Introduction: Why WhatsApp Privacy in 2026 Goes Beyond Compliance
WhatsApp is indispensable in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland (DACH region). With market penetration of over 94% of the internet population and open rates of up to 98%, the messenger is the most powerful channel for businesses according to chatarmin.com. However, for German CEOs, marketing directors, and data protection officers, the green messenger is often a red flag. The fear of warnings, fines, and loss of customer trust is omnipresent.
The situation has intensified further in 2026. It's no longer just about the question: "Am I allowed to use WhatsApp?" (The answer is: Yes, but only with a technically clean setup). It's about a new dimension: Artificial Intelligence.
Companies are increasingly relying on AI-powered product consultation. Unlike simple support bots ("Where is my package?"), these AI consultants ask about skin types, financial goals, or personal preferences to provide tailored recommendations. This generates profiling data. At the same time, consumer concerns are growing that their data is being misused to train global AI models, as reported by connect.de and aibusiness.com.
This article is the most comprehensive guide in the English-speaking web on WhatsApp data protection for businesses. We not only clarify the legal foundations of GDPR but also show you how to turn your AI consultation into a trusted safe space for your customers through "Privacy by Design" – setting yourself decisively apart from the competition. Understanding what is WhatsApp Business is the first step toward compliance.
Is WhatsApp Allowed for Businesses in Germany? (Quick Answer)
The question of WhatsApp's legality for business use cannot be answered with a simple yes or no. It critically depends on the technical version you use. The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) sets strict requirements for processing personal data.
Here is the distinction that determines legality versus fines:
1. The Private WhatsApp App
Status: ❌ Illegal for Businesses
Using the standard app on a company phone is a direct violation of GDPR.
- The Problem: As soon as the app is installed, it reads the entire address book of the smartphone and syncs phone numbers with Meta's servers (in the USA) to determine which contacts also use WhatsApp.
- The Violation: You transmit personal data (phone numbers) of third parties (your contacts) to Meta without those third parties having consented. This constitutes unlawful data processing according to hellomateo.de and serbusgroup.com.
2. The WhatsApp Business App
Status: ⚠️ Gray Area / High Risk
This free app targets small business owners. It offers features like business hours and catalogs.
- The Problem: This app also accesses the address book by default and synchronizes data with US servers according to sofortdatenschutz.de. While there are theoretical workarounds (e.g., using on an "empty" phone without contacts), these are hardly manageable in practice and error-prone.
- Conclusion: For professional companies that need legal certainty, this solution is unsuitable as confirmed by heydata.eu. Our comprehensive WhatsApp Business setup guide explains the differences in detail.
3. The WhatsApp Business API (Platform)
Status: ✅ GDPR-Compliant (with proper setup)
This is not an app you install on your phone but an interface connected to software (e.g., CRM, support tool, or AI solution).
- The Solution: The API has no access to your smartphone's address book. Contacts are only imported when they actively reach out to you (inbound) or when you have explicit opt-in consent.
- Hosting: Through Business Solution Providers (BSPs), data can be hosted on servers in the EU, which mitigates the problem of data transfer to the USA.
The 3 Biggest WhatsApp Data Protection Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
To understand why the API is necessary, we need to examine the specific data protection problems in detail.
1. The Metadata Problem & Address Book Sync
The biggest misconception is that end-to-end encryption (E2EE) solves all data protection problems. E2EE protects the content of the message. However, GDPR is also intensely interested in metadata.
- Who communicates with whom?
- When? How often? From which location?
- Device information and IP addresses.
This metadata is not covered by end-to-end encryption and is processed by Meta as documented by gesellschaft-datenschutz.de. When using the App (Private/Business), you have no control over this. With the API, however, the Business Solution Provider acts as a buffer, and you sign a Data Processing Agreement (DPA) that regulates the use of this data.
2. US Cloud Act & Server Locations
Even in 2026, data transfer to the USA remains a legal minefield. While the EU-US Data Privacy Framework (DPF) exists as a successor to "Privacy Shield," criticism from data protection advocates (like NOYB/Max Schrems) continues as reported by bakerbotts.com, dlapiper.com, and thefirewall-blog.com.
