What Is Order Management? Definition, Processes & AI's Role
When you search for "order management" in Germany, you'll discover two completely different worlds. One world deals with procurement—how companies source raw materials or office supplies. The other world, which is the focus of this article, is sales and e-commerce: How do merchants efficiently manage their customer orders?
Defining Order Management in the E-Commerce Context
In the classical sense, order management (also called order processing or order administration) encompasses all processes necessary to capture, process, deliver, and potentially handle returns for a customer order. According to Sendcloud, this traditional definition has shaped the industry for decades. However, this definition is fundamentally outdated.
In 2025, it's no longer sufficient to merely manage orders. Modern order management is the orchestration of the entire customer journey. It doesn't begin when the customer clicks "Buy," but in the moment when the need arises. It seamlessly connects consultation (pre-sales) with logistics (fulfillment). This is where AI product consultation becomes essential for forward-thinking businesses.
Why We Must Distinguish Between Procurement and Sales
Many software providers and guides conflate terminology, creating confusion in the marketplace. Understanding the distinction is crucial for implementing the right solutions.
- Procurement/Purchasing: Focuses on supplier approvals, purchase-to-pay processes, and cost control in procurement operations
- Order Management (Sales/Fulfillment): Focuses on customer satisfaction, inventory accuracy, omnichannel availability, and return prevention
This article concentrates on the sales side: How you as a retailer or B2B provider can optimize your order administration to not only ship packages but also build customer loyalty and reduce costs. The insights shared here apply whether you're running a small e-commerce store or managing enterprise-level B2B operations.
The Classic Tasks in Order Management Systems
To understand where innovation must occur, it's worth examining the status quo. A classic Order Management System (OMS) or the order administration in your ERP typically maps a chain of five distinct steps that form the backbone of traditional order processing.
Step 1: Order Entry and Capture
This is where the order arrives—whether through the online shop, a marketplace (Amazon, eBay), via EDI (in B2B), or manually by phone. The challenge here often lies in channel synchronization. When a customer purchases in-store, the online inventory must be updated immediately to prevent overselling and customer disappointment.
Step 2: Validation and Verification
The system automatically checks several critical factors to ensure order integrity and minimize risk:
- Is the customer creditworthy?
- Is the delivery address valid and complete?
- Is there fraud suspicion (fraud detection)?
- Are all order details accurate and consistent?
Step 3: Inventory Management and Allocation
The system decides where the goods will come from. In modern omnichannel scenarios, this is surprisingly complex: Does the item come from the central warehouse? Will it be drop-shipped directly from the manufacturer? Or will it be shipped from a retail location (ship-from-store)? According to OMR, this is where the OMS often differs from pure inventory management (WaWi), as the OMS logically sits above the various storage locations and "decides" which location is optimal.
Step 4: Shipping and Fulfillment Operations
The pick-and-pack process is initiated, the shipping label is printed, and the tracking ID is transmitted to the customer. Customer expectations for delivery speed are enormous: 56% of retailers now deliver within 1-2 days according to industry research. This pressure continues to intensify as same-day delivery becomes increasingly common.
Step 5: Returns Management (After-Sales)
The unloved part of the process that significantly impacts profitability. The goods return, must be inspected, re-inventoried, and credited. This is where businesses that leverage AI-powered customer service can significantly reduce manual intervention and processing time.
Order enters the system from various channels
Validation of stock availability and allocation
Pick, pack, and prepare for shipment
Carrier handoff and tracking communication
Handle returns, refunds, and restocking
The Big Problem: Where Traditional Order Management Fails
If we understand order management only as "working through lists," we ignore the biggest cost factor in retail: The wrong order. This oversight costs businesses billions annually and creates frustrating experiences for customers and operations teams alike.
The Content Gap: Why the Pre-Order Phase Gets Ignored
Most tools and guides focus on how to process an order faster. But hardly anyone discusses how to ensure the order is actually correct in the first place. This represents a massive blind spot in the industry.
The data situation is alarming and demands attention. According to Bitkom research, German online shoppers return an average of 11% of their purchases. For clothing and furniture, the rate is dramatically higher—reaching up to 50% in the fashion sector.
