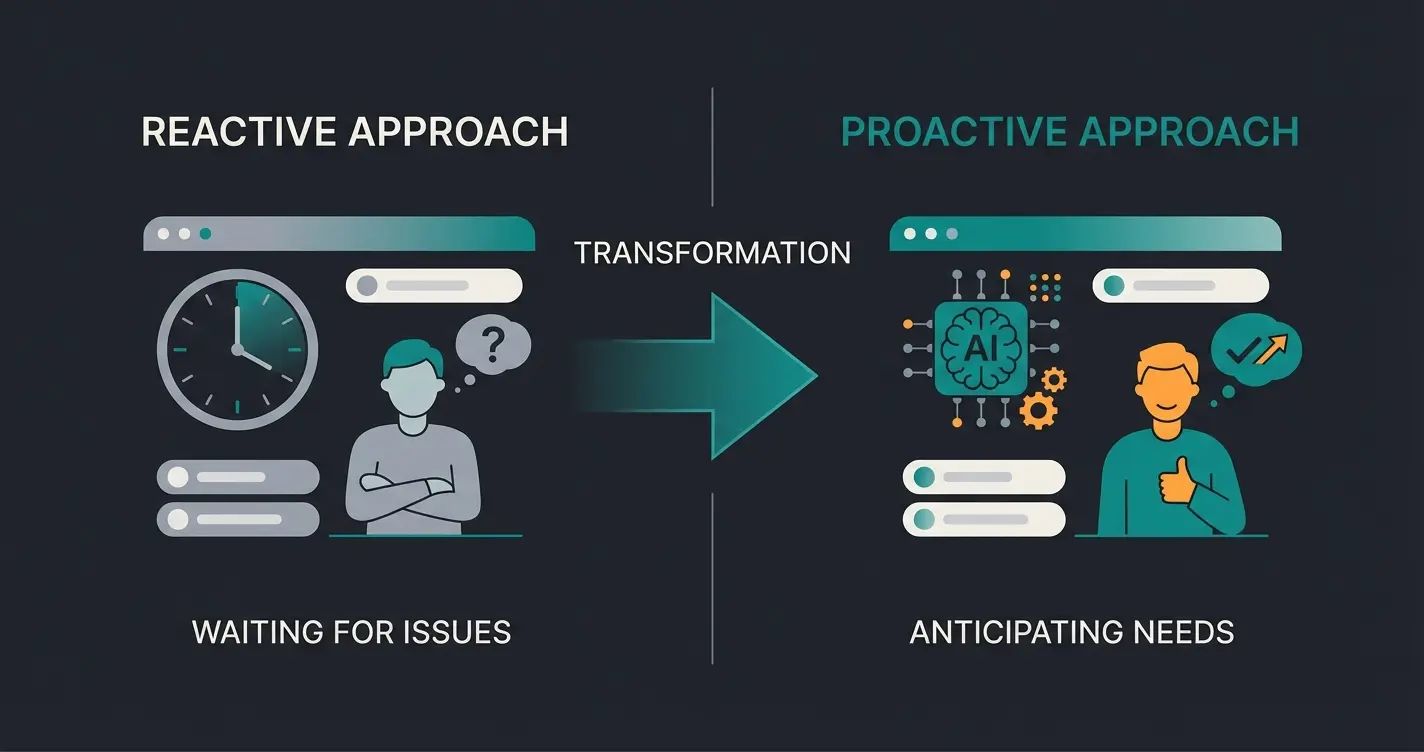
A helpdesk is the central point of contact (Single Point of Contact) within a company responsible for receiving, managing, and resolving technical inquiries or customer problems. While traditional helpdesks primarily focused on reactive troubleshooting (incident management), modern systems powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI) are increasingly evolving into proactive "Customer Success Centers" that don't just solve problems but actively provide product consultation and generate revenue.
In today's digital business landscape, the term "helpdesk" is omnipresent but often misunderstood or reduced to a mere "ticket-processing machine." If you're asking yourself: "What is a helpdesk really?" — the answer from 2010 simply no longer applies.
The customer support landscape is currently undergoing the most radical transformation since the invention of the telephone. Driven by generative AI and changing customer expectations, the helpdesk meaning is shifting massively: away from the pure "troubleshooter" who fixes broken things, toward a strategic advisor who influences purchasing decisions in real-time.