- The Risk: US authorities could theoretically access data from US companies (like Meta), even if located in Europe (Cloud Act).
- The Solution: By using the API through a German or European BSP (Business Solution Provider), you ensure that primary data storage occurs in the EU. The BSP acts as a "data protection shield."
3. Employee Phones (BYOD - Bring Your Own Device)
Do you allow employees to contact customers via WhatsApp on their private devices?
- The Trap: An employee saves a customer in their private address book. WhatsApp (private) sucks up this data. The employee leaves the company. The customer data is gone (with the employee) and simultaneously compromised (at Meta).
- The Solution: With the API and a central software platform, all chats are centrally stored in the company account. Employees don't access via private WhatsApp accounts but log into your GDPR-compliant software.
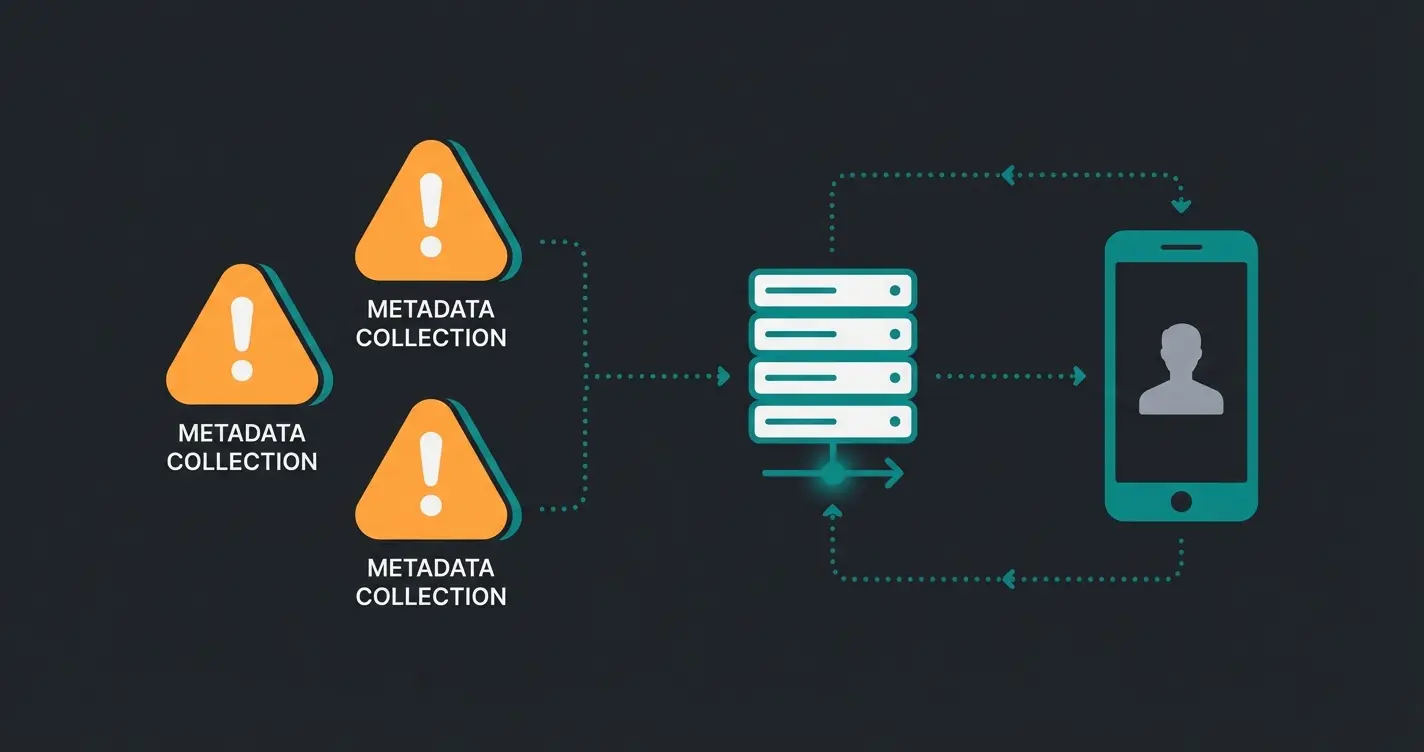
Why AI Consultation Needs Higher Privacy Standards Than Chatbots
Here lies your great opportunity for differentiation. The market is full of simple FAQ bots. But AI product consultation is in a different league – including when it comes to data protection.