Wrong size selection due to inadequate guidance
Quality issues upon arrival
Product doesn't match expectations
Gap between listing and reality
Fulfillment errors in processing
The Hidden Costs of Poor Pre-Purchase Consultation
A return isn't just annoying—it's expensive. According to the EHI Retail Institute study "Shipping and Returns Management in E-Commerce 2024," the cost breakdown is significant:
- 30% of retailers calculate €5 to €10 in costs per returned item
- 26% even calculate €10 to €20 per return
- Complex products and fashion items often exceed these estimates
These costs arise from shipping, inspection, repackaging, and value depreciation. But the actual cause often lies not in logistics, but in inadequate consultation before the purchase. This is precisely why companies are turning to AI lead generation solutions that qualify and guide customers from the very first interaction.
When a B2B customer orders the wrong spare part because they had to wade through complex PDF catalogs, or when a B2C customer orders three sizes because size guidance is missing, then order management has failed before the order even entered the system.
The Evolution: From Order Processor to Digital Advisor
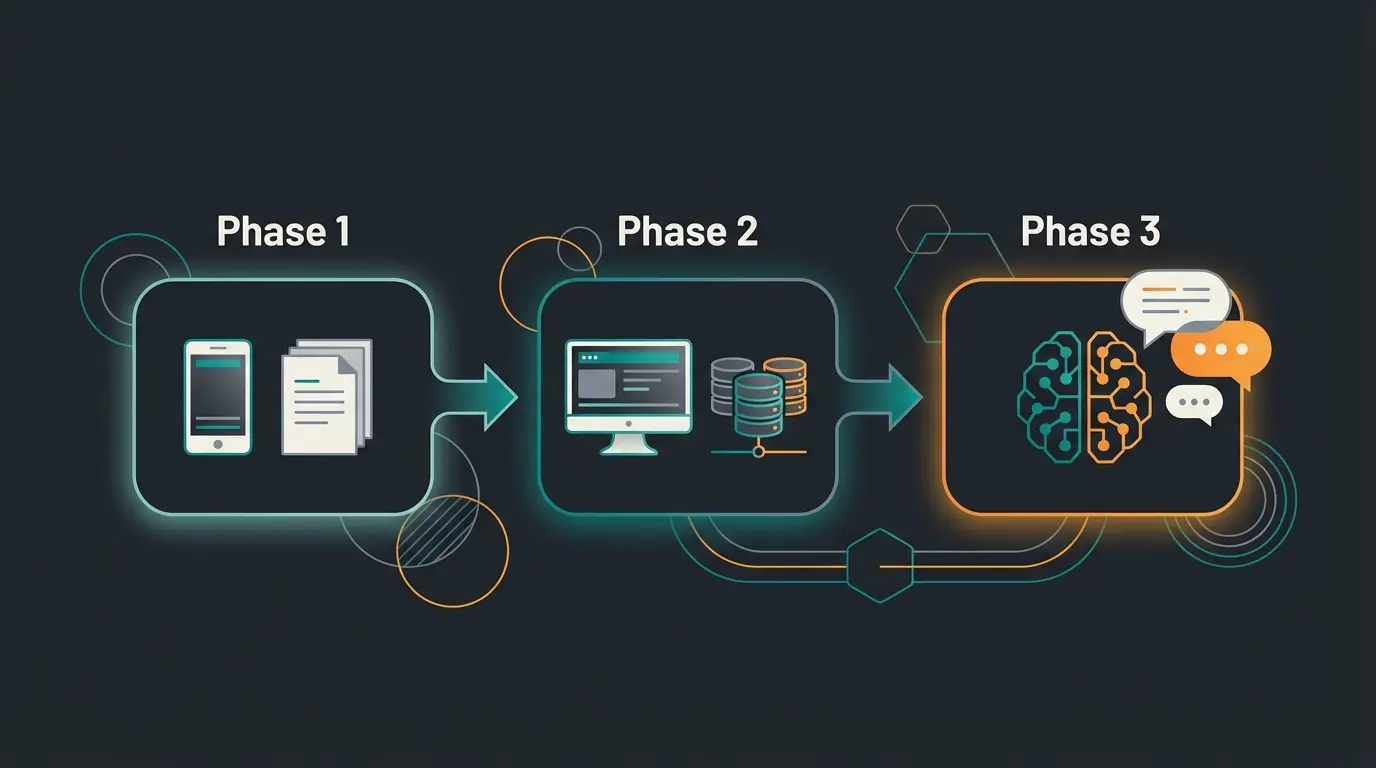
The future of order management lies in integrating consultation competence into the transaction process. We observe this evolution unfolding in three distinct phases, each representing a significant leap in capability and customer value.
Phase 1: Manual Administration (Excel & Phone Era)
In small businesses or traditional B2B sales, order processing often still runs manually. This approach has its merits but significant limitations.