In this comprehensive guide, you'll learn not only the classic helpdesk definition and the difference from a service desk, but we'll also illuminate why the rigid support structures of the past have become obsolete and how your helpdesk can become a profit center. As explored in our guide on AI customer service, this transformation is reshaping how businesses interact with customers.
Definition & Meaning: What Does a Helpdesk Actually Do?
To fully grasp the helpdesk meaning, we must first examine both the historical and functional dimensions. The term is composed of the English words "Help" and "Desk." Originally, this was physically the place you went when your computer stopped working.
Today, a helpdesk is a software-supported organizational unit. According to Atlassian, it functions as a Single Point of Contact (SPOC) — the only touchpoint a user or customer needs to receive help. This centralization is fundamental to effective support operations.
The Two Faces of the Helpdesk
It's important to distinguish between two fundamental orientations, as the term is used in both contexts:
- The IT Helpdesk (Internal): Here, the "customers" are the company's own employees. The goal is to ensure the company's productivity. When the printer won't print, the WiFi fails, or a password needs to be reset, the IT helpdesk is responsible. As Kyberna notes, the focus lies on restoring normal operations.
- The Customer Service Helpdesk (External): Here, external buyers contact the company. Traditionally, this involved complaints ("My package hasn't arrived") or defects ("The device won't turn on"). But this is exactly where the revolution is happening: The modern external helpdesk is increasingly being used for pre-sales questions and product consultation ("Does this replacement part fit my model?").
Helpdesk Explained: The Core Philosophy
At its core, a helpdesk is about bringing order to chaos. Without a helpdesk, inquiries arrive via email to various employees, get lost, or are handled twice. A helpdesk system centralizes this communication, makes it trackable, and measurable. Modern Conversational AI solutions take this concept even further by enabling natural language interactions.
The Classic Functions and Tasks of a Helpdesk
Regardless of whether it's internal or external support, there are core functions that every system must cover. These form the foundation upon which modern AI strategies are built.
1. Ticket Management (The Heart of the System)
Every inquiry — whether via email, phone, chat, or social media — is converted into a "ticket." This ticket receives a unique ID. As Salesforce explains, this enables:
- Tracking: Status retrieval at any time (Open, In Progress, Resolved).
- Prioritization: A server outage is handled before a color inquiry.
- Assignment: The ticket lands with the right expert.
2. Incident Management (Troubleshooting)
According to ITIL standards (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), the primary goal of the helpdesk is Incident Management. An "Incident" is an unplanned interruption of a service. The task is the fastest possible restoration of operations, often through workarounds, rather than analyzing the deep cause. OTRS provides excellent documentation on these ITIL-aligned practices.
3. Knowledge Base (Self-Service Database)
An efficient helpdesk documents solutions. According to Ivanti, this "Knowledge Base" serves two purposes:
- Internal Training: Agents find solutions for known problems faster.
- Self-Service: Customers can read articles and solve their problem themselves without opening a ticket (Ticket Deflection).
4. Routing and Escalation
Not every agent can know everything. A helpdesk system ensures through routing rules that complex technical questions don't land with the intern but are forwarded directly to specialized teams (2nd Level Support). Virima details best practices for implementing effective routing strategies.
Structure: The Support Level Model (Classic vs. Modern)
Traditionally, helpdesks are strictly hierarchically organized. This model comes from the IT world but is increasingly being disrupted by AI. Understanding different chatbot types helps clarify how automation fits into this structure.
The Classic "Waterfall" Model
This model is designed to conserve expensive expert resources. It creates a tiered approach where simpler issues are filtered at lower levels before reaching specialists.
| Level | Designation | Task & Profile | Resolution Rate (Traditional) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Level | Front Office / User Help Desk | Generalists. Take calls, classify tickets, solve simple standard problems (password reset, FAQ). | approx. 40-60% |
| 2nd Level | Back Office / Specialists | Experts. Handle more complex tickets that Level 1 couldn't solve. Have more access rights and expertise. | approx. 30% |
| 3rd Level | Experts / Development | Developers/Manufacturers. Fix bugs, architecture errors, or deep-seated problems. Highest cost per ticket. | approx. 10% |
The Modern Approach: AI as "Level 0" with "Level 3" Knowledge
The classic model has a massive problem: Time. Until a complex question migrates from 1st Level to 3rd Level, days often pass. In e-commerce or SaaS sales, that means: The customer buys elsewhere.