Support vs. Consultation: A Difference in Data
- Support Scenario: "Where is my package?" → Data: Order number, name. (Low risk).
- Consultation Scenario: "I have dry, acne-prone skin and I'm pregnant. Which cream can I use?" → Data: Health data (Art. 9 GDPR), personal preferences, life circumstances. (High risk).
When you use AI for consultation, you're effectively creating profiles of your users. GDPR prescribes particularly high protective measures for profiling and processing sensitive data. Implementing an AI-powered WhatsApp chatbot requires understanding these distinctions.
Order numbers, tracking info, simple FAQs
Health info, financial goals, personal preferences
Requires explicit consent and enhanced protection
The "Meta AI" Training Dilemma
Meta has begun using public data from users in the EU to train its own AI models as noted by dig.watch. Users must actively object (opt-out).
For businesses, the question arises: Does Meta's AI learn from my customer conversations?
- When using the WhatsApp Business App: The risk is opaque. Meta uses data to "improve services."
- When using your own AI via the API: You have control. Data flows from the API into your isolated AI environment (e.g., via RAG - Retrieval Augmented Generation). You can contractually assure that this data is not used to train public models (like GPT-4 or Llama).
The EU AI Act & WhatsApp: What Changes in 2026
Since August 2024, the EU AI Act has been in force, and transition periods are running. For the use of chatbots and AI on WhatsApp, concrete transparency obligations have applied since 2025/2026 (Art. 50 AI Act) according to digitalzentrum-berlin.de, ecovis.com, and rtr.at. For comprehensive compliance guidance, see our EU AI Act guide.
Labeling Requirements for Chatbots
Companies must ensure that users know they are interacting with a machine.
- Obligation: "Providers of AI systems intended for direct interaction with natural persons must design them so that persons are informed."
- Implementation: The chatbot must introduce itself. Example: "Hello! I'm the digital assistant from [Company]. I'm an AI and help you with product selection."
- Risk: Failure to do so risks not only GDPR fines but also sanctions under the AI Act (up to €35 million or 7% of turnover for serious violations, though transparency violations are usually lower but still significant) according to qualimero.com.
Our detailed guide on AI Act Compliance covers all requirements for chatbot operators in depth.
Private App vs. Business App vs. API Comparison Table
This table shows at a glance why the API is without alternative for mid-market and enterprise customers.
| Feature / Requirement | Private WhatsApp App | WhatsApp Business App | WhatsApp Business API (with BSP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDPR Compliance | ❌ No (Illegal) | ⚠️ Conditional / Gray Area | ✅ Yes (Complete) |
| Address Book Upload | ❌ Required | ❌ Required | ✅ No Access / No Upload |
| Server Location | 🇺🇸 USA | 🇺🇸 USA | 🇪🇺 EU (possible) |
| AI Integration | ❌ No | ❌ No (only Quick Replies) | ✅ Complete (Chatbots, LLMs) |
| Multi-User (Teams) | ❌ No | ⚠️ Limited (few devices) | ✅ Unlimited |
| Mass Messages | ❌ Blocking Risk | ⚠️ Limited (256 contacts) | ✅ Scalable (Newsletter) |
| Data Protection Contract | ❌ Terms of Use only | ⚠️ Limited | ✅ DPA (Data Processing Agreement) |
Sources for this comparison include onsync.co and bol7.com. For implementation guidance, consult our WhatsApp Business API chatbot guide.
Discover how our AI-powered consultation solution ensures complete data protection compliance while doubling your conversion rates on WhatsApp.
Start Free AnalysisChecklist: How to Use WhatsApp GDPR-Compliant (with AI)
To set up your AI product consultation securely, follow this process. This is the standard that data protection officers expect.