- Process: Customer calls or writes an email → Back office types order into Excel or an old ERP system
- Advantage: High personal consultation quality through human interaction on the phone
- Disadvantage: Not scalable, error-prone during data transfer, no 24/7 availability
Phase 2: ERP & Shop Systems (Automated Processing)
This is the current standard in e-commerce and represents what most businesses consider "modern" order management.
- Process: The customer serves themselves in the online shop (self-service). The system (Shopify, Shopware, SAP, etc.) processes the order automatically
- Advantage: Highly efficient, scalable, low transaction costs
- Disadvantage: Consultation gap. The customer is left alone with filters and search bars. The "human intelligence" from Phase 1 is missing. The result: the high return rates mentioned above due to incorrect purchases
Phase 3: AI-Powered Order Management (Intelligent Consultation)
Here's where we stand today. New technologies, particularly Agentic AI (autonomous AI agents), bring the consultation quality of Phase 1 into the scalability of Phase 2. According to Adesso, this represents the most significant shift in customer experience technology in decades.
What's different in Phase 3? Instead of the customer clicking through filters ("Men" → "Pants" → "Size 32"), they conduct a dialogue with an AI that understands context, preferences, and needs. This is exemplified by solutions like AI Employee Kira, which demonstrates how AI can transform customer interactions.
| Feature | Classic Chatbot (Phase 2) | AI Consultant / Agentic AI (Phase 3) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Answers FAQs ("Where is my package?") | Advises on products ("Which part fits my machine?") |
| Context Awareness | Reactive, static responses | Proactive, learns from customer history |
| Core Goal | Reduce support tickets | Build the perfect shopping cart |
| Technology Stack | Script-based / Simple NLP | LLMs (Large Language Models) + RAG (Real-time Data) |
| Customer Experience | Transactional, impersonal | Consultative, personalized |
The Consultation-First Model Explained
Modern order management places an AI agent before the shopping cart. This represents a fundamental paradigm shift in how we think about the customer journey. Companies like those featured in our AI Product Consultation case study have already implemented this approach with remarkable results.
The AI agent performs three critical functions that transform the ordering experience:
- Analyzes the Need: Asks targeted questions about application scenarios (e.g., "What surface do you need the drill for?")
- Validates Technically: Checks in the background (via API to the ERP) whether Component A is compatible with Component B
- Prevents Errors: Warns the customer before ordering ("Attention, this spare part doesn't match your purchase history")
According to Gartner, approximately 33% of enterprise software applications will have integrated such "Agentic AI" functions by 2028 to autonomously support decisions. This isn't hype—it's the necessary response to increasing complexity and decreasing attention spans. The success of implementations like KI Mitarbeiterin Flora demonstrates the practical viability of this approach.
Discover how AI-powered consultation can reduce returns by up to 50% while increasing customer satisfaction. Join leading e-commerce businesses already benefiting from intelligent pre-order guidance.
Start Your Free TrialOrder Management Software: What You Need to Consider
When searching for a solution for order management software or order administration, you'll be overwhelmed by providers. From classic ERP to specialized OMS tools (Order Management Systems), the market offers countless options. The key is knowing what truly matters for long-term success.
Beyond the "hygiene factors," in 2024/2025 you should pay attention to new criteria that secure your future viability. The landscape is evolving rapidly, and yesterday's best practices may not suffice tomorrow.
The Basics: Every System Must Handle These
- Multichannel Capability: Can the system centrally bundle orders from shop, marketplace (Amazon/eBay), and call center?
- Real-time Inventory Synchronization: Synchronization of stock levels across all channels to avoid overselling
- Interfaces (APIs): Clean connection to shipping providers (DHL, UPS, FedEx), payment providers, and accounting systems
- Automated Status Updates: Transactional emails to the customer ("Shipped," "Delayed," "Delivered")
The Game Changers: Features for Phase 3 Success
Here's where the wheat separates from the chaff. Modern software offers features that proactively secure revenue and reduce costs. These capabilities distinguish market leaders from laggards.
1. Consultative AI Core: Does the software have an AI interface that not only solves support tickets but can configure products? Can the AI place suitable products in the cart based on unstructured customer inputs ("I need something for winter, but not too heavy")? Solutions that answers questions about orders while also guiding purchase decisions represent the gold standard.
2. Smart Order Routing: Does the system use algorithms to determine the best shipping route? (e.g., "Ship Part A from the Berlin store because it's a slow-mover there, and Part B from the central warehouse"). This optimization can significantly reduce shipping costs and delivery times.