According to FluentSupport, modern AI consulting approaches turn this model on its head. The implementation of AI-powered chatbots enables this transformation:
- AI as Level 0: A generative AI (like ChatGPT-based agents) intercepts 100% of inquiries.
- Instant Expert Knowledge: Unlike the human 1st-level agent who must first flip through the manual, the AI has access to the entire technical documentation (Level 3 knowledge).
- Result: Complex product questions ("Is the API compatible with legacy system X?") are answered in seconds instead of wandering through escalation stages.
Generative AI intercepts all inquiries with full access to Level 3 expert knowledge base
Only complex emotional cases or edge cases requiring human judgment reach agents
Technical deep-dives for genuinely novel issues not in the knowledge base
Development team involvement only for product bugs or systemic issues
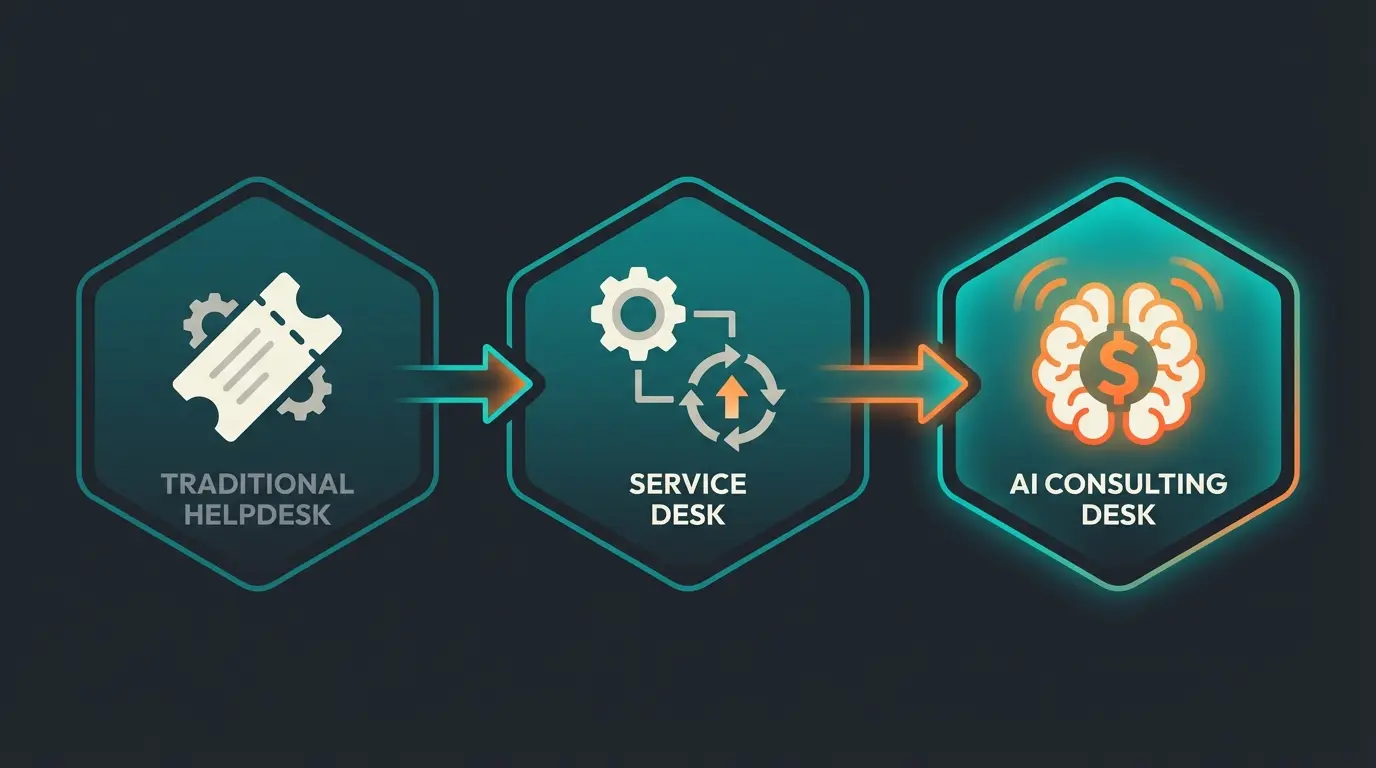
Helpdesk vs. Service Desk: What's the Difference?