Select a BSP guaranteeing EU servers (e.g., Sinch, Twilio, 360dialog)
Execute DPA per Art. 28 GDPR regulating data handling
Ensure explicit consent before any customer communication
Add WhatsApp-specific section with provider and legal basis
Disclose AI interaction and offer human handover option
Step 1: Choose Business Solution Provider (BSP)
Don't go directly to Meta. Choose a BSP (such as Sinch, Twilio, 360dialog, or specialized German providers) that guarantees servers in the EU.
- Why? The BSP is your contracting partner. They shield you legally and technically.
Step 2: Sign Data Processing Agreement (DPA)
You must sign a Data Processing Agreement (DPA) with the BSP according to Art. 28 GDPR.
- Content: The contract regulates that the provider only processes data according to your instructions and maintains technical security measures (TOMs).
Step 3: The Clean Opt-In Process
You may not simply message customers (cold outreach is prohibited on WhatsApp and subject to warnings). You need explicit consent.
- The "Wa.me" Link: The customer initiates the conversation (inbound).
- The Widget: Before clicking the WhatsApp button on the website, there must be a notice: "By clicking 'Start Chat,' you agree to the privacy policy."
- Double Opt-In (Recommended): The bot's first message should be: "Welcome! To advise you, please note our privacy information [link]. Do you agree?" – Only after a "Yes" does the AI consultation begin.
Step 4: Update Your WhatsApp Privacy Policy
Your website's privacy policy must contain a specific section about WhatsApp, including clear WhatsApp privacy guidelines.
- Naming of the BSP (service provider).
- Legal basis (usually Art. 6(1)(a) GDPR - consent).
- Note on data transfer to third countries (if relevant) and corresponding guarantees (DPF/SCCs).
- Note on automated decision-making (if the AI filters products).
Step 5: AI Transparency & "Human Handover"
According to the AI Act and GDPR, users should know they're talking to an AI. Additionally, there should always be an exit ("Human" button) to be connected to an employee. This not only increases compliance but massively boosts trust. Our AI customer service guide explains best practices for implementing this.
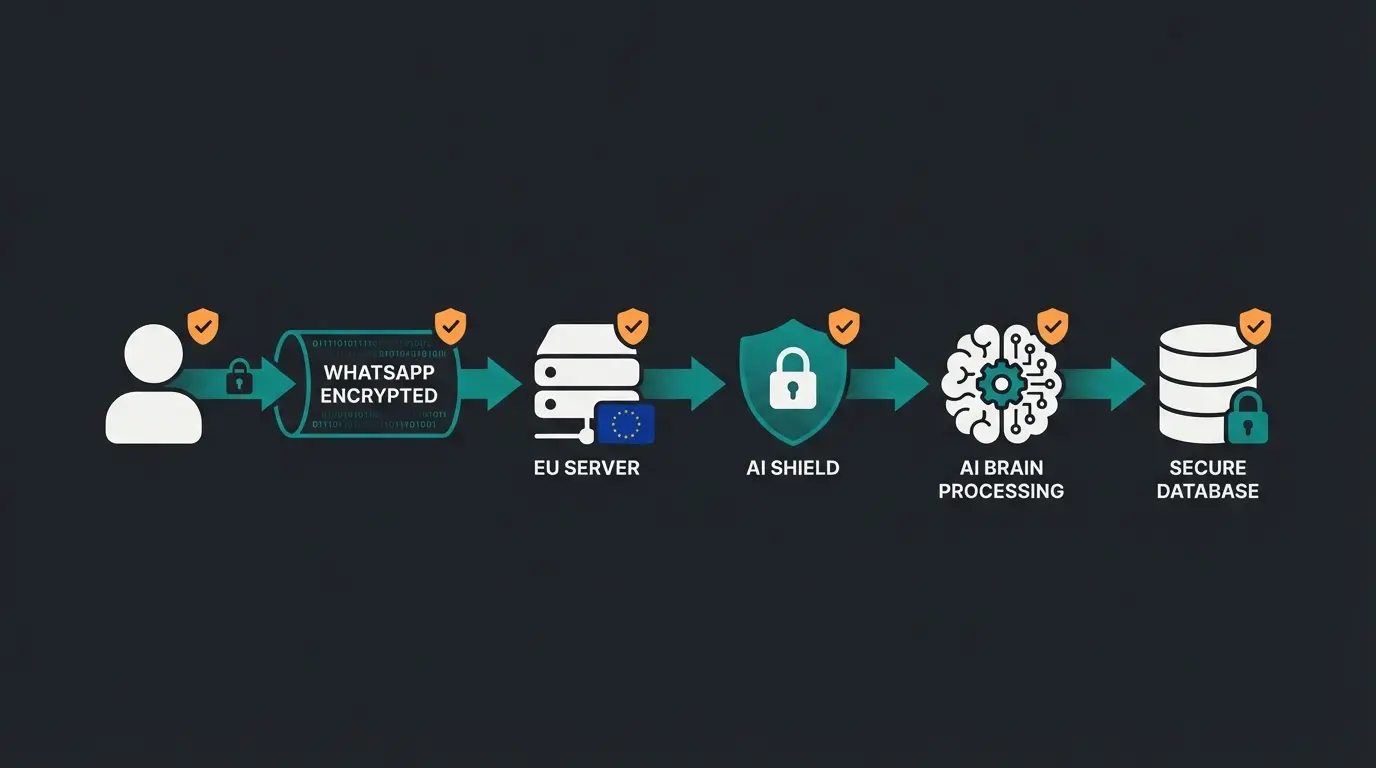
Visualization: The Secure Data Flow ("Privacy by Design")
Many companies fail to explain to their data protection officers how data flows. Here is the description of a secure setup as we recommend for AI consultation:
- User: Sends message ("I'm looking for a day cream").