3. Self-Correction Features: Can the customer still modify their order after submission (e.g., correct address) without calling support? This massively reduces manual effort in the back office and improves customer satisfaction.
4. B2B Logic Integration: Especially important in B2B order management: Can the system map individual price lists, approval processes (approval workflows), and customer budget limits? According to Mediagraphik, these features are essential for enterprise-level B2B operations.
Checklist: Is Your Current Process Leaky?
Consider this mental checklist carefully. If you answer more than 2 points with "Yes," you have a significant problem in order management that requires immediate attention:
- Do you have a return rate above 15%?
- Does your sales team spend more time answering technical product questions than actually selling?
- Do customers complain about "incorrectly ordered" goods even though the product description was accurate?
- Do you have to manually transfer orders from one system to another?
- Are customer service tickets dominated by pre-purchase questions that could be automated?
The Modern Order Management Lifecycle: A New Paradigm
Traditional order management models focus on what happens after the "Buy" button is clicked. But forward-thinking companies are extending their view to the left, incorporating the crucial pre-order consultation phase.
Intelligent needs analysis and product guidance before selection
AI-validated order with compatibility checks completed
Seamless fulfillment with optimized routing
Customer kept informed with predictive delivery updates
Minimal returns due to correct initial product selection
This extended model has been successfully implemented by companies featured in our AI Chat case study, demonstrating how the consultation-first approach transforms business outcomes. Similarly, AI Paul showcases how even specialty retailers can leverage AI to guide complex purchasing decisions.
FAQ: Common Questions About Order Management
Here we answer the most frequently asked questions that arise in connection with order management and order administration—based on actual search queries and customer conversations.
Inventory management (WaWi) primarily focuses on managing goods flows and stock levels (inventory tracking, goods receipt, stocktaking). Order management is broader and more customer-oriented. It manages the order across various systems (e.g., inventory, CRM, shop, logistics) and handles the customer experience. Think of it this way: Inventory management is the warehouse brain; order management is the conductor of the entire sales process.
Many retailers underestimate this significantly. According to the EHI Retail Institute, costs typically range between €5 and €10 per item (process costs, shipping, refurbishment). For more complex products or fashion items, costs quickly rise to €10-20 per return. These figures don't include the hidden costs of customer dissatisfaction and lost future revenue.
AI operates on two levels: Efficiency (Backend): Automated fraud detection, prediction of return probabilities, and inventory optimization. Revenue & Quality (Frontend): Through Agentic AI, the customer is advised before the purchase to choose the right product. This reduces return rates and increases conversion rates. Gartner predicts that autonomous AI agents will make approximately 15% of daily business decisions by 2028.
Absolutely not. As soon as you sell through more than one channel (e.g., own shop + Amazon) or have a complex product range, manual management becomes a significant risk. Even small retailers benefit from software that synchronizes inventory and automates return processes. The ROI is often realized within months, not years.
AI reduces returns by ensuring customers select the right product initially. This includes intelligent size recommendations, compatibility checks for technical products, needs-based product suggestions through conversational interfaces, and proactive warnings when a customer is about to order something that doesn't match their stated requirements or purchase history.
Conclusion: Efficiency Begins with Consultation
The traditional image of order management as a pure "logistics processor" has outlived its usefulness. In an era where customers expect Amazon-speed delivery but products become increasingly complex, the gap between desire and fitting product represents the greatest risk to your profit margins.
We've established three fundamental insights that should guide your order management strategy:
- Most problems (returns, support burden) arise from errors in the initiation phase before an order is placed
- Classic ERP and shop systems often leave customers alone during product selection
- The solution lies not in faster returns but in fewer returns through better consultation
The paradigm shift is clear: Successful order management in 2025 means understanding consultation as the first, integral step of the order process. With the deployment of AI agents, you can scale this consultation, eliminate incorrect purchases, and transform a pure administrative act into a genuine customer experience. Companies handling social media inquiries through AI are already seeing how this approach extends across all customer touchpoints.
The businesses that thrive in the coming years will be those that recognize order management as a holistic customer experience function, not merely an operational necessity. Ready to transform your approach? You can hire an AI employee today or schedule a free initial consultation to explore how AI-powered consultation can revolutionize your order management.

Join innovative companies already using AI consultation to reduce returns, increase conversions, and deliver exceptional customer experiences. Start your transformation today.
Get Started Free