When researching helpdesk definition, you'll inevitably encounter the term "Service Desk." They're often used synonymously, but in technical language (especially ITIL), there are significant differences. InvGate and TechTarget provide detailed breakdowns of these distinctions.
Here is the crucial differentiation — expanded with the modern "consulting" perspective:
| Feature | Helpdesk (Classic) | Service Desk (ITSM/ITIL) | AI-Consulting Desk (Future) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Reactive: "What is broken?" | Strategic: "How do we manage services?" | Proactive/Sales: "Which solution do you need?" |
| Main Task | Incident Management (Troubleshooting) | Lifecycle Management, Change Management, Asset Mgmt. | Pre-Sales Consultation, Customer Success, Upselling |
| Goal | Quick Repair (Break/Fix) | Holistic Service Quality & IT Strategy | Revenue Generation & Conversion Optimization |
| Users | Frustrated users with problems | Users requesting or changing services | Potential buyers & loyal customers |
| Technology | Ticketing System | ITSM Suite (e.g., ServiceNow, Jira Service Mgmt) | Generative AI, Sentiment Analysis, CRM Integration |
In summary: A helpdesk is often a subdivision of a service desk. While the service desk keeps the "big picture" of IT strategy in view, the helpdesk takes care of the acute "here and now." The AI-Consulting Desk, however, leaves the pure support corner and becomes part of the sales team. Our analysis of how AI transforms support explores this evolution in depth.
Why Classic Helpdesks Often Fail at Product Consultation
Many companies try to use their classic support helpdesk for pre-sales inquiries as well. The scenario: A potential customer writes an email: "Can you tell me if ski boot X also fits binding Y?"
This reveals the content gap in most definitions: A system built for troubleshooting is deadly for sales conversations. This is where understanding AI in customer care becomes crucial.
1. The "Ticket ID Barrier"
When a customer wants purchasing advice, they don't want an automatic response: "Your inquiry has been recorded under Ticket #99283. We'll get back to you in 24-48 hours." According to FullView.io and research from AgentiveAIQ, statistics show: 59% of customers expect a response within 5 seconds. A ticket system is psychologically a bureaucratic act, not a sales conversation.
2. Lack of Expertise at 1st Level
Classic support agents are often trained on complaints ("Where is my package?"), not on in-depth technical consultation. If the agent can't answer the question about the ski binding, they must escalate. Response time increases, the customer's purchase intent drops to zero.
3. Reactive vs. Proactive Attitude
A classic helpdesk waits for input. A salesperson (or a Sales-AI) would proactively ask: "If you're looking for this ski boot, do you ski more off-piste or on-piste? I can also recommend the matching helmet." Classic helpdesk software often doesn't map these dialogues at all. Understanding AI employee solutions helps bridge this gap.
Customers expect near-instant answers for pre-sales questions
Average wait time kills purchase intent completely
Every delayed consultation response risks losing the entire sale
Stop losing sales to slow ticket responses. Discover how AI-powered consultation can answer complex product questions in seconds and convert browsers into buyers.
Start Your Free TrialThe Evolution: From "Troubleshooter" to "Product Consultant"
We are at a turning point. The helpdesk meaning is transforming from a cost factor (Cost Center) to a revenue driver (Revenue Center). The key to this is the use of Generative AI. Comparing modern chatbot AI solutions reveals how far this technology has come.