- WhatsApp (Meta): Transports the message encrypted. Meta doesn't see the content, only metadata.
- Business API (BSP): Receives the message on EU servers. Decrypts it for processing.
- AI Shield (Your Solution): Here, personal data (names, phone numbers) is pseudonymized. Only the context ("day cream") is sent to the AI model (e.g., OpenAI/Azure Europe).
- AI Engine: Generates the response.
- Database: The conversation log is stored in your secured database (for history), not in the public cloud of AI providers.
This setup guarantees that no training data flows to third parties. For detailed implementation, our GDPR compliant consultation guide provides comprehensive instructions.
Understanding WhatsApp Business for Different Use Cases
Whether you're exploring using WhatsApp Business privately or seeking a comprehensive WhatsApp Business Guide, understanding the privacy implications is crucial for any implementation.
FAQ: Common Questions About WhatsApp Data Protection
The fines can be drastic. GDPR provides for penalties of up to €20 million or 4% of worldwide annual turnover. Prominent cases like the €225 million fine against WhatsApp itself (as documented by termly.io and enzuzo.com) show that authorities look closely at messengers. For SMEs, however, warnings from competitors or consumer advocates are the more immediate risk.
No. For marketing messages (outbound), you need explicit opt-in for exactly this channel. An opt-in for email newsletters is not sufficient for WhatsApp. Additionally, you must comply with WhatsApp's strict template requirements for marketing messages.
If you use the private app: Meta uses data to improve services. If you use a professional API solution: The AI only 'reads' what you technically allow. In a professional setup, data is not used to train base models (like GPT-4) but only for specific response generation within the session (Zero-Data-Retention Policies with enterprise models).
WhatsApp Channels are 'one-to-many' communication (like a broadcast). Here, subscribers' phone numbers are not visible to other subscribers, which is advantageous from a data protection perspective. However, as a company, you also don't receive data about subscribers, making individual AI consultation in channels impossible. Channels are good for news, unsuitable for consultation.
Since 2025/2026, the EU AI Act requires transparency for AI systems interacting with users. This means your WhatsApp chatbot must clearly identify itself as AI at the start of conversations. Non-compliance can result in significant fines up to €35 million or 7% of global turnover.
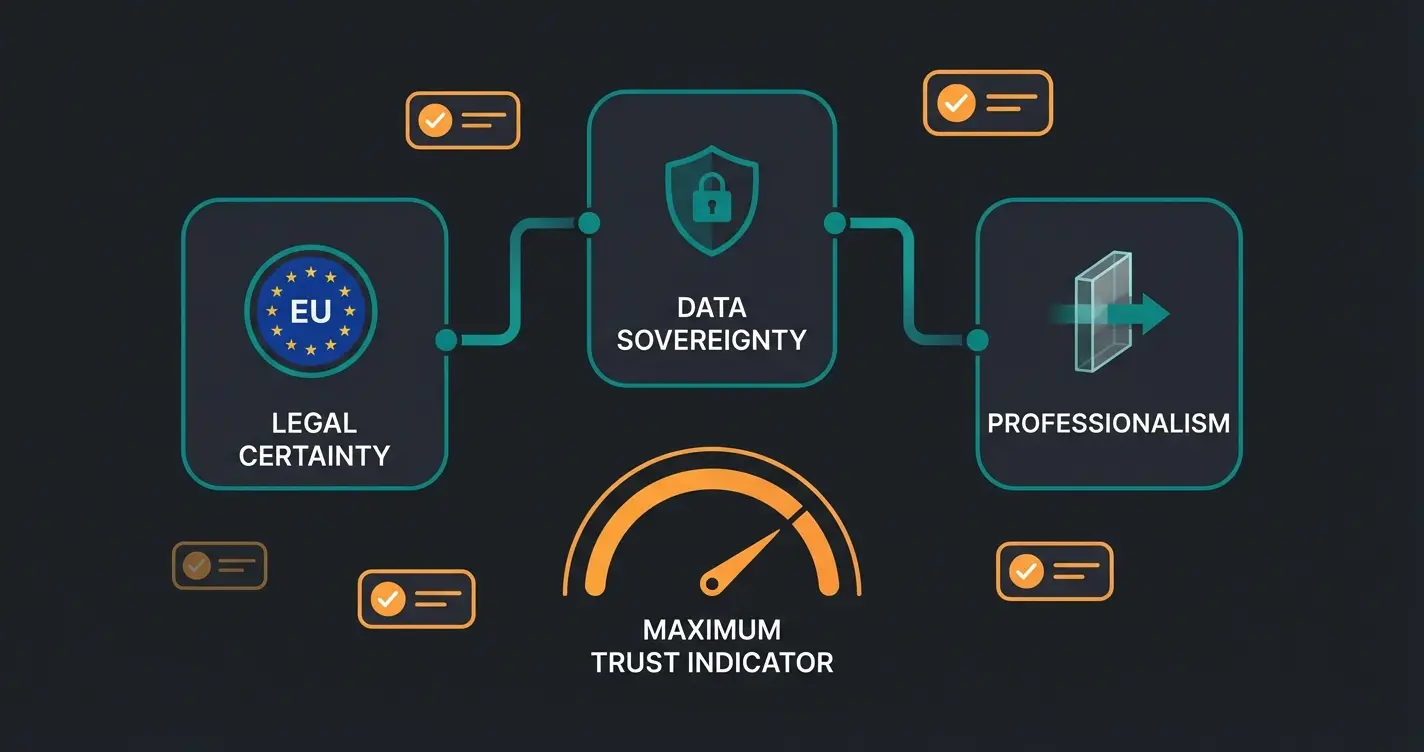
Conclusion: Data Protection as Foundation for Excellent AI Consultation
The discussion about WhatsApp data protection is often fear-driven. "What am I not allowed to do?" is the wrong question. The right question for 2026 is: "How do I build a setup that my customers trust?"
If you want to use AI for product consultation, trust is your currency. A customer will only confide their skin problems, financial situation, or style preferences to you if they feel safe.
The WhatsApp Business API is not only the only legal solution – it's also the foundation for this trust. It enables you to achieve:
- Legal certainty through EU hosting and Data Processing Agreements.
- Data sovereignty by preventing your customer data from being used to train others' AIs.
- Professionalism through transparent opt-ins and AI labeling.
Don't hide behind compliance checklists. Use data protection offensively as a quality feature of your AI consultation.
Start our free AI Potential Analysis now. We not only check your compliance but show you how to double your conversion rate on WhatsApp with GDPR-compliant AI consultation.
Start Potential Analysis Now