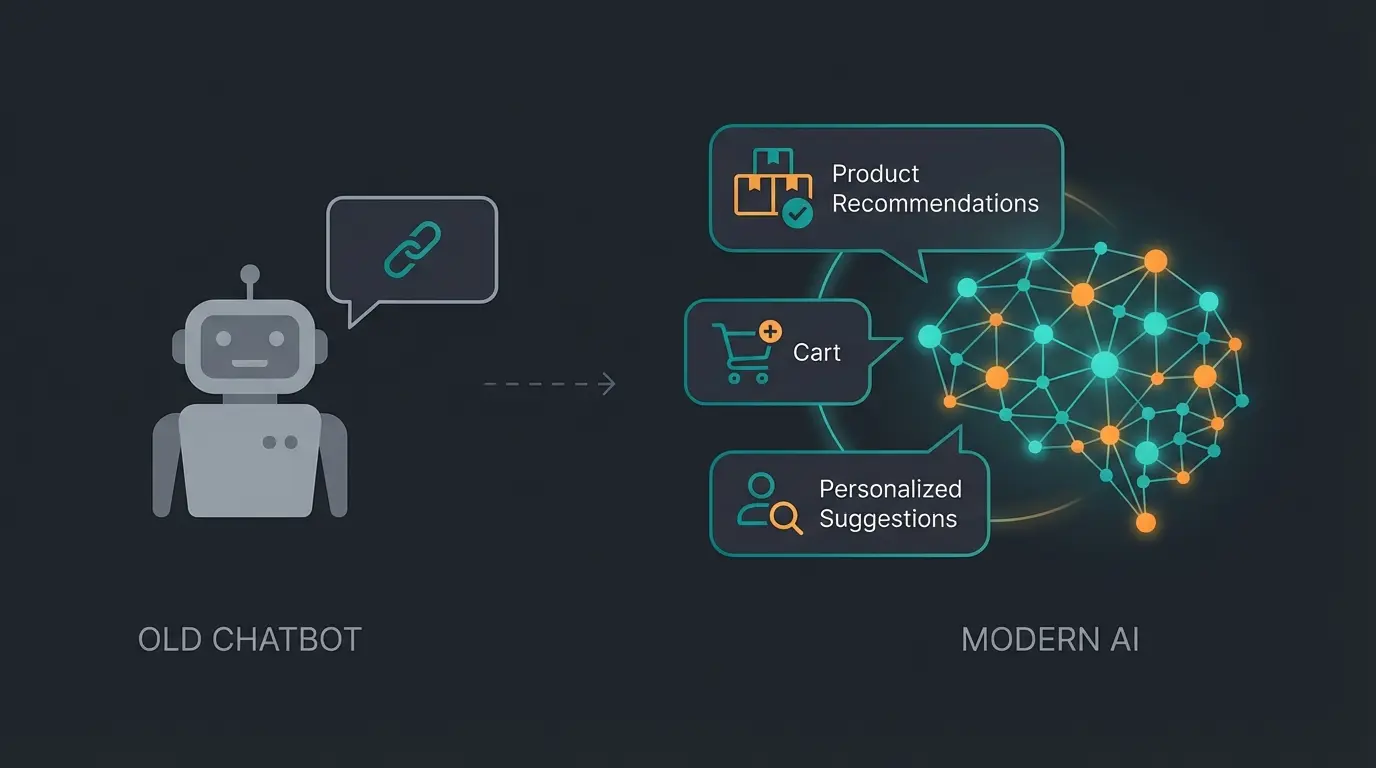
Generative AI vs. Old Chatbots
Forget the dumb chatbots of the past that could only post links to FAQ articles ("Have you tried restarting the device?"). Modern AI models (LLMs) in the helpdesk understand context, nuances, and complex product relationships. The emergence of KI-Mitarbeiter (AI Agents) represents the cutting edge of this evolution.
Real-World Example:
- Old Helpdesk: Customer asks about compatibility. Bot delivers a link to the user manual (PDF). Customer must search themselves.
- New AI-Helpdesk: Customer asks about compatibility. The AI scans the technical documentation in milliseconds and responds: "Yes, ski boot X fits binding Y, but you'll need the GripWalk sole plates for that. Should I add those directly to your cart?"
The Advantages of This Evolution
- Scalable Consultation: An AI can conduct 1,000 consulting conversations simultaneously without getting tired.
- Consistent Quality: The answers are always based on the most current product data, not on an employee's memory.
- Instant Availability: 24/7 consultation, even on weekends when many purchasing decisions are made.
Helpdesk as Profit Center: Revenue Instead of Just Costs
Helpdesk as Profit Center: Revenue Instead of Just Costs
An often overlooked aspect in the helpdesk explanation is the economic leverage effect. Studies from Bain & Company show that a 5% increase in customer retention rate can increase profits by 25% to 95%. This aligns with findings from Forbes and Clootrack on customer retention economics.
How do you transform the helpdesk into a money-making machine?
1. Retention Through Excellence
Customers don't switch because of price, but because of poor service. Research from VisionPoint Systems, FANews, and WinTheCustomer shows that 86% of customers are willing to pay more for a better customer experience. An excellent helpdesk is the best insurance against customer churn.
2. Cross-Selling and Up-Selling
A support conversation is often the most trusting moment in the customer relationship. When a problem is solved, the customer is open to recommendations. According to DCKAP, Vicasso, and SuperOffice, this creates prime upselling opportunities:
- Scenario: Customer reports that their storage is full.
- Reaction: Helpdesk solves the acute problem and seamlessly offers an upgrade to the next higher plan (Up-Selling).
Our comparison of AI product consultation solutions demonstrates how leading companies leverage these moments.
3. Data-Driven Product Development
The helpdesk sits on a goldmine of data. It knows exactly what customers want, what bothers them, and which features are missing. According to Perficient, this data is invaluable for product management to develop market-ready solutions that sell better.
From just a 5% improvement in customer retention rates
Customers willing to pay more for better service
AI tools save support staff significant time through automation
Advantages of Modern Helpdesk Software
Why should companies invest in modern, AI-powered helpdesk solutions instead of simply using Outlook or Excel? The benefits of implementing proper AI customer support systems are substantial:
- Efficiency Increase: AI tools save support staff an average of over 2 hours per day by pre-formulating answers and automatically categorizing tickets, as documented by FluentSupport.
- Omnichannel Presence: Customers expect support where they are — WhatsApp, Instagram, Chat, Email. Modern systems bundle all channels in one interface, as noted by Help-Desk-Migration.
- Personalization: Through CRM integration, the agent (or AI) immediately sees who the customer is, what they've purchased, and their "sentiment" (mood). According to Zendesk, this enables personal addressing instead of "Dear Customer."
- Error Reduction: Automated workflows prevent inquiries from "falling through the cracks."
Understanding the role of intelligent AI employees in this ecosystem helps organizations plan their digital transformation effectively.
Conclusion: The Future Belongs to the Consulting Helpdesk
The question "What is a helpdesk?" can no longer be answered in 2025 with "An office for computer problems."
A helpdesk today is the nerve center of the customer experience. It's evolving from a reactive repair shop to a proactive consulting authority. Companies that continue to view their helpdesk only as a cost center and put off customers with ticket numbers will lose market share.
The winners will be those who combine AI and human empathy: The AI takes over the immediate, technical product consultation and resolution of standard problems (Level 0-3 knowledge), while human experts focus on complex, emotional cases and strategic customer relationships.
Is your helpdesk ready for this change? Or are you still managing tickets while your competition is already consulting?
FAQ: Common Questions About Helpdesks
The main difference lies in focus: A helpdesk is tactically and reactively oriented; it takes care of the quick resolution of acute problems (incidents) and inquiries. A service desk is strategic and more broadly positioned (often according to ITIL standards). It considers the entire lifecycle of IT services, including change management, asset management, and long-term service quality. You could say: The helpdesk is often a subset of the service desk.
Classic tasks include: Receiving inquiries via phone, email, chat (First Level Support); Classification and prioritization of tickets (Triage); Solving standard problems (e.g., password resets, installation help) using a knowledge base; Escalation of complex problems to specialists (Second Level Support); Documentation of solutions in the ticket system. In modern environments, employees increasingly take on consulting activities and train AI systems.
Yes, absolutely. A modern helpdesk can function as a Revenue Center. This happens through: 1. Increased customer retention (Retention): Fast problem resolution prevents churn. A 5% increase in retention can increase profits by 25-95%. 2. Pre-Sales Consultation: AI-powered helpdesks can answer product questions in real-time, preventing purchase abandonment. 3. Cross- and Up-Selling: Satisfied customers are open to additional offers that can be placed in the support conversation.
This describes the escalation levels in support: 1st Level (User Help Desk): The first point of contact. Generalists who take calls and apply standard solutions. Resolution rate approx. 50-60%. 2nd Level (Specialists): Experienced technicians who analyze more complex problems for which the 1st Level had no solution. 3rd Level (Experts/Manufacturers): Highest level. Developers or system architects who fix bugs in code or make deep changes. Modern AI systems blur these boundaries by making expert knowledge (Level 3) available at first contact (Level 1).
AI fundamentally disrupts the traditional tiered support model by introducing 'Level 0' capability with instant access to Level 3 expert knowledge. Instead of routing simple questions to generalists and complex ones through escalation chains, AI can answer both types immediately. This reduces response times from days to seconds, transforms support from a cost center to a revenue center through instant product consultation, and allows human agents to focus on emotionally complex cases requiring empathy.
Join leading companies that have turned their helpdesk from a cost center into a profit center. Our AI-powered consultation platform answers complex product questions instantly, boosting conversions and customer satisfaction.
Start Your Free Trial Today
